Key Regions of the Human Brain and Their Roles
The concept of diagram of brain is essential in biology and helps explain real-world biological processes and exam-level questions effectively. Understanding and drawing a well-labeled brain diagram prepares students for board exams, gives clarity about brain parts and functions, and is a fundamental topic in nervous system studies.
Understanding Diagram of Brain
Diagram of brain refers to a labeled illustration or drawing that shows all the main parts of the human brain, such as the cerebrum, cerebellum, brainstem, and the different lobes. This concept is important in areas like brain anatomy, brain parts and functions, and visual aids for class revision. A clear brain diagram helps students identify regions, understand their functions, and label them accurately in exams.
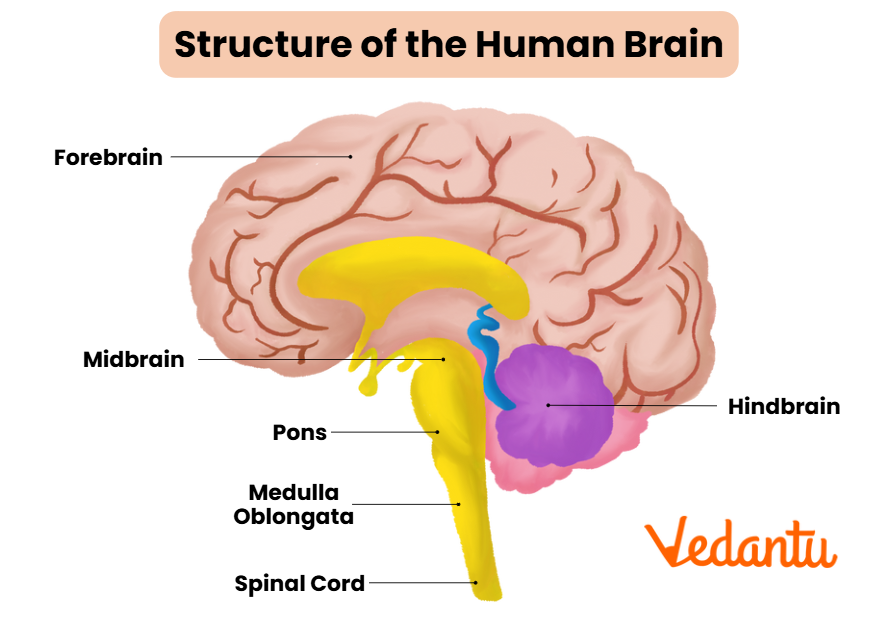
Main Parts of the Brain
The human brain is mainly divided into three key parts:
- Forebrain (Cerebrum, Thalamus, Hypothalamus)
- Midbrain (Tectum, Tegmentum, Cerebral peduncles)
- Hindbrain (Cerebellum, Pons, Medulla oblongata)
Each of these regions consists of smaller parts that control important functions such as movement, balance, learning, sensory perception, and vital processes like breathing. A labeled diagram of the brain is frequently asked in board exams and is a must-know for students of Class 10 and 12.
Lobes of the Brain and Their Functions
The cerebrum—the largest part of the brain—is further divided into four lobes, each with distinct functions. A diagram of brain lobes and functions helps clarify their roles:
| Lobe | Main Function |
|---|---|
| Frontal Lobe | Speech, reasoning, planning, motor functions |
| Parietal Lobe | Sensory perception, spatial orientation, body awareness |
| Occipital Lobe | Visual processing |
| Temporal Lobe | Hearing, recognition, processing of auditory stimuli |
Brain Stem and Ventricles
The brain stem consists of the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata. It connects the brain with the spinal cord and controls breathing, heartbeat, and reflexes. The ventricles are fluid-filled spaces inside the brain that protect it by circulating cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
Easy Brain Diagram for Kids and Beginners
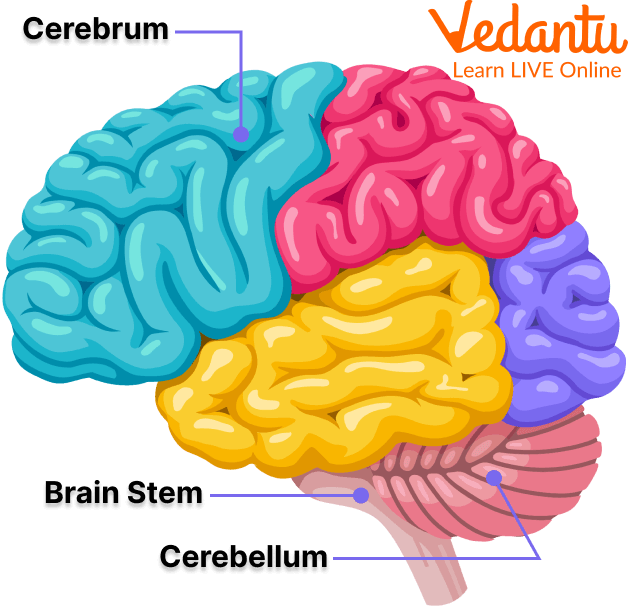
For younger students, a simple brain drawing includes the major sections—cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem. Use big labels and simple outlines for easy remembering. Vedantu recommends drawing step by step:
- Draw an oval for the cerebrum.
- Add a small rounded portion beneath it for the cerebellum.
- Draw the stem below for the brainstem.
- Label all parts clearly.
Quick Revision Table – Parts of the Brain
| Part | Location | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Cerebrum | Top, largest region | Controls voluntary actions, thinking, memory |
| Cerebellum | Back, below cerebrum | Balance and coordination |
| Brainstem | Base, connects to spinal cord | Breathing, heartbeat, reflexes |
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Confusing cerebellum with cerebrum when labeling.
- Missing out on labeling smaller parts like pons and medulla.
- Not connecting each label to its function in the diagram.
Real-World Applications
The knowledge of diagram of brain helps in medicine, psychology, and understanding diseases and injuries. For example, doctors use MRI brain diagrams to diagnose stroke or tumor locations. Students using Vedantu resources gain a practical view of how understanding the brain supports learning, health, and everyday safety.
In this article, we explored diagram of brain, its labeled parts, their functions, lobes, and tips for drawing and revision. Proper practice helps in perfect labeling and understanding. To learn more about the human nervous system or specific brain parts, continue exploring with Vedantu.
Related Reading
- Human Brain – Deep dive on brain anatomy and structure for class revision.
- Parts of the Brain – Explains each brain part with diagrams for exam reference.
- Cerebrum – Focuses on cerebrum’s structure, location, and functions.
- Cerebellum – Detailed look at the cerebellum, a key diagram label.
- Brain Tumour Symptoms – Links brain anatomy to real-life health.
- Central Nervous System – Connects brain diagrams to the rest of the nervous system.
- Difference Between Brain and Spinal Cord – Clarifies confusion about brain vs spinal cord diagrams.
- Nervous System – Explains brain’s connection to nerves and body function.
- Neuron – Shows how neurons are organized in the brain’s structure.


FAQs on Brain Diagram with Labeled Parts, Structure & Their Functions
1. What is a diagram of the brain?
A diagram of the brain is a labeled visual representation showing the major parts of the human brain such as the cerebrum, cerebellum, brainstem, and different brain lobes. It helps students understand brain anatomy clearly and is essential for effective learning and exam preparation.
2. How do you label the diagram of the brain?
To label a brain diagram accurately, start by identifying the main sections: cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem. Then, label the four major lobes of the brain: frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal. Include important substructures like the thalamus, hypothalamus, and ventricles. Use arrows and a key for clarity.
3. What are the 3 main parts of the brain?
The human brain is divided into three main parts: forebrain (includes the cerebrum and related structures), midbrain, and hindbrain (consisting of the cerebellum, pons, and medulla oblongata). Each part has distinct functions important for body coordination, sensory processing, and cognition.
4. What are the functions of each brain lobe?
Each of the four brain lobes has specific functions: frontal lobe controls reasoning, planning, speech, and motor functions; parietal lobe manages sensory information, spatial orientation, and body awareness; occipital lobe is primarily responsible for visual processing; and the temporal lobe is involved in hearing, speech recognition, and memory. Understanding these helps in linking structure to function in the brain diagram.
5. How do you draw a simple diagram of the brain for exams?
To draw a simple brain diagram, begin with an oval shape representing the cerebrum. Add smaller structures like the cerebellum at the back base and the brainstem below. Clearly mark the four major lobes with simple lines and label them. Use arrows and neat handwriting for clarity. Practice helps improve accuracy and speed.
6. What is the function of the brain stem and ventricles?
The brainstem connects the brain to the spinal cord and regulates vital autonomic functions such as breathing, heartbeat, and sleep cycles. The ventricles are fluid-filled cavities that produce and circulate cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), which cushions the brain and removes waste. Both are important components to label in a comprehensive brain diagram.
7. Why is labelling the brain diagram important for board exams?
Labeling the brain diagram correctly is crucial in board exams because it demonstrates a clear understanding of brain anatomy and functions. Exams often require precise identification of parts like lobes, brainstem, and ventricles. Proper labelling can significantly improve exam scores by showcasing detailed knowledge.
8. Why do students confuse the cerebellum with cerebrum?
Students often confuse the cerebellum with the cerebrum because both are large brain parts, but they differ in location and function. The cerebrum is the largest part, responsible for higher mental functions, while the cerebellum is smaller and located at the brain’s base, controlling balance and coordination. Clear diagram labels and revising functions help reduce this confusion.
9. How to remember all parts in a brain diagram visually?
Visual memory techniques help in remembering brain parts: use color-coded diagrams, mnemonic devices (e.g., "F-POT" for Frontal, Parietal, Occipital, Temporal lobes), and repeatedly draw the diagram. Associating each part with its function and location strengthens recall during exams.
10. Does every board/NCERT exam expect the same brain diagram?
Most boards, including NCERT, follow similar guidelines for brain diagrams, emphasizing the main parts and lobes with clear labels. However, complexity and detail can vary between classes (e.g., Class 5 vs. Class 10). It’s important to refer to the specific syllabus and marking scheme for exact requirements.
11. Why are different diagrams used for Class 5, 8, and 10?
Different classes use diagrams tailored to their learning levels. Class 5 diagrams are simpler with basic shapes and major parts. Class 8 includes more details such as lobes and some functions. Class 10 diagrams are more detailed and require accurate labelling of all main parts and functions, aligning with exam requirements and cognitive development.










