Learn and Understand Neural Control And Coordination Questions And Answers With Vedantu's Expert Guidance
Chapter 18 Biology Class 11 NCERT Solutions for Neural Control and Coordination are essential study materials that will help the students to secure better marks in the exam. Expert and proficient Biology teachers prepare the Class 11 Bio Chapter 18 NCERT Solutions. NCERT solution comprises precise answers, along with diagrams and explanations. The questions presented in solution books are organised by NCERT (CBSE), thus holding higher chances of appearing on CBSE question papers.
 Table of Content
Table of ContentClass: | |
Subject: | |
Chapter Name: | Chapter 18 - Neural Control and Coordination |
Content-Type: | Text, Videos, Images and PDF Format |
Academic Year: | 2025-26 |
Medium: | English and Hindi |
Available Materials: | Chapter Wise |
Other Materials |
|
Note:➤Unlock your dream college possibilities with our NEET College Predictor!
Grab the solutions of ch 18 Bio Class 11 to get answers to the chapter. The solutions are easily accessible and are also free to download.
Neural Control and Coordination Chapter at a Glance - Class 11 NCERT Solutions
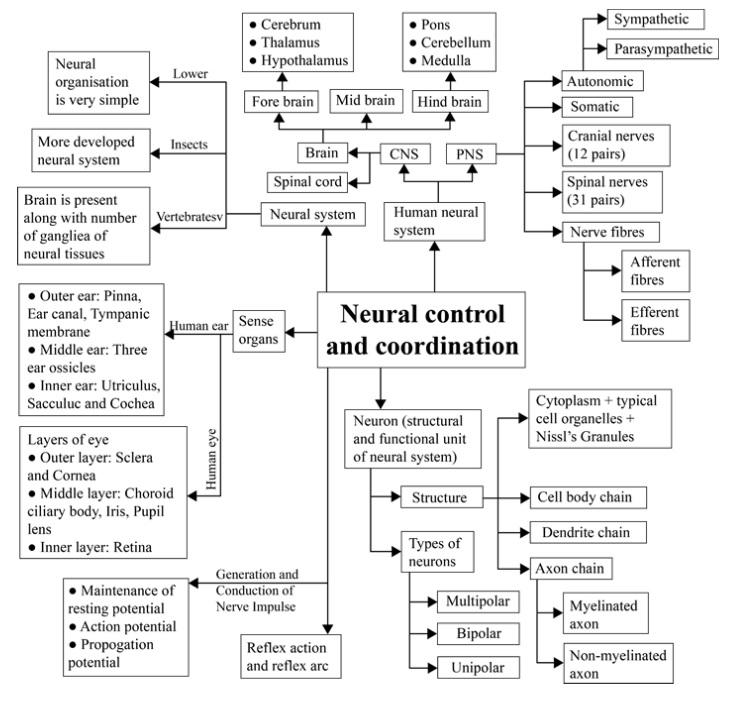
Neural Control and Coordination
Master Neural Control And Coordination Questions And Answers With Vedantu's Expert Guide
1. Briefly describe the structure of the following:
(a) Brain
Ans: The skull protects the human brain. There are three layers of meninges in the skull, one is the dura mater, the next is the arachnoid, and the third (which is directly attached to the brain) is the pia mater. There are three major parts to the brain:
(i) Forebrain: The forebrain consists of the cerebral cortex, hypothalamus, and thalamus.
(ii) Midbrain: Located between the thalamus and hypothalamus of the frontal lobes, it is the brain's intermediate portion.
(iii) Hindbrain: It consists of the pons, cerebellum, and medulla.
(b) Eye
Ans: Lens- The human eyeball is almost cylindrical in shape. There are three layers to the eyeball. X-rays can reveal the existence of a dense connective tissue layer that surrounds the eyeball called the sclera. This layer includes the cornea on its anterior portion. A blue-coloured layer at the middle of the choroid is composed of blood vessels. As the eyeball approaches the middle, the choroid layer becomes thin but becomes thicker underneath. Iris, the coloured portion of the eye, is formed from the pigmented ciliary body. An eyeball is supported by a clear crystalline lens whose position is maintained by ligaments attached to the ciliary body. Iris muscle fibres control the diameter of the pupil, the pupil's opening surrounding the lens.
The retina is the inner layer of the eye, which is composed of three layers of neural cells beginning on the outside and continuing inwards - ganglion cells, bipolar cells, and photoreceptor cells. Both rods and cones can serve as photoreceptor cells. A cone is responsible for vision in daylight (photopic) and colour vision, and a rod is responsible for vision in twilight (scotopic). Ganglion cells from the optic nerve fibres are connected to the brain by the optic nerve in each eye.
(c) Ear
Ans: It is a sensory organ that protects the body from danger, and it helps keep it balanced. The outer ear is made up of the pinna and external auditory meatus (canal). The middle ear consists of the eustachian tube and the otoliths. As sounds are created in the air, the pinna collects its vibrations. An external auditory meatus runs from the tympanic membrane (eardrum) inward. In the pinna and meatus skins, hairs are very fine and wax glands are present. Connective tissues cover the outside of the tympanic membrane and mucous membrane covers the inside.
→ Middle Ear: The middle ear is divided into three ossicles—the malleus, the incus and the stapes. The incus and the stapes are linked together in a chain-like arrangement. This complex of bones is attached to the tympanic membrane and the oval window of the cochlea by the malleus and stapes. It increases the efficiency of sound waves being transmitted to the inner ear through ear ossicles. Middle ear cavities connect to the pharynx through a Eustachian tube. As the pressure is equalized on both sides of the eardrum, the Eustachian tube works.
→ Inner Ear: Also referred to as a labyrinth. Bony labyrinths and membranous labyrinths exist within the labyrinth. The bony labyrinth is filled with perilymph, whereas the membrane labyrinth is filled with endolymph. The vestibular apparatus and cochlea are the two parts of the labyrinthine membrane. There are three semicircular canals and an otolith in the vestibular apparatus (the macular nerve forms the sensory pathway between the utricle and saccule). Several semicircular canals lie at right angles to one another in a different plane. Perilymph surrounds the bony canals, permitting the membranous canals to travel. Canals are swollen at the bottom and have thick ridges called ampullae, which attach to a projection called crista ampullaris. Maculas are ridges that project from the saccule and utricle. In addition, the vestibular apparatus maintains posture and balance when the crista and macula are activated.
An extension of Sacculus is the Cochlea. Besides being the main organ for hearing, it also controls balance. Three membranes make up the cochlea. A hearing organ called the organ of Corti is found on the basilar membrane, which is covered in hair cells.
2. Compare the following:
(a) Central neural system (CNS) and Peripheral neural system (PNS)
Ans: The difference between the central neural system (CNS) and Peripheral Nervous System is given below:-
Central Neural System (CNS) | Peripheral Neural System (PNS) |
The central nervous system coordinates the body's functions. | The body's main coordination centre is not here. |
It is found inside the skull. | It is not situated inside the skull. |
The brain and spinal cord are composed here. | Nerves to do with the central nervous system are included here. |
(b) Resting potential and action potential
Ans: The difference between resting potential and action potential is given below:-
Resting Potential | Action Potential |
The difference in electrical potential across a nerve fibre at no time when no nerve impulses are being conducted across the fibre. | During nerve conduction, it is the potential difference between nerve fibres. |
Neurons are electronegative on the inside and electropositive on the outside. | Neurons are electropositive internally and electronegative externally. |
Pumps that use sodium act as active sodium pump. | The sodium pump does not operate. |
(c) Choroid and Retina
Ans: The difference between choroid and retina is given below:-
Choroid | Retina |
The choroidal layer is a layer of vascular tissue in the eye. | A retina is the innermost layer of nerves in the eye. |
It is abundant in blood cells | It is abundant in neurons
|
It is involved in supplying nutrients and oxygen.
| Its function is to form an image for other parts of the eye i.e. the retina forms an image of the object. |
3. Explain the following processes:
(a) Polarization of the membrane of a nerve fibre
Ans: The membrane becomes polarized when its resting potential changes. The $K^+$ and negatively charged proteins in the axoplasm are higher than the $Na^+$ concentration inside the axon when in resting condition. Thus, potassium ions move faster from the inside to the exterior than sodium ions. A positively charged membrane becomes negatively charged inside and a positively charged membrane becomes negative. An example of this would be polarized nerves or polarized membranes.
(b) Depolarization of the membrane of a nerve fibre
Ans: An action potential occurs when a nerve fibre receives an electrical stimulus. As sodium ions pass through the membrane, potassium ions are less permeable. Consequently, the nerve fibre becomes positively charged inside, and negatively charged outside. This depolarization of the membrane is referred to as depolarization.
(c) Conduction of a nerve impulse along with a nerve fibre
Ans: Nerve fibres are divided into two types - myelinated and unmyelinated. Since Schwann cells surround the axon of a myelinated nerve fibre and form the myelin sheath, the impulse travels back and forth rapidly in the myelinated nerve fibre. Ions cannot pass through the myelin sheath. The nerve fibres do not exchange ions and depolarise efficiently along their entire length as a result. Ranvier's nodes occur only at some points. A normal unmyelinated nerve fibre experiences ionic exchange along its full length, which then causes repolarization of depolarized areas and depolarization of other areas.
(d) Transmission of a nerve impulse across a chemical synapse
Ans: On chemical synapses, there is a fluid-filled space between pre-and postsynaptic neurons, called a synaptic cleft. After receiving an impulse, synaptic vesicles move toward the plasma membrane and fuse with the plasma membrane in the synaptic cleft, where they release their neurotransmitters. A number of receptors are present on the postsynaptic membrane, which binds to released neurotransmitters. Postsynaptic neurons form new potentials in response to ion channels opened by this binding. An excitatory or inhibitory potential can be developed.
4. Draw labelled diagrams of the following:
(a) Neuron
Ans :
(Image will be uploaded soon)
(b) Brain
(Image will be uploaded soon)
(c) Eye
(Image will be uploaded soon)
(d) Ear
(Image will be uploaded soon)
5. Write short notes on the following:
(a) Neural coordination
Ans: A neural system facilitates the interaction and complementing of the activities of two or more organs. Interconnected and interdependent are all of the body's physiological functions. Coordinating and integrating all the organ's functions, the brain and endocrine system work together. Brain systems provide fast coordination by organising a network of interconnected points. Hormones enable chemical integration by the endocrine system.
(b) Forebrain
Ans: Among the three parts of the cortex are the cerebrum, thalamus, and hypothalamus.
→ The brain's main structure is the cerebrum. The Left and right cerebral hemispheres are separated by a fissure in the cerebrum. Connecting the hemispheres is the corpus callosum. Cells that cover the cerebral hemisphere make up the cerebral cortex, which is a layer of pronounced folds. It is referred to as grey matter because of its greyish colouration. Several portions of the cerebral cortex have no obvious sensory or motor function. A variety of complex activities are performed by association areas, including intercessory associations, memory, and communication. In the cerebral hemisphere-interior section, the fibres of the tract are protected by the myelin sheath. White matter is named as a result of its impenetrable appearance. Intercessory associations, memory, and communication are all tasks that the association areas are accountable for. The myelin sheath, which makes up the interior section of the cerebral hemisphere, protects the tract fibres. They give the layer an impenetrable white appearance, thus the name "white matter."
→ Thalamus: There is a region within the cerebrum wrapped around the middle of the forebrain named the Thalamus. Sensory and motor signalling are coordinated at this centre.
→ Hypothalamus: In the hypothalamus, there are numerous centres that regulate body temperature, urges for eating, and thirst. In addition to controlling growth and sexual behaviour, it is connected with the pituitary gland.
(c) Midbrain
Ans: The midbrain: From the forebrain to the hindbrain, the midbrain lies between the thalamus and the hypothalamus. This section of the brain passes through a canal known as the cerebral aqueduct.
(d) Hindbrain
Ans: In the hindbrain, you will find pons, cerebellum, and medulla.
There are many neurons in the cerebellum, so its surface is very convoluted in order to accommodate those extra neurons.
In the brain, the medulla and spinal cord are connected.
The medulla is home to centres that regulate respiratory functions, cardiovascular reflexes, and gastric secretions.
(e) Retina
Ans: Retina, also known as the photoreceptor, is a layer of neural cells located at the back of the eye. It includes ganglion cells, bipolar cells and astrocytes. They act as photoreceptors. Rods and cones make up photoreceptor cells. A cone is a sensory organ that is responsible for the perception of daylight and colour whereas the rods are responsible for twilight vision. Images of objects are formed on the retina by the light entering through the cornea and the lens.
(f) Ear Ossicles
Ans: Malleus, incus, and stapes are three ossicles located in the middle ear, which are connected one to another through a chainlike arrangement. Among the three components of the ear, malleus is connected to the tympanic membrane, incus is attached to the stapes, and stapes is attached to the cochlea's oval window. By transmitting sound waves effectively into the inner ear, ear ossicles increase hearing efficiency.
(g) Cochlea
Ans: The cochlea is the coiled section of the labyrinth. There is an upper and a lower scala tympani in the cochlea, composed of reissner's and basilar membranes. Scala media, which fills the cochlea, contains endolymph. A rectangular window open to the middle ear accompanies the oval window at the base of the cochlea, and around the window opens to it at the base of the cochlea.
(h) Organ of Corti
Ans: In the organ of Corti, hair cells function as auditory receptors located on the basilar membrane. On the inside surface of the Corti organ, hair cells are arranged in rows.
(i) Synapse
Ans: The synaptic cleft is a gap between postsynaptic cells and presynaptic cells that divides the synaptic membranes. Synapses are of two different types: chemical and electrical.
6. Give a brief account of:
(a) Mechanism of Synaptic Transmission
Ans: A synapse is a point where two neurons meet. It exists between one neuron's axon terminal and the dendrite of the next neuron, divided by a cleft.
Synaptic transmission occurs in two ways.
(1) Chemical Transmission - A neurotransmitter (acetylcholine) is released across the synaptic cleft when a nerve impulse reaches the endplate of an axon. This substance is produced in the neuron's cell body and delivered to the axon terminal. Acetylcholine diffuses over the cleft and attaches to receptors on the surface of the next neuron's membrane. This results in membrane depolarization and the initiation of an action potential.
(2) Electrical Transmission - An electric current is created in the neuron in this sort of transmission. This electric current causes an action potential, which results in nerve impulse transmission across the nerve fibre. This technique of nerve conduction is quicker than the chemical method of transmission.
(b) Mechanism of Vision
Ans: The retina is the eye's innermost layer. Inner ganglion cells, middle bipolar cells, and outermost photoreceptor cells make up the three layers. A photoreceptor cell is made up of a protein called opsin and a vitamin A aldehyde known as retinal. The separation of the retinal from opsin protein occurs when light rays are focused on the retina through the cornea. Opsin's structure is altered as a result of this. The permeability of the membrane changes as the structure of opsin changes, resulting in a potential differential in the cells. This causes an action potential in the ganglionic cells, which is then communicated to the brain's visual cortex via optic nerves. The impulses are analysed in the cortex portion of the brain, and an image is generated on the retina.
(c) Mechanism of Hearing
Ans: Sound waves are collected by the pinna of the external area and sent to the eardrum or external auditory canal. Vibrations are formed when these waves hit the tympanic membrane. The vibrations are then conveyed to the oval window, fenestra ovalis, via the malleus, incus, and stapes, three ear ossicles. These ossicles in the ear operate as a lever, transmitting sound waves to the inner ear. The vibrations of the fenestra ovalis are conveyed to the cochlea. The lymph produces sound waves as a result of this. A ripple in the basilar membrane is caused by the creation of waves. The sensory hair cells on the organ of Corti bend against the tectorial membrane as a result of this action. Sound waves are turned into nerve impulses as a consequence of this. Auditory nerves then carry these signals to the auditory cortex of the brain. The impulses are analysed and sound is identified in the cerebral cortex of the brain.
7. Answer Briefly:
(a) How do you perceive the colour of an object?
Ans: Color vision is mediated by cones. Cones respond to different types of light depending on their characteristics, such as green, blue and red. Light from different sources stimulates these cells in different ways. We see different colours due to the combination of signals generated.
(b) Which part of our body helps us in maintaining body balance?
Ans: Cochlear canals are formed by three semicircles in the inner ear. Keeping the body in balance is the job of the Cochlea.
(c) How does the eye regulate the amount of light that falls on the retina?
Ans: The pupil is a small opening between the iris and the lens of the eye that regulates light entering the eye. In the dim light, they expand to let more light fall on the retina, whereas in the presence of intense light they contract.
8. Explain the following:
(a) Role of Na+in the generation of the action potential.
Ans: Ionization of Na+ is responsible for the action potential. By diffusion into the inside of the axoplasm, the Na+channels, which are normally closed, become opened and allow the inflow of Na+ions. After the membrane has depolarized, its electrical potential moves from 70 mV toward zero.
(b) Mechanism of generation of light-induced impulse in the retina.
Ans: Photopigments composed of both retinal and opsin in the eye are photosensitive and pigmented substances. Retinal dissociates from opsin when exposed to light, altering the structure of opsin. The bipolar neurons generate action potentials. In order to recognize the rect image, the brain analyzes the neural signals and action potentials presented by the optic nerves.
(c) Mechanism through which a sound produces a nerve impulse in the inner ear.
Ans: Acoustic energy is transmitted to the inner ear when it falls on the eardrums. Vibrations are transferred to the lymphatic fluid from the oval window in the cochlea. When the waves are accompanied by ripples in the basilar membrane, the cells of the hair are bent, forcing them against the tectorial membrane. The result of this is the generation of nerve impulses in the associated afferent neurons and their transmission to the auditory cortex of the brain, where they are analyzed and recognized as sound.
9. Differentiate Between:
(a) Myelinated and unmyelinated axons
Ans: Differences between Myelinated and unmyelinated axons:-
Myelinated Axons | Non-Myelinated |
These are whitish in colour. | The colour of these seems greyish. |
Myelin sheaths are found. | It lacks a myelin sheath. |
At intervals, Ranvier nodes can be found. | There are no nodes of Ranvier. |
Neural impulses travel faster. | Nerve impulses are transmitted more slowly. |
A node is the only place where ions can be exchanged. | A large amount of ion exchange occurs on the surface. |
(b) Dendrites and Axons
Ans: Differences between Dendrites and axons:-
Dendrites | Axons |
The axons arise from the cytons present anteriorly. | At their posterior position, these are extensions of cytons. |
Cellular impulses are transmitted through these pathways. | Cells use them to conduct impulses away from their bodies. |
There is no myelin sheath in dendrites. | The axons may or may not be myelinated. |
Dendrites become receptors at their terminals. | There are many terminal arborizations at the end of each axon. |
(c) Rods and cones
Ans: Differences between Rods and Cones:-
Rods | Cones |
Dim light affects rods. | Bright light is the only thing that can stimulate cones. |
Rhodopsin is the purple pigment responsible for its visual appearance. | Their visual pigment is iodopsin, which is violet. |
Rod cells do not show colours. | Colours can be seen better with cones. |
(d) Thalamus and Hypothalamus
Ans: Differences between Thalamus and Hypothalamus:-
Thalamus | Hypothalamus |
The diencephalon is represented by it. | It is a part of the diencephalon located at the bottom. |
Sensory and motor signalling are coordinated by this centre. | Among other things, it regulates body temperature, thirst, hunger, etc. |
The gland does not secrete any hormones. | A number of hormones are produced by this gland. |
(e) Cerebrum and Cerebellum
Ans: Differences between Cerebrum and Cerebellum:-
Cerebrum | Cerebellum |
This part of the brain is located in the front. | It is located in the hindbrain. |
The cerebral hemispheres are divided into two. | A median vermis forms the middle between the cerebellar hemispheres. |
Voluntary movements are initiated by it. | Maintaining posture and equilibrium is achieved by it. |
10. Answer the following:
(a) Which part of the ear determines the pitch of a sound?
Ans: Cochlea
(b) Which part of the human brain is the most developed?
Ans: Cerebrum
(c) Which part of our central neural system acts as a master clock?
Ans: Hypothalamus
11. The region of the vertebrate eye, where the optic nerve passes out of the retina, is called the (a) fovea
(b) iris
(c) blind spot
(d) optic charisma
Ans : (c) blind spot
12. Distinguish between
a) Afferent neurons and Efferent neurons
Ans:
Afferent Neurons | Efferent Nerve Cells |
They transmit impulses toward the central nervous system. | Impulses are conducted away from the central nervous system by these fibres. |
It stimulates the senses and evokes them. | It causes the effectors to respond. |
Their nature is sensory. | In nature, they have motor functions. |
Information is taken from the receptors. | The effectors receive the information.. |
b) Impulse conduction in a myelinated nerve fibre and an unmyelinated nerve fibre
Ans:
Impulse Conduction in Myelinated Nerve Fibre | Impulse Conduction in an Unmyelinated Nerve Fibre |
If a node of Ranvier lacks a myelin coating, depolarization occurs. | The nerve fibres are depolarized along their entire length. |
There is a jump between different nodes of Ranvier regarding action potential. | Fibres carry action potential along their entire length. |
The pace of conduct is faster. | The pace of conduct is slower. |
It requires less energy. | Energy is required in greater amounts. |
c) Aqueous humour and Vitreous humour
Ans:
Aqueous Humour | Vitreous Fluid |
It is transparent and watery in nature. | A transparent, thick gel-like fluid is present. |
Lenses and corneas are in contact with it. | The lens and retina are connected by this structure. |
Ciliary glands continuously secrete it, which drains from the eyes. | There is no replacement for it. |
Lenses, corneas, and other parts of the anterior chamber receive nourishment from it. | There is no nutritional value to it. |
d) Blindspot and Yellow spot
Ans:
Blindspot | Yellow Spot |
Blind spots are prominent at the origin of the optic nerve - an area of the retina containing a solitary yellow spot. | A yellow spot is a small area of the retina located lateral to the blind spot, at the posterior pole of the eye. |
There is no shallow depression. | The fovea centralis is a shallow depression. |
In this region, no photoreceptors are present. | In this region, only cones exist. |
Light has no effect on it. | Bright light affects its sensitivity. |
A photoreceptor cell is not present in this region. | In this region, there are only cones. |
A blind spot does not form an image. | At the yellow spot, an image is formed. |
e) Cranial nerves and Spinal nerves
Ans:
Cranial Nerves | Spinal Nerves |
These originate from the brain. | They are nerves that originate in the head and originate in the spinal cord. |
The brain is composed of 12 pairs of cranial nerves. | 31 spinal nerves make up the spine. |
The brain and body are connected by them.
| Parts of the spinal cord are connected to them. |
Depending on their nature, they could be sensory, motor, or mixed. | In nature, they are mixed. |
NCERT Biology Class 11 Neural Control and Coordination PDF Download
Class 11th Biology Chapter 18 NCERT Solutions will grant you the basic idea about the chapter. It will help the students to understand the neural system of humans and the terms related to its means. The format of the answers will assist you in learning the chapter very well. Students can download the PDF files of Class 11 Neural Control and Coordination NCERT Solutions to solve the questions and understand the chapter.
Class 11 Neural Control and Coordination NCERT Solutions
The NCERT Biology Class 11 Neural Control and Coordination PDF will help you to understand the neural system of a human body precisely.
In the chapter, the students will discuss the mechanisms of neural coordination like transmission of nerve impulse, the physiology of reflex action and impulse conduction across a synapse, central neural system and reflex arc. The elements of the central nervous system(CNS) like the hindbrain, forebrain, midbrain, peripheral nervous system, spinal cord, autonomic nervous system, and sense organs like eyes and ears are also explained in the chapter.
The functions and structure of the Human Nervous Systems like the brain, spinal cord, nerves are explained with diagrams and comprehensive text in the Chapter 18 Biology Class 11 PDF. The students will also get to learn the mechanism of impulse conduction, hearing and vision in an interesting way.
In Neural Control and Coordination Class 11 PDF solutions, the students will acquire all the answers and will help them to obtain good marks in the exam.
Important Topics Covered in Chapter 11
The Neural Control and Coordination chapter of Biology constitutes the discussion of the following topics:
18. Neural Control And Coordination |
18.1 Neural System |
18.2 Human Neural System |
18.3 Neuron as Structural and Functional Unit of Neural System |
18.3.1 Generation and Conduction of Nerve Impulse |
18.3.2 Transmission of Impulses |
18.4 Central Neural System |
18.4.1 Forebrain |
18.4.2 Midbrain |
18.4.3 Hindbrain |
18.5 Reflex Action and Reflex Arc |
18.6 Sensory Reception and Processing |
18.6.1 Eye |
18.6.1.1 Parts of an Eye |
18.6.1.2 Mechanism of Vision |
18.6.2 The Ear |
20.6.2.1 Mechanism of Hearing |
Key Learnings from the Chapter
All of the organs' operations, as well as metabolic and homeostatic processes, are coordinated and integrated by the nervous system.
Coordination refers to the process by which two or more organs interact and complement one another's functions.
The neural system is made up of neurons, which are highly specialised cells that can receive and transmit many types of information.
Neurons are the functional units of the nervous system.
They are excitable cells because of a difference in ion concentration across the membrane.
The cell body, dendrites, and axon are the three major elements of a neuron.
Cell organelles and a few granules known as Nissl's granules are found in the cytoplasm of the cell body.
A wave of depolarization and repolarization transports the nerve impulse down the axon membrane.
The central neural system (CNS) and the peripheral neural system (PNS) make up the human neural system.
The brain and spinal cord make up the CNS.
The PNS is made up of all of the body's nerves that are connected to the CNS.
The somatic neural system and autonomic neural system are the two divisions of the PNS.
The autonomic neural system sends impulses from the CNS to the involuntary organs and smooth muscles of the body, while the somatic neural system conveys impulses from the CNS to skeletal muscles.
Responding to peripheral nerve stimulation is an involuntary procedure that necessitates the involvement of a component of the CNS known as a reflex action.
At least one efferent neuron and one afferent neuron make up the reflex pathway.
The afferent neuron receives signals from sensory organs and sends them to the CNS, while the efferent neuron sends messages from the CNS to the effector organ.
CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 18 NCERT Solutions - Weightage Marks
The Neural Control and Coordination Class 11 NCERT PDF will build a strong understanding of the textbook questions and also help you learn the question patterns and how to write an answer for a particular type of question. The overall marks for Class 11 Biology are 70 marks for theory and 30 marks for the practical exam.
NCERT Grade 11 Biology Chapter 18 is a part of unit 5 human physiology. The marking scheme for unit 5 holds a weightage of 18 marks. The Neural Control and Coordination chapter will carry 2 to 5 marks excluding Viva Voce and Practical Records. Class 11th Biology Chapter 18 NCERT Solutions will guide the students regarding the chapter.
Benefits of NCERT Biology Class 11 Chapter 18 PDF
Class 11 Neural Control and Coordination NCERT Solutions will help the students to understand the chapter accurately. Here are some of the benefits of studying the Class 11 Biology Chapter 18 NCERT Solutions.
The questions and answers of the chapter are accurate and precise.
The solutions of the chapters are prepared by expert and experienced science teachers to assist the students in understanding the chapter quickly.
NCERT Solutions gives a brief knowledge of the subject matter and saves a lot of time during the preparation of the exam.
All the answers and the methods provided in the PDF are according to the CBSE guidelines.
The PDF files of Class 11 Bio Chapter 18 NCERT Solutions are easily accessible and free to download.
All essential questions are covered in the Class 11 Biology Chapter 18 NCERT Solutions. Students will not have any difficulty gathering the study contents.
Therefore, the Class 11 Neural Control and Coordination NCERT Solutions will help the students in understanding the Biology chapter and will help them secure good marks in the exam.
Study Materials for Class 11 Biology Chapter 18 Neural Control and Coordination NCERT Solutions
S. No | Important Links for Chapter 18 Neural Control and Coordination |
1. | |
2. | |
3. |
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology FREE PDF | Other Chapter-wise Links
Below are the other chapter-wise Links for the Solutions for Biology NCERT Class 11. You can download FREE PDFs of these chapter-wise solutions to familiarise yourself with the concepts.
S. No | Chapter-wise Links for Class 11 Biology NCERT Solutions |
1 | |
2 | |
3 | |
4 | |
5 | |
6 | |
7 | |
8 | |
9 | |
10 | |
11 | |
12 | |
13 | |
14 | |
15 | |
16 | Chapter 16 - Excretory Products and Their Elimination Solutions |
17 | |
18 | Chapter 19 - Chemical Coordination and integration Solutions |
Related Important Links for CBSE Class 11 Biology NCERT Solutions
S. No | Related Links for Class 11 Biology |
1. | |
2. | |
3. | |
4. | |
5. | |
6. | CBSE Class 11 Biology Sample Paper |

























