Vedantu's Complete Guide To Respiration In Plants Class 11 Questions And Answers
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Biology Chapter 12 Respiration In Plants - 2025-26
1. What are the main steps of aerobic respiration in plants, as explained in the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 12?
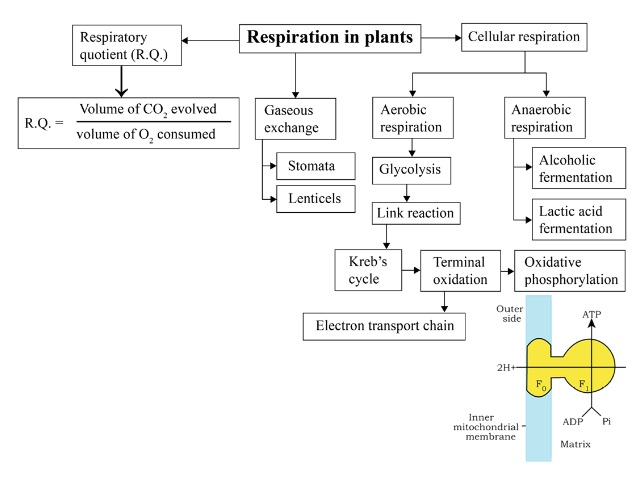
The main steps of aerobic respiration in plants are glycolysis, link reaction, Krebs’ cycle, and terminal oxidation (electron transport system). Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm, the link reaction and Krebs' cycle in the mitochondrial matrix, and terminal oxidation along the inner mitochondrial membrane. Each stage sequentially extracts energy from glucose, ultimately forming ATP, CO2, and H2O as end products.
2. According to the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 12, what are the differences between glycolysis and Krebs’ cycle?
- Location: Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm, while Krebs’ cycle takes place in the mitochondrial matrix.
- Nature: Glycolysis is anaerobic and common to both aerobic and anaerobic respiration, whereas Krebs’ cycle operates only in aerobic respiration.
- End Products: Glycolysis produces pyruvate, ATP, and NADH, while Krebs' cycle fully oxidizes acetyl-CoA to CO2 and generates NADH, FADH2, and ATP/GTP.
- CO2 Evolution: No CO2 is released during glycolysis; CO2 is evolved in Krebs’ cycle.
3. How do the NCERT Solutions describe the differences between aerobic respiration and fermentation?
- Oxygen Requirement: Aerobic respiration requires oxygen; fermentation does not.
- End Products: Aerobic respiration forms CO2 and H2O; fermentation forms ethanol or lactic acid.
- Energy Yield: Aerobic respiration yields much more ATP (around 38 per glucose) compared to fermentation (only 2 ATP per glucose).
- Completeness: Aerobic respiration completely oxidizes glucose, whereas fermentation is incomplete.
4. What is an amphibolic pathway according to Chapter 12 NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology, and why is the respiratory pathway termed amphibolic?
An amphibolic pathway is one that functions in both catabolism (breakdown) and anabolism (synthesis). The respiratory pathway is called amphibolic because its intermediates serve as precursors for biosynthetic processes and as points of entry for the degradation of fats, amino acids, and other metabolites, thus linking breakdown and synthesis within the cell.
5. What are the main assumptions made during the calculation of net gain of ATP in aerobic respiration, as outlined in CBSE NCERT Solutions?
- All metabolic pathways (glycolysis, Krebs' cycle, and ETC) occur in strict sequence, with each substrate converted fully before the next enters.
- NADH produced in glycolysis transfers its electrons efficiently to mitochondria for oxidative phosphorylation.
- No pathway intermediates are withdrawn for other cellular functions.
- Only glucose is used as substrate; no alternatives intervene at any stage.
6. How is the respiratory quotient (RQ) defined in NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology, and what is its value for fats?
The respiratory quotient (RQ) is defined as the ratio of the volume of CO2 evolved to the volume of O2 consumed in respiration. For fats, the RQ is less than one, typically around 0.7, indicating more oxygen is used than CO2 produced during fat oxidation.
7. What is oxidative phosphorylation according to the Class 11 Biology Chapter 12 NCERT Solutions?
Oxidative phosphorylation is the process of ATP synthesis powered by the transfer of electrons from NADH or FADH2 to O2 via the electron transport system in mitochondria. It is the primary pathway for ATP generation in aerobic organisms.
8. Why is energy released in a stepwise manner during cellular respiration, as per NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology?
Stepwise energy release ensures that chemical bond energy from substrates is captured efficiently in ATP, prevents excessive heat build-up in cells, reduces energy waste, provides metabolic intermediates for biosynthesis, and allows for tighter regulation of the process via specific enzymes at each step.
9. What is the significance of the electron transport system (ETS) in plant respiration as described in NCERT Solutions?
The electron transport system (ETS) couples electron transfer from NADH and FADH2 to oxygen, producing water and creating a proton gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane. This gradient drives ATP synthesis through ATP synthase, making ETS the main producer of ATP in respiration.
10. In the context of CBSE 2025–26, how do NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 12 aid in CBSE exam preparation?
- They provide stepwise, CBSE-aligned answers for all textbook exercises, enhancing understanding and exam readiness.
- Concepts are simplified and explained with diagrams and tables as needed.
- Practicing from these solutions helps with time management and answering in the format expected by CBSE evaluators.
- Solutions reinforce topic retention for both direct and application-based questions, maximizing score potential.
11. Explain the core stages of aerobic respiration and state where each occurs in the plant cell (as per NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 12).
- Glycolysis: Cytoplasm
- Link Reaction (Pyruvate to Acetyl-CoA): Mitochondrial matrix
- Krebs’ (Citric Acid) Cycle: Mitochondrial matrix
- Electron Transport System (ETS)/Oxidative Phosphorylation: Inner mitochondrial membrane
12. What if oxygen is not available during respiration in plant cells, as per the discussion in NCERT Biology Solutions?
If oxygen is absent, aerobic respiration halts at glycolysis, and pyruvate is converted via fermentation to either ethanol (in some microbes) or lactic acid (in some animal cells), resulting in far less energy (only 2 ATP per glucose) and the buildup of end products that can inhibit cell activity if accumulated.
13. How can studying the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 12 help avoid common misconceptions in respiration topics?
The solutions clarify key distinctions (e.g., respiration vs. combustion, aerobic vs. anaerobic respiration), demystify stepwise ATP production, emphasize the interconnection of metabolic pathways, and highlight the actual physiological roles and limitations of each stage. This reduces errors in conceptual and application questions in CBSE exams.