How to Identify and Differentiate Ascaris Male vs Female in Exams
The concept of Ascaris male and female diagram is essential in biology and helps explain real-world biological processes and exam-level questions effectively. Understanding and identifying the structural differences between male and female Ascaris lumbricoides is a frequently asked topic in board exams, NEET, and practical assessments.
Understanding Ascaris Male and Female Diagram
Ascaris male and female diagram refers to the scientific illustrations and structural representations that show the morphological and reproductive differences between male and female Ascaris lumbricoides, which are parasitic roundworms (Nematoda). This concept is important in areas like sexual dimorphism, reproductive system anatomy, and comparative animal biology.
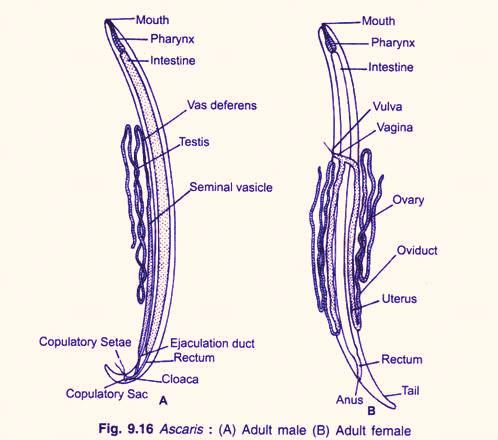
Key Morphological and Reproductive Differences
The Ascaris male and female diagram highlights important features that help you distinguish between the two sexes. Here’s a helpful table to understand this concept better:
Differences Between Male and Female Ascaris
| Characteristic | Male Ascaris | Female Ascaris |
|---|---|---|
| Body Length | 15–30 cm (shorter) | 20–35 cm (longer) |
| Body Diameter | 2–4 mm (thinner) | 4–5 mm (thicker) |
| Posterior End | Curved ventrally | Straight, pointed |
| Genital Aperture | Not visible externally (cloacal aperture at tail) | Present, ~1/3 from anterior end (vulva) |
| Reproductive Organs | Single testis, vas deferens | Two ovaries, uteri, oviducts |
| Penial Spicules | Present (two) | Absent |
| Function | Sperm production and transfer | Egg production |
Detailed Features of Ascaris Male and Female
- Both male and female Ascaris exhibit a cylindrical, unsegmented, bilaterally symmetrical body.
- Sexual dimorphism is clear—males are smaller and have a curved tail. Females are larger with a straight, pointed tail.
- Male tail has a cloacal aperture, through which penial spicules (setae) project for mating.
- Female vulva (genital pore) is a noticeable opening about one-third from the anterior end.
- Both sexes lack a distinct head and have three lips at the mouth (one dorsal, two subventral).
- Reproductive system organization is key: males have a single testis, while females have paired ovaries and a Y-shaped reproductive tract.
- Digestive and excretory systems are similar in both sexes, but only females lay eggs.
Step-by-Step: How to Draw and Label Ascaris Male and Female Diagrams
Follow these simple steps to score high in diagram questions:
- Draw a cylindrical, elongated outline with both ends tapered.
- For male, curve the posterior end ventrally (downward). For female, keep it straight and pointed.
- Mark and label lips (three at the anterior end).
- Draw and label the genital aperture (female: vulva; male: cloacal opening with two spicules).
- Indicate body length differences visually by scaling accordingly.
- Show internal reproductive organs only in dissected/longitudinal diagrams if asked.
- Use proper labeling lines and keep handwriting neat as per NCERT style.
Practice Questions
- Draw and label a well-labelled Ascaris male and female diagram.
- List three differences between male and female Ascaris with the help of diagrams.
- How can you identify male Ascaris in a practical examination?
- Why is the posterior end of male Ascaris curved?
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Mixing up the curved tail feature—only the male has it, not the female.
- Mislabeling the vulva (female) and cloacal aperture (male).
- Drawing incorrect proportions—remember, the female is always larger and thicker.
- Omitting penial spicules in the male or drawing extra organs not shown in board diagrams.
Real-World Applications
The concept of Ascaris male and female diagram is used in medicine (diagnosis of Ascariasis), parasitology, and veterinary science. Understanding these diagrams also helps in comparative zoology and strengthens diagramming skills for practical exams. Vedantu helps students make connections between such biology topics and their use in real examinations and daily life observations.
In this article, we explored Ascaris male and female diagram, its key processes, real-life significance, and how to solve questions based on it. To learn more and build confidence, keep practicing with Vedantu.
Related Biology Resources
- Nematoda
- Reproductive System in Animals
- Common Diseases in Humans: Ascariasis
- Animal Kingdom: Classification
- Morphology and Anatomy of Earthworm
- Reproductive System of Earthworm
- Life Cycle of Ascaris
- Vertebrates and Invertebrates
- Animal Kingdom: Concept Map
- Amoeba Diagram


FAQs on Ascaris Male and Female Diagram: Labeled Comparison Guide
1. What is the Ascaris male and female diagram?
The Ascaris male and female diagram is a labeled visual representation showcasing the structural and morphological differences between the male and female Ascaris lumbricoides, a parasitic roundworm. These diagrams highlight key features such as body length, shape of the posterior end, and reproductive organs, helping students accurately identify and differentiate the sexes for board exams and competitive tests.
2. How to differentiate male and female Ascaris in diagrams?
To differentiate the male and female Ascaris in diagrams:
- The male is smaller in size (15-30 cm), has a curved or hooked posterior end, and contains two penial spicules near the cloacal aperture.
- The female is larger (20-35 cm), with a straight and pointed posterior end.
- The female also exhibits a genital aperture located about one third from the anterior end.
These visual cues are essential for correct diagram labeling.
3. What are the main features of male Ascaris?
The male Ascaris is characterized by:
- Smaller size relative to female (15-30 cm in length, 2-4 mm diameter).
- Curved or hooked posterior end.
- A cloacal aperture through which two equal penial spicules (or setae) project.
- Smaller and thinner body compared to female.
- Presence of four longitudinal lines on the body (two lateral, one dorsal, one ventral).
- Male reproductive system includes testes, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, and cloaca.
4. Are there any simple PDFs for these diagrams?
Yes, simple and printable PDF diagrams of male and female Ascaris are available for download. These PDFs provide clear, exam-oriented labeling and concise explanations, ideal for revision. Students can find such PDFs linked on reputable educational platforms like Vedantu and BYJU’S to support their practical and theory preparations.
5. Why do students mix up Ascaris diagram labels?
Students often mix up Ascaris diagram labels due to:
- Similar anterior structures in both sexes.
- Lack of focus on distinct male features such as the curved tail and penial spicules.
- Overlapping body parts without clear labeling in some study materials.
- Insufficient practice distinguishing reproductive apertures.
Using step-by-step labeling guides and clear comparison tables helps avoid these common errors.
6. Which system is different in male and female Ascaris?
The primary system differing between the male and female Ascaris is the reproductive system. The male has testes, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, and penial spicules that aid in reproduction, while the female has ovaries, oviducts, uterus, and a distinct genital aperture used for egg-laying. Other systems like digestive and excretory systems are the same in both sexes.
7. What is the difference between female and male Ascaris?
The female Ascaris is generally longer (20–35 cm) and thicker (4–5 mm diameter) than the male (15–30 cm length, 2–4 mm diameter). Females have a straight and pointed posterior end, while males have a curved or hooked tail with penial spicules visible. Females feature a genital pore about one-third from the anterior end, used for egg-laying; males have a cloacal aperture for reproductive discharge.
8. How are the male and female Ascaris distinguished?
Male and female Ascaris are distinguished by their size, tail shape, and reproductive openings:
- Males are shorter, with a ventrally curved tail and two penial spicules.
- Females are longer, with a straight tail and a genital opening farther anterior.
- Both sexes have the same anterior mouthparts but differ posteriorly.
These features are vital for practical diagrams and biological classification.
9. What are the male characters of Ascaris?
The male characters of Ascaris include:
- Smaller and thinner body compared to females.
- Curved and hooked posterior end.
- Presence of two penial spicules at the cloacal aperture used during mating.
- Cloaca instead of a separate anus.
- Four longitudinal lines on the body remain consistent across sexes.
- Reproductive system adapted for sperm production and transfer.
10. How to tell if Ascaris is male or female?
You can identify if an Ascaris is male or female by:
- Observing the posterior end shape: males have a ventrally curved tail, females have a straight, pointed tail.
- Checking body size: females are longer and thicker.
- Looking for reproductive structures: penial spicules in males and genital aperture in females.
- Using labeled diagrams as reference guides to confirm key features visually.
11. What is the color of the male Ascaris?
Both male and female Ascaris lumbricoides appear yellowish-white or pinkish in color due to their cuticle. There is no distinct color difference between the sexes; identification relies on morphological and structural features rather than coloration.
12. Do examiners mark off for extra labels not in NCERT diagrams?
Examiners usually prefer labeling that matches the NCERT prescribed diagrams or the syllabus-specific references. Including extra unrelated or incorrect labels may lead to deduction of marks. It is best to stick to key terms shown in NCERT and Vedantu materials to ensure full marks and avoid confusion.










