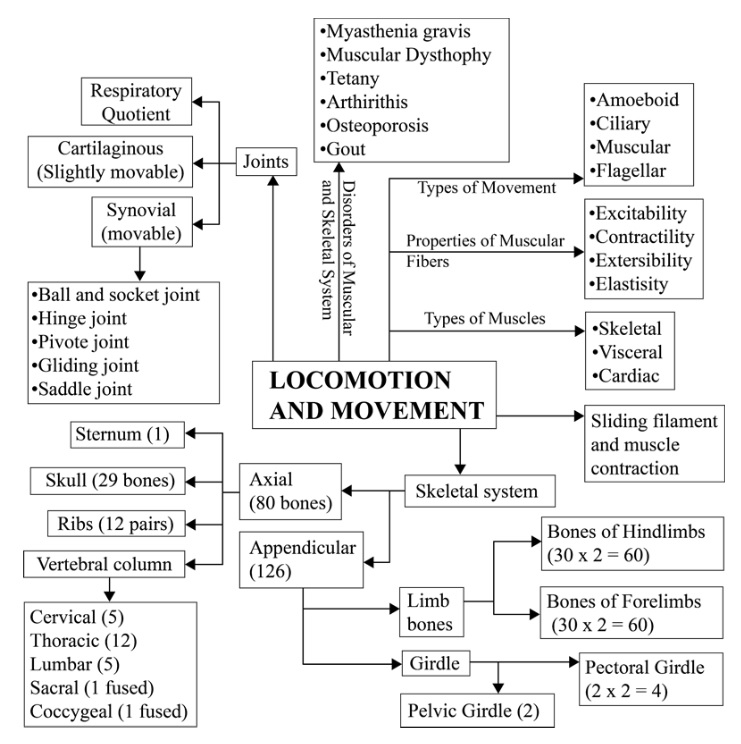
Class 11 Biology Chapter 17 Question Answer for Better Understanding
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Biology Chapter 17 Locomotion And Movement - 2025-26
1. Where can I find stepwise NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 17 Locomotion and Movement in PDF format?
Stepwise NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 17 Locomotion and Movement, in PDF format, are available as per the latest CBSE 2025–26 syllabus on Vedantu. These solutions follow the NCERT answer format and provide detailed, textbook-based explanations for all exercise and intext questions of Chapter 17.
2. Are the answers in Class 11 Biology Chapter 17 NCERT Solutions aligned with the official CBSE 2025–26 syllabus?
Yes, all answers in Class 11 Biology Chapter 17 NCERT Solutions strictly follow the updated CBSE 2025–26 syllabus and the NCERT pattern, ensuring that students get accurate and CBSE-approved answers for Locomotion and Movement.
3. How are exercise questions solved in NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 17?
The exercise questions are solved using a stepwise, NCERT-recognized method. Each answer is structured to match the textbook answer key, with clear explanations, proper diagrams, and point-wise solutions where required for Chapter 17: Locomotion and Movement.
4. Do the Class 11 Biology Chapter 17 NCERT Solutions cover both short and long answer questions as per the NCERT textbook?
Yes, the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 17 provide stepwise answers for all types of questions, including short, long, and intext questions, exactly as framed in the official NCERT textbook for the 2025–26 academic session.
5. Are the provided answers for NCERT Class 11 Biology Chapter 17 suitable for CBSE board preparations?
All answers are prepared as per the CBSE-approved NCERT format, making them ideal for CBSE board preparation. They include textbook answer keys, in-depth explanations, and diagrams to support every point asked in Chapter 17 Locomotion and Movement.
6. Can I use these NCERT Solutions for Biology Class 11 Chapter 17 for last-minute exam revision?
Yes, since these solutions present each answer stepwise as per the NCERT textbook and CBSE guidelines, they are perfect for quick revisions and doubt-clearing before exams for Locomotion and Movement.
7. Are the MCQs from Class 11 Biology Chapter 17 solved using official NCERT answer keys?
All MCQs and objective-type questions in Class 11 Biology Chapter 17 are solved using the latest NCERT answer key, following the prescribed CBSE and NCERT answer format for 2025–26.
8. Do Class 11 Biology Chapter 17 NCERT Solutions include labelled diagrams for descriptive answers?
Yes, complete labelled diagrams are provided in the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 17 wherever required by the exercise or intext questions, ensuring answers are fully aligned with NCERT's marking scheme.
9. Can I find stepwise NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 17 in Hindi medium as well?
Stepwise NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 17 are available in both English and Hindi medium, ensuring that students from all linguistic backgrounds can access CBSE-approved answers as per the latest syllabus.
10. What is the best approach to solve application-based questions in NCERT Class 11 Biology Chapter 17 Locomotion and Movement?
For application-based questions in Class 11 Biology Chapter 17, start by understanding the core NCERT concepts, use point-wise reasoning, and support answers with textbook diagrams. The NCERT Solutions follow this stepwise and CBSE-approved approach to ensure students score maximum marks.
11. How does the NCERT answer format help in understanding complex processes like muscle contraction in Chapter 17?
The NCERT answer format breaks down complex processes such as muscle contraction into step-by-step explanations, with clear labels and references to textbook diagrams. This approach, used in the solutions, follows the official answer key style, making detailed topics easy to grasp and write in exams.
12. Are these solutions sufficient for scoring full marks in NCERT exercise questions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 17?
Yes, following the NCERT answer format and the latest CBSE marking guidelines, these solutions are comprehensive and precise, increasing the likelihood of scoring full marks in both intext and exercise questions for Locomotion and Movement.
13. Is the method given for solving diagram-based questions in these solutions as per updated CBSE marking scheme?
All diagram-based questions in Class 11 Biology Chapter 17 NCERT Solutions are addressed as per the latest CBSE marking scheme. The diagrams are labelled and explained, reflecting the expected structure of answers in board examinations.