Class 11 Biology Chapter 14 Questions and Answers with Detailed Solutions
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Biology Chapter 14 Breathing And Exchange Of Gases - 2025-26
1. What is the vital capacity of the lungs, and why is it important? (as per NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 14)
Vital capacity is the maximum amount of air a person can exhale after a deep inhalation. It is significant because it reflects the capacity to supply fresh oxygen and remove carbon dioxide efficiently, ensuring optimal gas exchange between tissues and the environment as per CBSE 2025–26 syllabus.
2. According to Class 11 Biology NCERT Solutions, how do lungs maintain gas exchange efficiency during breathing?
Lungs maintain efficient gas exchange by providing a
- Large surface area through numerous alveoli
- Thin, moist, and highly permeable alveolar membranes
- Rich vascular supply for continuous blood flow
3. How is carbon dioxide transported in human blood, according to NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 14?
CO2 is transported mainly in three forms:
- As sodium bicarbonate (about 70%) in plasma
- As carbaminohemoglobin (about 25%) with red blood cells
- Dissolved directly (about 7%) in plasma
4. What is the partial pressure difference of O2 and CO2 in atmospheric versus alveolar air, based on Chapter 14 NCERT Solutions?
The partial pressure of oxygen (pO2) is higher and CO2 (pCO2) is lower in atmospheric air compared to alveolar air. This gradient drives oxygen into blood and removes CO2 efficiently. For example, atmospheric pO2 ≈ 159 mm Hg, alveolar pO2 ≈ 104 mm Hg; atmospheric pCO2 ≈ 0.3 mm Hg, alveolar pCO2 ≈ 40 mm Hg.
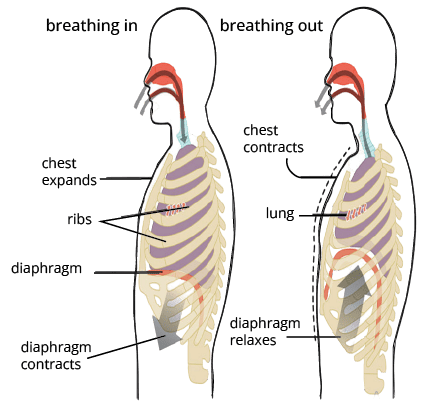
5. Explain how breathing is regulated in humans, as per Class 11 Biology Chapter 14 NCERT Solutions.
Breathing is controlled by the respiratory centre in the medulla oblongata and pons. Chemoreceptors detect changes in blood CO2 and H+ levels, while neural circuits adjust the rate and depth of breathing. Increased CO2 triggers more rapid respiration to restore normal levels.
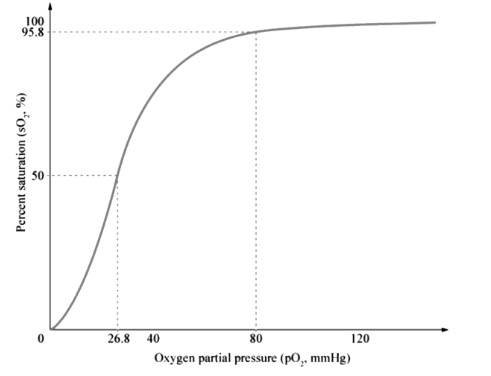
6. What is the oxygen dissociation curve and why is its shape significant? (NCERT Class 11 Biology Solution)
The oxygen dissociation curve depicts the % saturation of haemoglobin at various pO2 levels. It is sigmoidal due to cooperative binding: as one O2 molecule binds, haemoglobin’s affinity for O2 increases. This allows efficient O2 pickup in lungs and release in tissues.
7. How does altitude impact the respiratory process in humans? (Refer to NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 14)
At higher altitudes, atmospheric O2 decreases, resulting in lower oxygen availability per breath. The body compensates by increasing breathing and heart rates to meet oxygen demand, but less O2 still reaches tissues, requiring physiological adaptation.
8. What is the function of the alveoli in the lungs, according to Class 11 Biology NCERT Solutions?
Alveoli are the primary sites for gas exchange in the lungs. Their thin, moist, and vascular walls enable rapid diffusion of O2 into the blood and CO2 out, driven by partial pressure gradients, as described in the CBSE 2025–26 Biology syllabus.
9. Define tidal volume and state its average value for a healthy adult according to NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 14.
Tidal volume is the amount of air inspired or expired during normal breathing—typically about 500 mL per breath in a healthy adult (or 6000–8000 mL/minute), as per standard CBSE values.
10. How does the body adjust oxygen transport when CO2 levels rise in tissues? (Application-type FUQ)
Rising tissue CO2 decreases blood pH, reducing haemoglobin’s affinity for O2 (Bohr effect). This promotes O2 unloading from oxyhemoglobin, ensuring active tissues receive more oxygen, a key concept tested in Class 11 Chapter 14 NCERT Solutions.
11. Distinguish between Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV) and Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV) as per NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 14.
IRV is the maximum volume of air that can be inhaled after a normal inspiration (about 2500–3500 mL). ERV is the maximum that can be exhaled after normal expiration (about 1000–1100 mL), as per the 2025–26 syllabus values.
12. What features of the alveolar membrane make it ideal for respiratory gas exchange? (FUQ)
The alveolar membrane is
- Extremely thin, minimizing diffusion distance
- Moist and highly permeable for O2 and CO2
- Richly supplied with capillaries ensuring a strong concentration gradient
13. Explain the main difference between Vital Capacity (VC) and Total Lung Capacity (TLC) according to Class 11 Biology Chapter 14 NCERT Solutions.
Vital Capacity (VC) is the maximum air that can be forcefully exhaled after a maximum inspiration (≈4000 mL). Total Lung Capacity (TLC) is the total air the lungs can hold after maximal inspiration (≈5000–6000 mL). TLC includes VC plus residual volume (RV).
14. Why does gas exchange only occur in alveoli and not in other respiratory passages? (FUQ, concept probe)
Only alveoli have the essential traits for efficient gas exchange:
- Extremely thin walls
- Large surface area
- Extensive capillary networks
15. What are the main transport mechanisms for CO2 in blood, and why is bicarbonate the dominant form? (HOTS/FUQ)
CO2 is primarily transported as bicarbonate ions due to the action of carbonic anhydrase, which rapidly converts CO2 and water into carbonic acid and then bicarbonate. This mechanism allows the blood to carry much more CO2 than if it remained dissolved, supporting physiological needs efficiently as per NCERT Solutions Class 11 Biology Chapter 14.