Why Are the Five Functions of the Skeletal System Important?
The concept of five major functions of skeletal system is essential in biology and helps explain real-world biological processes and exam-level questions effectively. Learning these five main functions gives students a solid foundation for understanding movement, body structure, organ protection, mineral balance, and blood cell production. This is especially useful for quick revision and MCQs in exams.
Understanding Five Major Functions Of Skeletal System
Five major functions of skeletal system refers to the main roles played by the skeleton and bones in the human body. These include providing structure & support, protecting internal organs, enabling movement, storing minerals, and producing blood cells. This concept is important in areas like human anatomy, physiology, and medical science.
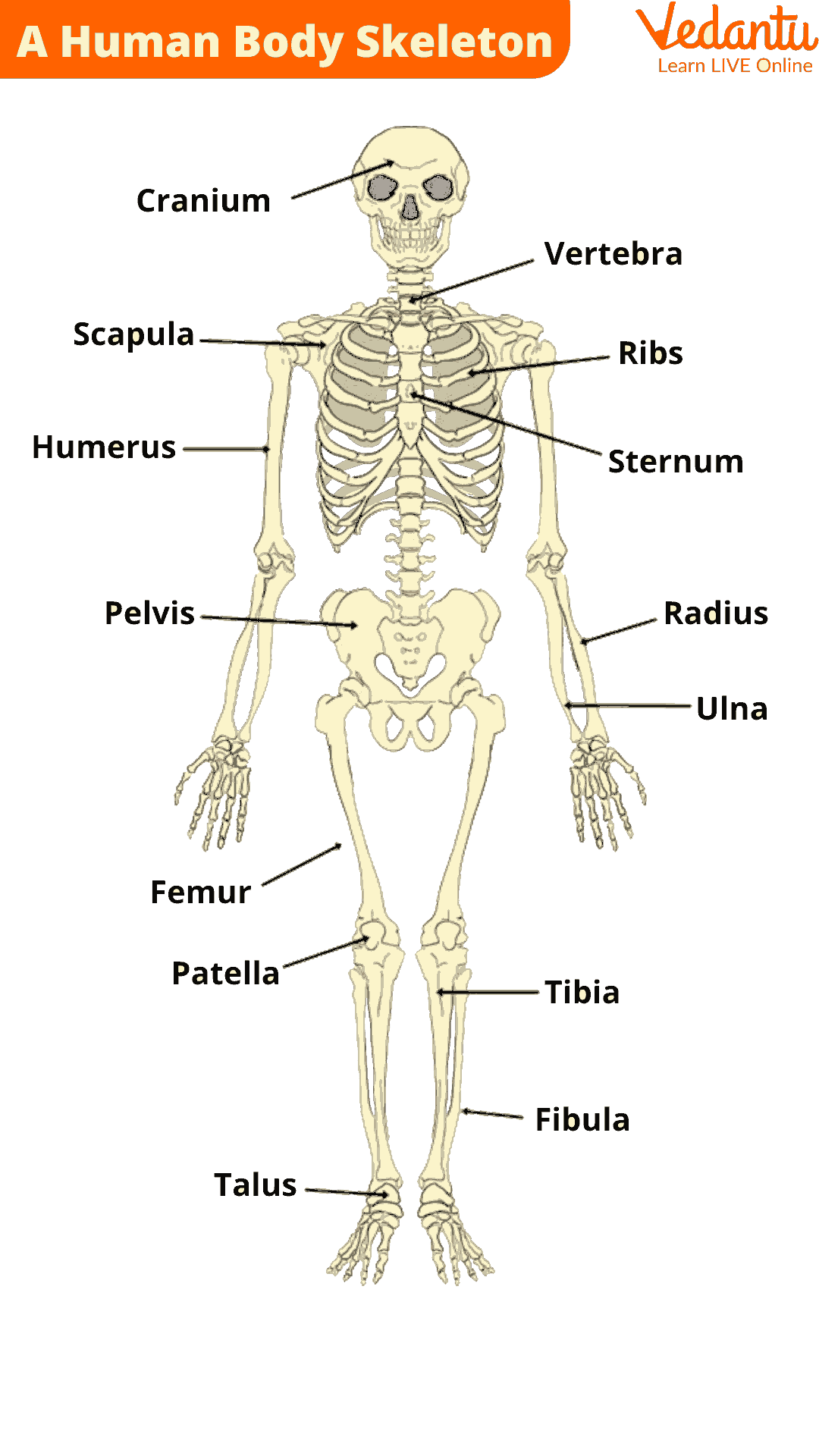
Below is the list of the five major functions of the skeletal system. Remember this list for quick exam revision:
- Support
- Protection
- Movement
- Mineral Storage
- Blood Cell Formation
Detailed Explanation of Five Major Functions Of Skeletal System
Let’s look into each function step by step with examples:
- Support
Bones form a rigid framework that supports the entire body and gives shape to our structure. For example, the vertebral column holds the upper body upright. - Protection
Many vital organs are protected by bones. The skull protects the brain, and the rib cage shields the heart and lungs from damage. - Movement
Bones act as levers. Joints and bones work with skeletal muscles for various body movements, such as running or writing. The long bones of the legs (like femur and tibia) enable walking and jumping. - Mineral Storage
Bones store minerals such as calcium and phosphorus. These can be released into the bloodstream to maintain balance as needed by the body. - Blood Cell Formation
The bone marrow inside certain bones produces red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets – a process known as hematopoiesis.
Here’s a helpful table to understand the five major functions of skeletal system better:
Five Major Functions Of Skeletal System Table
| Function | Description | Example/Occurs In |
|---|---|---|
| Support | Provides body shape, supports soft tissues | Vertebral column, leg bones |
| Protection | Shields organs from injury | Skull (brain), rib cage (heart/lungs) |
| Movement | Works as levers for muscles | Joints, limbs, leg/arm bones |
| Mineral Storage | Stores calcium, phosphorus for need | All bones (especially long/flat bones) |
| Blood Cell Formation | Makes new blood cells in marrow | Bone marrow (pelvis, femur, humerus) |
Visual Revision: Summary Diagram
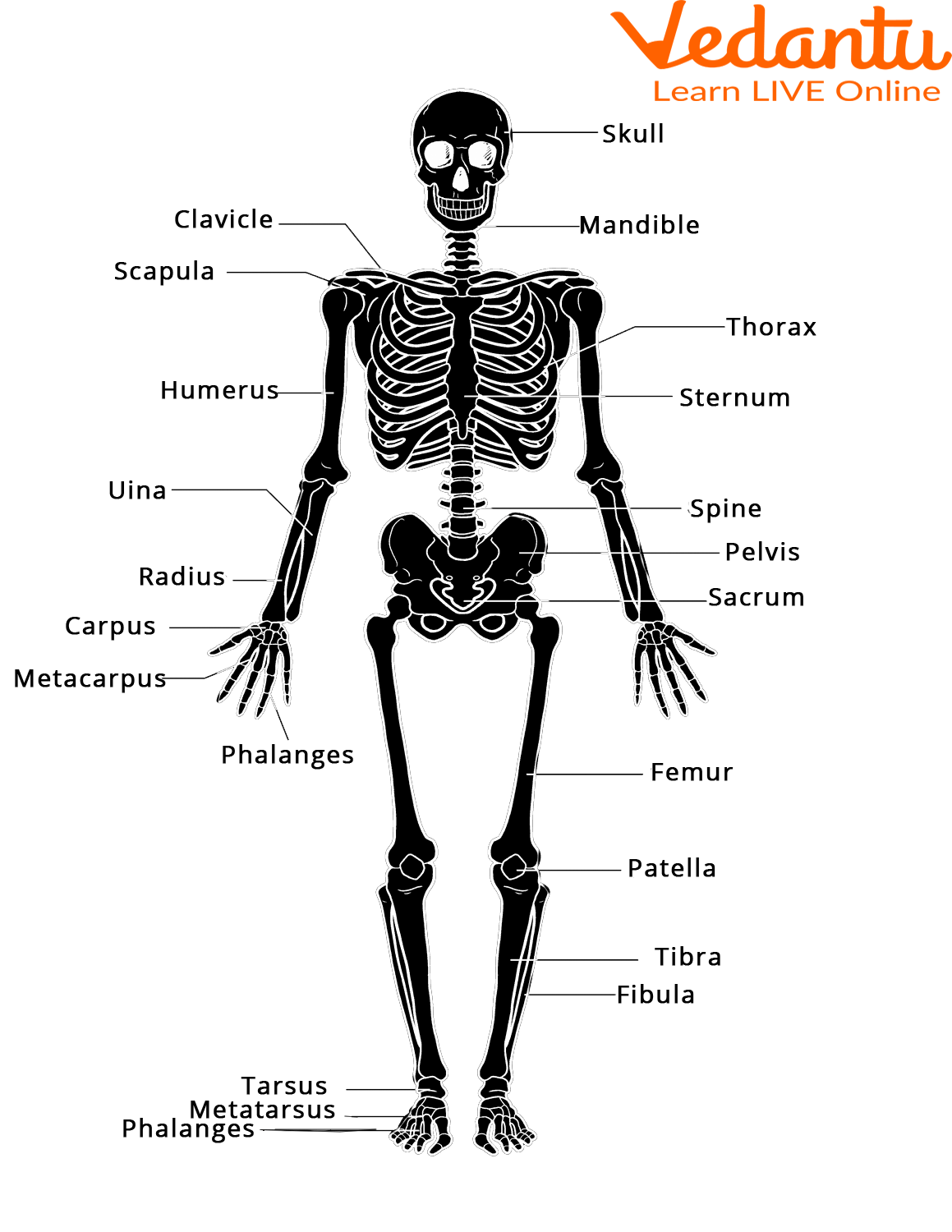
Real-Life Applications and Example Uses
Understanding the five major functions of skeletal system is important in daily life. For example, helmets protect our skull (protection), sports require good bone support and movement, and calcium-rich diets help with bone mineral storage. Injuries or diseases (like osteoporosis) can affect these functions. Doctors use bone marrow tests to diagnose blood disorders. Vedantu explains these functions with real-world contexts to help students connect theory with practical use.
Exam Corner: Tips & Model MCQs
- Remember "SPMMB" (Support, Protection, Movement, Mineral storage, Blood formation) for quick recall.
- MCQ Tip: If a question asks which function is related to red marrow – answer is "blood cell formation."
- Short question: "List the five major functions of the skeletal system"
- Long question: "Explain how the skeletal system protects organs and helps in movement with examples."
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Confusing skeletal system (bones) with skeletal muscle (movement is joint effort!)
- Forgetting bone marrow’s role in blood cell formation
- Mixing up mineral storage (bones store, blood transports!)
Page Summary
In this article, we explored the five major functions of skeletal system: support, protection, movement, mineral storage, and blood cell formation. Each is vital for the human body’s health and proper functioning. Practice this topic regularly with Vedantu and use these concepts for quick revision and strong exam results.
Useful Internal Links for Deeper Understanding
- Human Skeletal System – Full structure, bones & parts
- Bones Of Leg – Bones enabling movement and support
- Locomotion and Movement – Joints and muscle cooperation
- Bone Anatomy – Structure and mineral storage
- Vertebral Column – Support and protection focus
- Skeletal Muscle – Difference vs skeletal system
- Types of Joints – Movement and structure explained
- Blood Cell Formation – How marrow makes blood cells
- What are the functions of the human skeletal system – Alternate explanations for exam prep
- Skull – Example of protection
- Rib Cage – Organ protection & breathing support


FAQs on Five Major Functions of the Skeletal System Explained for Students
1. What are the five major functions of the skeletal system?
The five major functions of the skeletal system are:
1. Support - providing a framework for the body
2. Protection - safeguarding vital organs
3. Movement - acting as levers for muscles
4. Mineral storage - storing minerals like calcium and phosphorus
5. Blood cell formation - producing blood cells in the bone marrow.
2. How do bones protect organs?
Bones protect organs by forming rigid structures around them. For example, the skull shields the brain, the rib cage protects the heart and lungs, and the vertebral column safeguards the spinal cord. This protection helps prevent injury from external forces.
3. Which bones are crucial for movement?
Bones that are crucial for movement include the long bones like the femur, humerus, and bones of the arms and legs. These bones act as levers and work with joints and skeletal muscles to enable various types of body movements.
4. Where is blood produced in the skeletal system?
Blood is produced in the red bone marrow, which is found in certain bones such as the pelvis, sternum, humerus, and femur. This process is called hematopoiesis and is a vital function of the skeletal system.
5. How is mineral storage important?
Mineral storage in bones, primarily of calcium and phosphorus, is important because it maintains essential mineral balance in the body. These stored minerals help in bone strength and can be released into the bloodstream when needed for other physiological functions like nerve transmission and muscle contraction.
6. Why are there exactly five major functions and not more?
The five major functions of the skeletal system represent the key physiological roles essential for survival and daily functioning. While bones can have additional regulatory roles (like producing the hormone osteocalcin), these five functions—support, protection, movement, mineral storage, and blood formation—are the primary, universally recognized roles taught in the NCERT syllabi for clarity and exam focus.
7. Do all living things have the same five skeletal functions?
Not all living things have the same five skeletal functions. For example, animals with exoskeletons (like insects) have different protective structures, and some simple organisms lack a skeleton altogether. However, in vertebrates, these five functions are common, though some animals may have specialized skeletal adaptations.
8. Can a bone perform more than one function at a time?
Yes, a bone can simultaneously perform multiple functions. For example, the femur supports body weight (support), helps in movement by acting as a lever, stores minerals in its matrix, and contains bone marrow that produces blood cells (hematopoiesis).
9. Why do exam MCQs confuse skeletal muscles with the skeletal system?
Exam MCQs often confuse skeletal muscles with the skeletal system because both are involved in body movement and share the term 'skeletal.' However, the skeletal system refers to bones and cartilages, while skeletal muscles are the muscles attached to bones that enable movement. Understanding their distinct functions helps avoid confusion.
10. How to remember the five functions quickly during a test?
A helpful mnemonic to remember the five major functions is: Silly People Make Memorable Bones, standing for Support, Protection, Movement, Mineral storage, and Blood cell formation. Using such acronyms or simple stepwise lists aids quick recall during exams.










