Class 11 Biology Chapter 19 Questions and Answers for CBSE Exams
Updated Chapter 19 Chemical coordination and integration, NCERT Solutions are now available on Vedantu. Our subject experts prepare these solutions, referencing the latest NCERT Class 11 Biology textbook edition. All the important topics and sub-topics, such as endocrine glands, hormones of the heart, kidney, lungs, hormone action, etc., in the Class 11 Biology chapter 19 have been covered in these solutions.
 Table of Content
Table of ContentNCERT Solutions Chapter 19 is designed by Vedantu master teachers and is updated according to the latest CBSE Class 11 Biology syllabus. Therefore, students can rely upon these NCERT Solutions to prepare for their exams.
Class 11 Biology Chapter 19 Questions and Answers for CBSE Exams
1. Define the following:
(a) Exocrine Gland
Ans: Exocrine glands, such as sebaceous glands, sweat glands, salivary glands, and intestinal glands, secrete their secretions on the surface or into a specific region via ducts in order to conduct a metabolic function.
(b) Endocrine Gland
Ans: The endocrine gland is a unique gland (from the epithelium that forms it) that secretes informational molecules or hormones that are injected into the venous blood or lymph to reach the target organ because there is no duct connecting the gland to the target organ. As a result, endocrine glands, such as the thyroid gland, are sometimes known as ductless glands.
(c) Hormone
Ans: Hormone is a chemical produced by an endocrine gland or a specialized nerve cell and released in very minute amounts into the bloodstream to control the growth or function of a specific tissue organ in a distant area of the body, such as insulin.
2. Diagrammatically Indicates the Location of the Various Endocrine Glands in Our Body.
Ans:
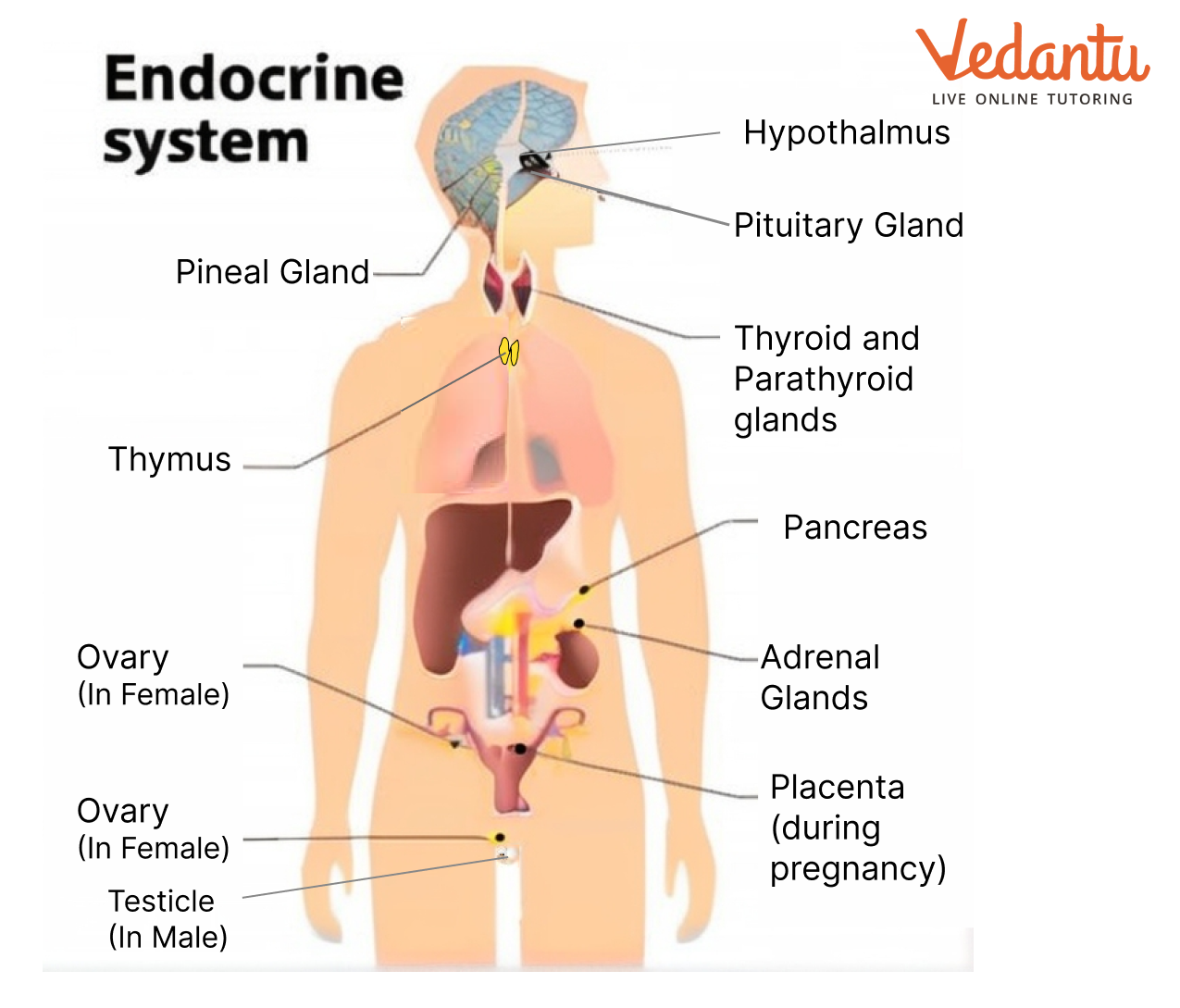
3. List the Hormones Secreted by the Following:
Ans.
Gland | Hormones | Function |
Hypothalamus | Releasing & Inhibiting Hormones | Regulate hormone secretion from the pituitary gland |
Pituitary (Anterior Lobe) | FSH, LH, TSH, ACTH, GH, Prolactin | Regulate various functions including reproduction, metabolism, growth, and stress response |
Pituitary (Posterior Lobe) | Oxytocin, Vasopressin | Regulate muscle contractions (uterus) and water balance |
Thyroid | Thyroxine, Triiodothyronine, Calcitonin | Regulate metabolism, growth and development, and calcium levels |
Parathyroid | Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) | Regulates calcium levels in the blood |
Adrenal Cortex | Glucocorticoids (cortisol), Mineralocorticoids (aldosterone), Sex hormones | Regulate metabolism, blood pressure, and sexual development and function |
Adrenal Medulla | Epinephrine (adrenaline), Norepinephrine (noradrenaline) | Help the body respond to stress (fight-or-flight response) |
Pancreas | Insulin, Glucagon, Somatostatin | Regulate blood sugar levels |
Testis | Androgens (testosterone) | Promote male sexual development and function |
Ovary | Estrogens, Progesterone, Relaxin | Regulate female sexual development and function, and prepare the body for childbirth |
Thymus | Thymosin | Plays a role in the development of the immune system |
Atrium | Atrial Natriuretic Factor (ANF) | Helps regulate blood pressure |
Kidney | Renin, Erythropoietin | Regulates blood pressure and red blood cell production |
G-I Tract | Gastrin, Secretin, Cholecystokinin, Enterocrinin, Duocrinin, Villikinin | Regulate digestion and nutrient absorption |
4. Fill in the Blanks:
Hormones Target Gland
Hypothalamic hormones ........................
Thyrotrophin (TSH) ........................
Corticotropin (ACH) ........................
Gonadotrophins (LH, FSH) ........................
Melanotropin (MSH) ........................
Ans:
Pituitary
Thyroid
Adrenal cortex
Gonads – Tests in male and ovaries in female
Skin.
5. Write short notes on the functions of the following hormones:
Parathyroid Hormones (PTH)
Ans: Parathyroid hormone raises calcium levels while lowering phosphate levels in the blood.
Thyroid Hormones
Ans: Thyroxine, triiodothyronine, and calcitonin are the three hormones secreted by the thyroid gland. Thyroxine and triiodothyronine regulate the body's overall metabolism, encourage tissue development, and induce tissue differentiation. Calcitonin is a hormone that controls calcium levels in the blood.
Thymosin
Ans: Thymosin is produced by the thymus gland. Cell division is accelerated, T-lymphocyte growth and differentiation are stimulated, and sexual maturity is accelerated.
Androgens
Ans: The testis secretes androgens. They influence male sexual behavior and sex drive by stimulating the development of the male reproductive system, the production of sperm, and the development of male accessory sex characteristics.
Estrogens
Ans: Estrogens are produced by the ovaries. They encourage the female reproductive system to mature and become fully functional, as well as the differentiation of ova and the development of accessory sex characteristics.
Insulin and Glucagon.
Ans: Insulin is produced in the pancreas by the -cells. It reduces blood glucose levels and stimulates protein and fat synthesis. The a-cells of the pancreas produce glucagon. It causes a rise in blood glucose levels.
6. Give an example(s) of
Hyperglycemic Hormone and Hypoglycemic Hormone
Ans: Parathormone (PTH)
Hypercalcemic Hormone
Ans: Glucagon, Insulin
Gonadotrophic Hormones
Ans: Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and Luteinizing hormone (LH)
Progestational Hormone
Ans: Progesterone
Blood Pressure-Lowering Hormone
Ans: Atrial natriuretic factor
Androgens and Estrogens.
Ans: Testosterone and Estradiol.
7. Which Hormonal Deficiency is Responsible for the Following?
Diabetes Mellitus
Ans: Diabetes mellitus is characterized by excessively high blood glucose levels caused by a lack of the hormone insulin.
Goiter
Ans: Goitre is a condition in which the thyroid gland enlarges abnormally owing to a lack of thyroxine hormone in the body.
Cretinism.
Ans: Cretinism is a condition in which a baby's development is slowed owing to a lack of thyroid hormone in the body.
8. Briefly Mention the Mechanism of Action of FSH.
Ans: (Follicle-stimulating hormone) is a glycoprotein that is lipid insoluble and so cannot penetrate target cells. It forms a hormone-receptor complex by binding to particular receptor molecules on the cell membrane's surface. The enzyme adenylate cyclase is released from the receptor site as a result of this combination. From ATP, this enzyme produces cell cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). The cAMP stimulates the cell's existing enzyme system. The metabolic processes in the cell are accelerated as a result of this. The hormone is referred to as the first messenger, whereas cAMP is referred to as the second messenger. The hormone-receptor complex alters the permeability of the cell membrane to allow items to pass across it more easily. As the cell obtains the required ingredients, its actions grow.
Question 9:
Column I Column II
T4 (i) Hypothalamus
PTH (ii) Thyroid
GnRH (iii) Pituitary
LH (iv) Parathyroid.
Ans:
Column I | Column II |
T4 | Thyroid |
PTH | Parathyroid |
GnRH | Pituitary |
LH | Hypothalamus |
Class 11 Biology Chemical Coordination And Integration: Quick Overview of Topics Covered
S. No | Class 11 Chapter 19: Chemical Coordination and Integration Topics |
1 | Endocrine Glands and Hormones |
2 | Human Endocrine System
|
3 | Hormones For:
|
Benefits of Class 11 Biology Chapter 19 - Chemical Coordination and Integration
Some of the benefits of chemical coordination and integration NCERT are:-
Solutions for NCERT Chemical coordination and integration are prepared according to the guidelines and format issued by the CBSE board, thus giving the students a preview of the exam's format.
Description of major endocrine glands, including the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, pancreas, and gonads, and their respective hormones are the most likely to come in the exams, thus making the more complex concept simpler.
Explanations of how hormones exert their effects on target cells through specific receptors, leading to changes in cellular activities and gene expression, are discussed in the chapter.
The solutions given here are detailed, which gives the students a step-by-step explanation of every concept in the particular chapter.
Important Study Material Links Class 11 Chapter 19
S. No | Important Links for Chapter 19 Chemical Coordination and Integration |
1. | |
2. | |
3. | Chemical Coordination and Integration NCERT Exemplar Solutions |
Conclusion
Chapter 19 Chemical Coordination and Integration NCERT provides students with simple and detailed definitions and explanations of each concept covered in the chapter. Therefore, it is highly recommended that students download and refer to our comprehensive and expert-curated chemical coordination and integration class 11 NCERT PDF to get a gist of the chapter before the exam and to know how to answer the questions in the exam. Students can also refer to our plethora of other study resources related to this chapter, which are free on our website.
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology FREE PDF | Other Chapter-wise Links
Below are the other chapter-wise Links for the Solutions for Biology NCERT Class 11.
S. No | Chapter-wise Links for Class 11 Biology NCERT Solutions |
1 | |
2 | |
3 | |
4 | |
5 | |
6 | |
7 | |
8 | |
9 | |
10 | |
11 | |
12 | |
13 | |
14 | |
15 | |
16 | Chapter 16 - Excretory Products and Their Elimination Solutions |
17 | |
18 |
Related Important Links for Class 11 Biology NCERT Solutions
S. No | Related Links for Class 11 Biology |
1. | |
2. | |
3. | |
4. | |
5. | |
6. | |
7. | CBSE Class 11 Biology Sample Paper |

























