In this article, we will learn about reproduction in plants through concept maps and discuss mind maps of living things and types of reproduction in plants. After reading this article, reader will be able to explain:
Reproduction in plants
Types of reproduction
What are Sexual and asexual reproduction
Why Is Plant Reproduction Essential? Insightful Answers for Students
Reproduction is one of the essential processes to continuing life on earth. Is there any difference between reproduction in plants or animals? Do you know what is the sexual reproductive unit of plants? You might be surprised that new plant material can be produced by leaves, roots, and stems in vegetative propagation. Sexual reproduction and asexuality in plants are explained through a concept map in this article. Androecium and gynoecium are the two reproductive structures found in a flower, some plants have both types of reproductive structure known as monoecious or bisexual plants, and some have only a single type of structure either androecium or gynoecium. To know more about the reproduction of plants, continue reading this article.
Reproduction in Plants Concept Map
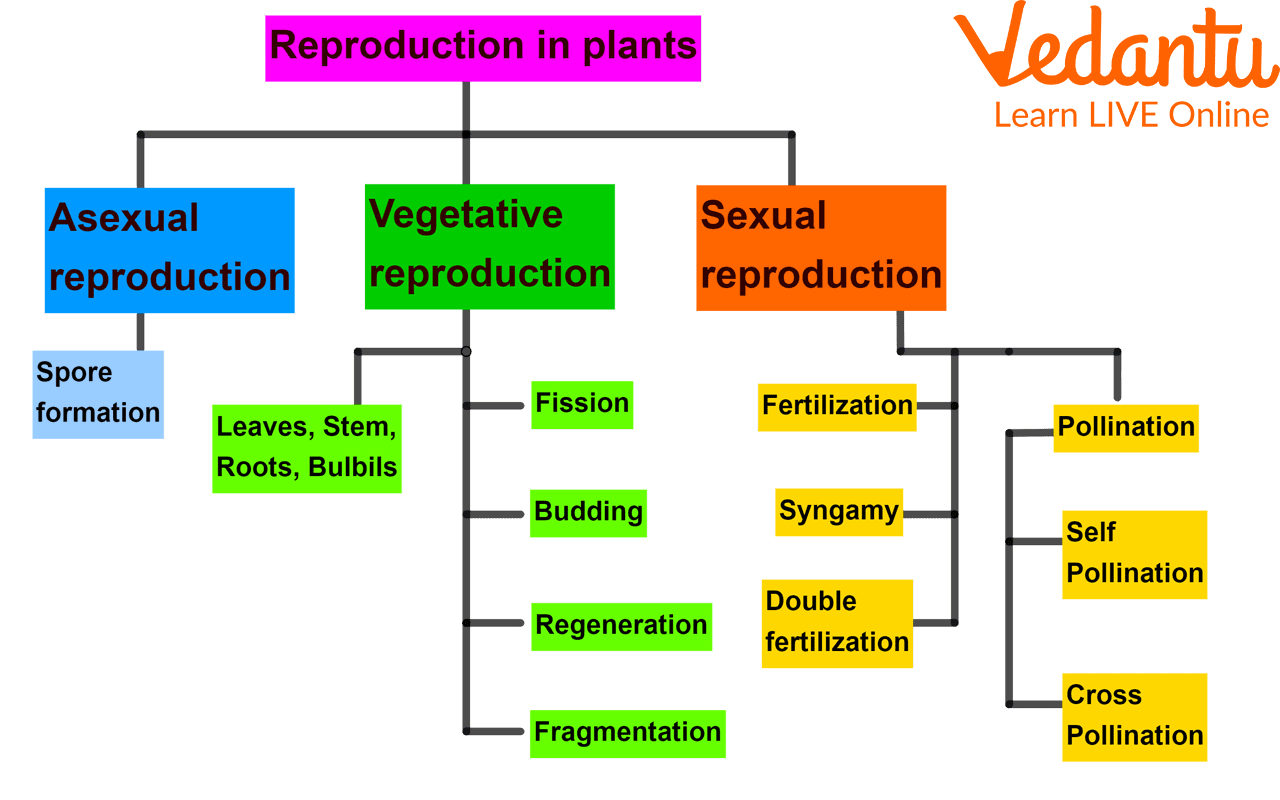
Types of Reproduction
Reproduction is already defined as a process of producing new plants from parent plants. There are many types of reproduction. Different plants use different methods of reproduction. Some of the methods are explained here. The vegetative method is sometimes involved in the asexual method, and reproduction occurs through a single parent. It involves fusion, budding fragmentation, vegetative propagation, spore formation, etc. Sexual reproduction occurs through the involvement of two parents, where fertilization occurs and the zygote forms. Then zygote is converted into a new plant.
Types of Reproduction in Plants
There are three types of reproduction in plants - Asexual, vegetative, and sexual reproduction. Asexual reproduction takes place through spores. Vegetative reproduction takes place through vegetative parts of plants, such as roots, stems, and leaves. Sexual reproduction takes place through a reproductive unit of plants which is flowers.
Asexual Reproduction Concept Map
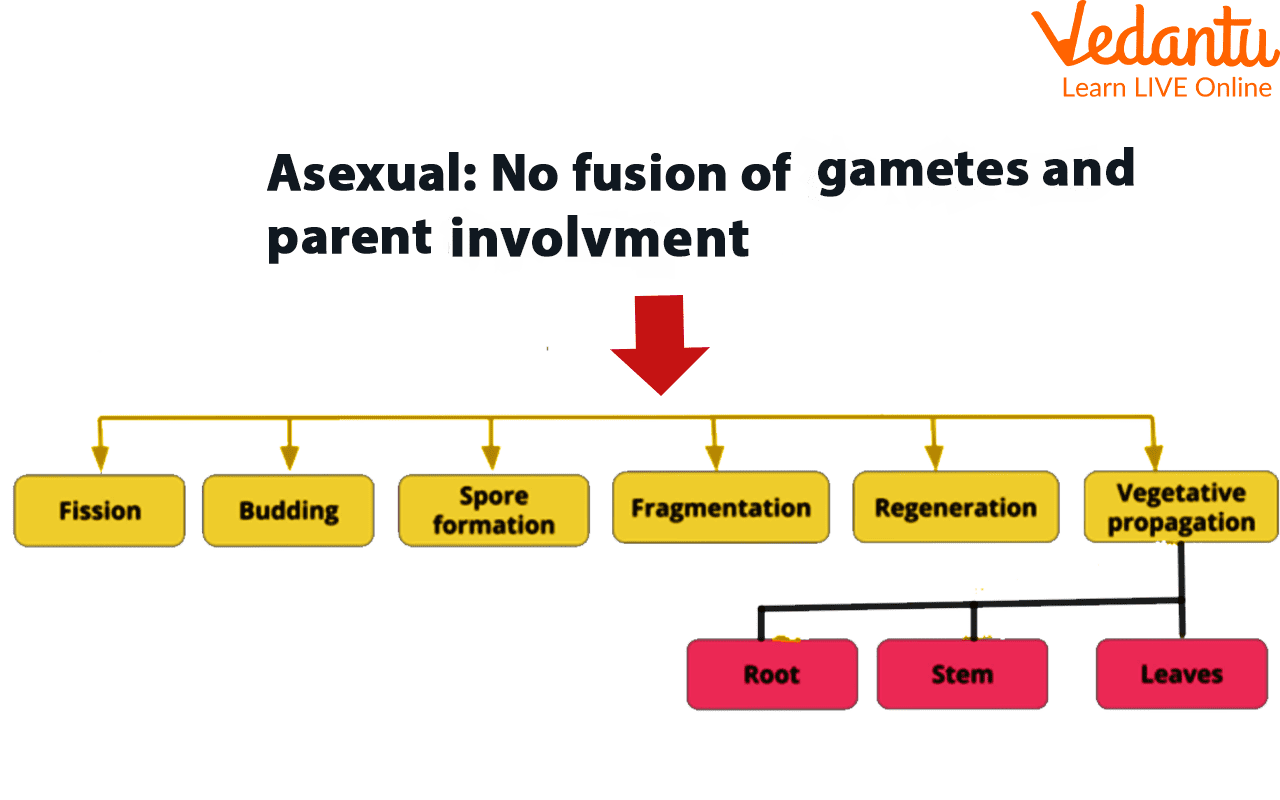
Types of Asexual Reproduction
Asexual reproduction in plants takes place through many methods. These methods are budding, spore formation, fragmentation, and vegetative propagation.
Sexual Reproduction Concept MAP
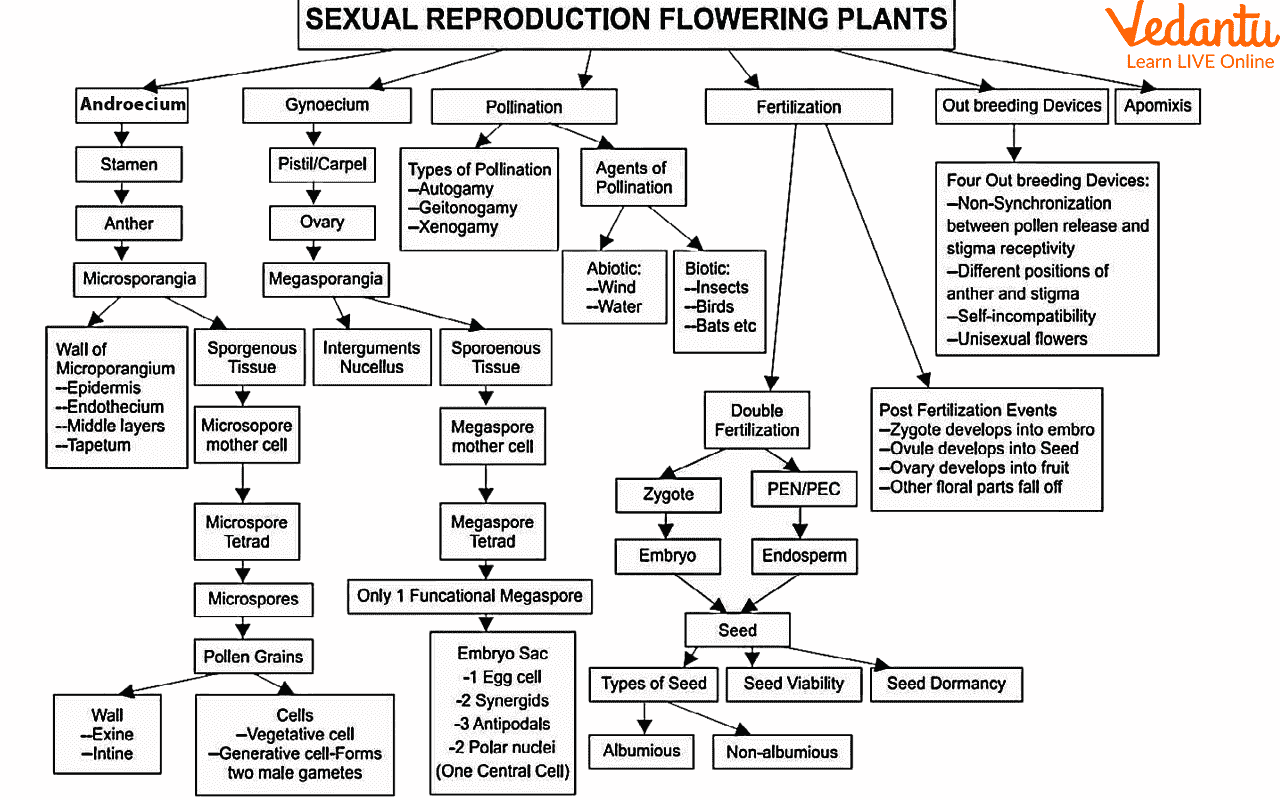
Concept Map of Sexual Reproduction in plants
As is already explained that in sexual reproduction, two parents are involved. One is a male parent, and the other is a female parent. Male parents form male gametes, whereas female parents form female gametes. The flower is the reproductive organ of plants. There are two main important reproductive parts in flowers- one is the male part which is the androecium, and the other is the female part which is the gynoecium. Now androecium is a bundle of stamen, and the gynoecium is a bundle of the pistil. There are two main parts of stamen- anther and filament. Pollen grains are the male gametophyte produced in other flowers. These pollen grains later divide into male gametes. Now carpel is the female reproductive part of a flower. It has three important parts- stigma, style, and ovary. In the ovary, there is a female gamete that is the ovum.
Now, most of the plant pollen grain lands on the stigma, where it forms a male gamete; the male gamete then reaches to ovary through style, where it fuses with the female gamete ovum, a process known as fertilization. The fusion of male and female gametes leads to the formation of a zygote which undergoes development to make the embryo process known as embryogenesis.
Important Questions
1. What factors affect plant reproduction?
The important factors which affect plant reproduction are - the intensity of light, duration, quality of light, temperature, etc.
2. What are the different purposes of reproduction in plants?
The important purpose of plant reproduction is to ensure species' continuity.
3. What are the different things plants need to grow?
Plants need various factors for growth. These factors are proper temperature, light, water, humidity, and nutrients.
Interesting Facts
Originally carrots were purple or white colored. Genetic mutations produce orange carrots.
One strawberry contains, on average, 200 seeds.
The bamboo tree is the fastest-growing plant; it can grow 1 inch per month
Snapdragon flower is the flower that resembles a snapdragon
Gingko is a gymnosperm and is the only plant that is still alive yet.
Practice Questions
1. Explain the life process mind map
2. What are the different modes of reproduction in plants?
3. What happened during plants reproduction
4. What are the benefits of reproduction?
5. What are the features of reproduction?
Key Features
In this article, we have discussed reproduction in a plants concept map
We have discussed types of reproduction in plants - there is a mainly sexual, asexual, and vegetative methods of reproduction in plants
An asexual reproduction concept map is also discussed in this article. Budding, fragmentation, and Vegetative propagation are important methods of asexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction involves gamete formation and fertilization.
The mind map of reproduction in plants is the same as the Concept Map of reproduction in plants


FAQs on Reproduction in Plants: Definitions, Types, and Examples
1. What is meant by reproduction in plants?
Reproduction in plants is the fundamental biological process through which new individual plants, or offspring, are produced from their parent plants. This process is crucial for the continuation of a plant species. Plants can reproduce through two primary methods: sexual reproduction, which involves the fusion of male and female gametes, and asexual reproduction, which involves only one parent.
2. What are the two main types of reproduction found in plants?
The two main types of reproduction in plants are:
- Asexual Reproduction: This method involves a single parent plant giving rise to a new plant. The offspring are genetically identical to the parent. Examples include budding in yeast and vegetative propagation in potatoes.
- Sexual Reproduction: This method involves the fusion of male and female gametes to produce a seed, which then grows into a new plant. This process introduces genetic variation and typically involves flowers.
3. Explain the process of asexual reproduction in plants with examples.
Asexual reproduction is a method where a new plant grows from a part of a single parent plant, without the involvement of gametes or fertilisation. The new plant is a clone of its parent. Common types include:
- Vegetative Propagation: New plants arise from vegetative parts like roots, stems, or leaves. For example, new potato plants grow from the 'eyes' (buds) on a tuber.
- Budding: A small bulb-like projection, or bud, grows on the parent cell (like in yeast) and eventually detaches to form a new individual.
- Fragmentation: The parent plant's body breaks into distinct pieces, and each fragment can grow into a new plant. This is common in algae like Spirogyra.
- Spore Formation: Plants like ferns and mosses produce tiny, resilient spores that can germinate under favourable conditions to form new plants.
4. What are the main parts of a flower and their functions in reproduction?
A flower's reproductive parts are essential for sexual reproduction. The main parts are:
- Stamen (Male Part): Consists of the anther, which produces pollen grains (containing male gametes), and the filament, a stalk that holds up the anther.
- Pistil or Carpel (Female Part): Consists of the stigma, a sticky tip that receives pollen; the style, a tube connecting the stigma to the ovary; and the ovary, which contains ovules (female gametes).
- Petals: Often brightly coloured to attract insects and birds for pollination.
- Sepals: Green, leaf-like structures that protect the flower in its bud stage.
5. What is the difference between self-pollination and cross-pollination?
The primary difference is the source and destination of the pollen grains.
- Self-pollination occurs when pollen from a flower's anther is transferred to the stigma of the same flower or another flower on the same plant.
- Cross-pollination occurs when pollen from the anther of a flower on one plant is transferred to the stigma of a flower on a different plant of the same species. This process relies on agents like wind, water, or animals.
6. Describe the process of fertilisation in flowering plants.
Fertilisation is the process that occurs after pollination. Once a pollen grain lands on a compatible stigma, it grows a tube called a pollen tube down through the style to reach the ovary. The male gamete from the pollen travels down this tube and fuses with the female gamete inside the ovule. This fusion of gametes is called fertilisation, and the resulting cell is known as a zygote, which develops into an embryo.
7. How does a flower develop into a fruit after fertilisation?
After fertilisation is complete, the flower undergoes significant changes. The primary purpose of the flower, which is reproduction, has been fulfilled. Consequently:
- The ovary of the flower begins to swell and develops into the fruit.
- The ovules inside the ovary develop into seeds, with each seed containing an embryo.
- Other parts of the flower, such as the petals, sepals, and stamens, typically wither and fall off.
The fruit serves to protect the seeds and aids in their dispersal.
8. Why is seed dispersal important for the survival of a plant species?
Seed dispersal, which is the scattering of seeds away from the parent plant, is critically important for several reasons:
- It prevents overcrowding near the parent plant, reducing competition for essential resources like sunlight, water, and soil nutrients.
- It allows plants to colonise new habitats and expand their geographical range.
- By spreading out, it increases the chances of survival for the species, as a localised disaster (like disease or fire) will not wipe out the entire population.
Dispersal happens through agents like wind, water, animals, and even explosive mechanisms in some fruits.
9. What are the key advantages of sexual reproduction over asexual reproduction in plants?
Sexual reproduction offers significant advantages over asexual reproduction, primarily because it promotes genetic variation. Since offspring are formed from the combination of gametes from two different parents (or through cross-pollination), they have a unique combination of genes. This genetic diversity allows a plant population to better adapt to changing environmental conditions, resist new diseases, and evolve over time, which enhances the long-term survival of the species.
10. What are some common examples of artificial vegetative propagation?
Artificial vegetative propagation refers to man-made methods used to grow new plants from the parts of a parent plant, often in agriculture and horticulture. Common examples include:
- Cutting: A piece of a stem or branch with nodes is cut from a parent plant (e.g., rose, sugarcane) and planted in the soil to grow a new plant.
- Layering: A low-lying branch of a plant (e.g., jasmine) is bent and covered with soil while still attached to the parent. Once roots develop, it is cut and grown as an independent plant.
- Grafting: A stem piece (scion) from a desired plant is attached to the rooted stem (stock) of another plant. This is used to combine desirable traits, like in many fruit trees such as mangoes and apples.
In this article, we will learn about reproduction in plants through concept maps and discuss mind maps of living things and types of reproduction in plants. After reading this article, reader will be able to explain:
Reproduction in plants
Types of reproduction
What are Sexual and asexual reproduction










