Key Roles in a Food Web: Producers, Consumers & Decomposers
Energy is the driving force behind every process on Earth. From the smallest bacterium to the largest predator, all organisms need energy to grow, reproduce, and survive. In nature, this energy is transferred through complex interrelationships known as food webs. But what is a food web? Let’s explore this essential concept in an accessible way.
A food web is a complex network of interconnected food chains that illustrates how energy flows between living organisms in an ecosystem. In simple terms, what is a food web in an ecosystem? It is a visual and functional representation of who eats whom and how energy moves from one level to the next.
A simple food web begins with producers (like plants) that capture the sun’s energy through photosynthesis.
This energy is then passed on to primary consumers (herbivores) and continues to secondary and tertiary consumers (carnivores and apex predators).
Decomposers, such as fungi and bacteria, complete the cycle by breaking down dead material and returning nutrients to the soil.
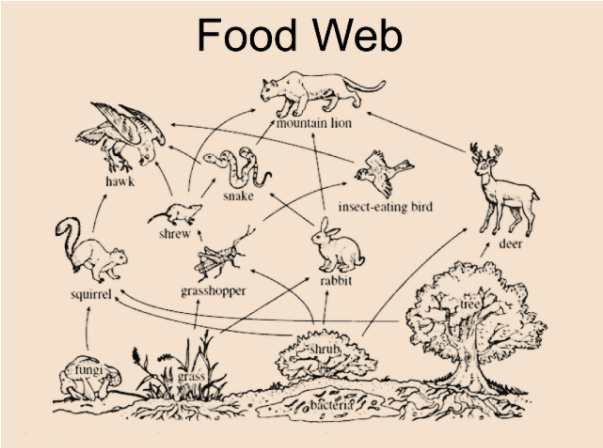
Components of a Food Web
Understanding the main players in a food web is crucial:
Producers: These are organisms (mostly plants, algae, and some bacteria) that create their food using sunlight via photosynthesis. They form the foundation of every food web.
Primary Consumers: Herbivores such as deer, insects, and small fish feed on producers. Due to the 10% energy rule, these consumers only receive a fraction of the energy stored in plants.
Secondary Consumers: These animals (carnivores like snakes, birds, and small mammals) feed on primary consumers.
Tertiary Consumers: Apex predators such as lions, hawks, and sharks are at the top of the chain. Although many believe humans are apex predators, research places our trophic level differently.
Decomposers: Organisms like fungi and bacteria break down dead matter, ensuring that nutrients are recycled within the ecosystem.
Energy Flow and the 10% Rule
In every trophic level, only about 10 per cent of the energy is transferred to the next level. This is because energy is lost as heat and through metabolic processes. For example, even though plants capture energy from the sun, only a small portion is passed on when herbivores feed on them. This fundamental concept is well illustrated in a food web diagram and can be observed in many food web examples across diverse habitats.
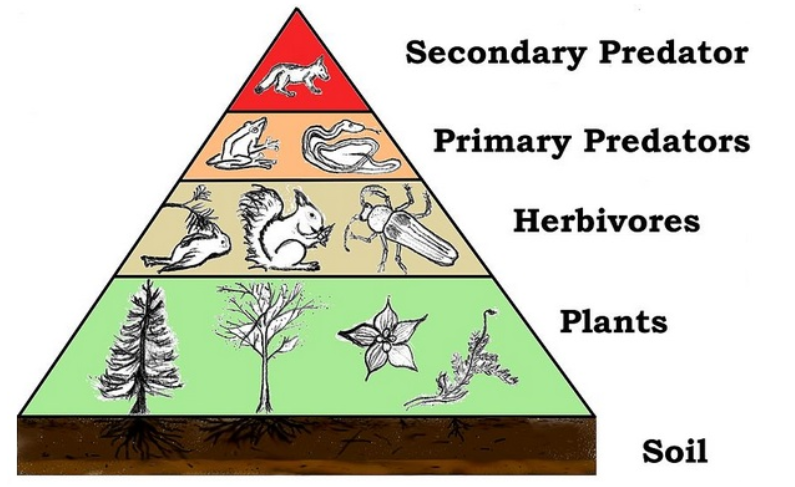
Food Chain vs Food Web
While a food chain is a single, linear sequence of energy flow—from producer to consumer—a food web is a network of multiple food chains that overlap and interconnect. So, when you ask, what is a food web in an ecosystem, remember that it offers a more comprehensive picture of how species interact and depend on each other. Understanding both concepts is key to recognising the complexity and resilience of natural environments.
Also Read: Difference Between Food Chain and Food Web
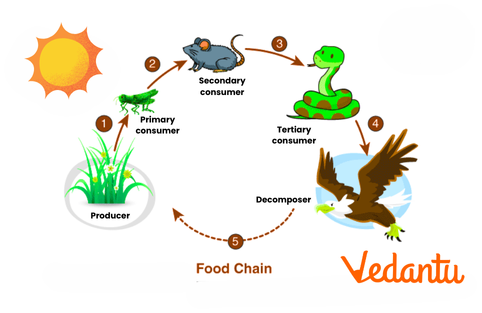
Unique Insights: The Role of Humans and Keystone Species
Humans often wonder where we fit in this network. Despite consuming a variety of foods, research suggests that humans typically occupy a lower trophic level than true apex predators. Moreover, certain species, known as keystone species, have a disproportionately large effect on their ecosystems by regulating population dynamics. Recognising what is a food web in an ecosystem also means understanding how these keystone species maintain balance within their communities.
Interactive Food Web Diagram and Food Web Examples
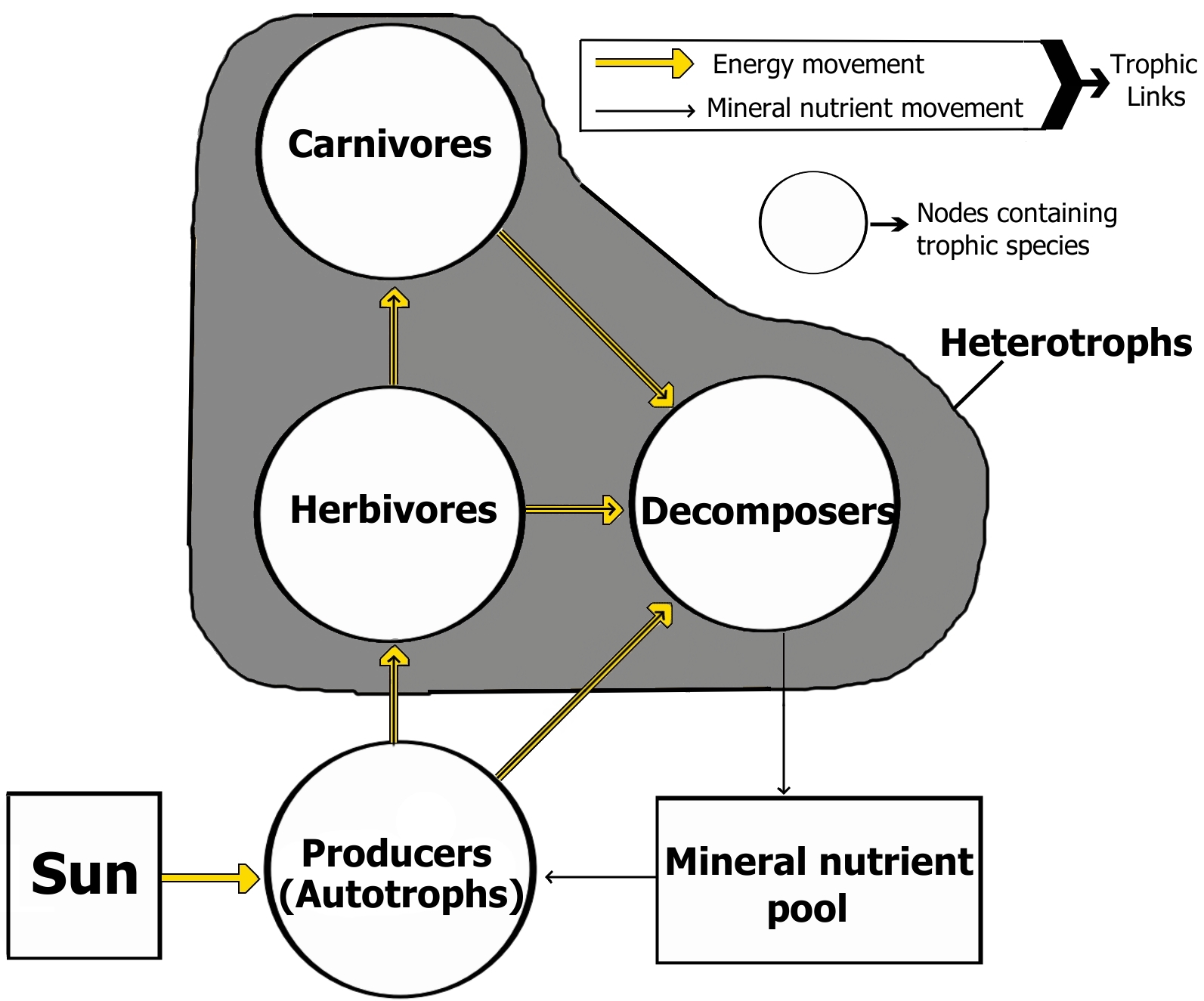
Visual tools are invaluable for learning. Below is a simple food web diagram that outlines the energy flow from producers to apex predators. This interactive resource, along with multiple food web examples, will help you see the practical application of these concepts. For instance:
In a forest ecosystem, plants serve as the producers for herbivores like rabbits and insects. These, in turn, sustain carnivores such as foxes and birds of prey.
In marine environments, plankton forms the base of the food web, supporting fish, which then become food for larger predators like sharks and marine mammals.
These food web examples enhance understanding and highlight the delicate balance required for a healthy ecosystem.
Environmental Impacts on Food Webs: Climate Change and Human Activities
A unique aspect of food webs is their sensitivity to environmental changes. Factors such as habitat destruction, pollution, and climate change can disrupt energy flow and alter the dynamics illustrated in any food web diagram. When exploring what is a food web in an ecosystem, it is important to consider:
Habitat Loss: Deforestation and urban development reduce the availability of producers, affecting the entire web.
Pollution: Chemical pollutants can reduce the health of producers and consumers alike, leading to a collapse in certain food chains.
Climate Change: Altered weather patterns affect species distribution, timing of life cycles, and the balance of predator-prey relationships.
Understanding these impacts emphasises why conservation efforts and sustainable practices are essential for maintaining robust and resilient ecosystems.
Related Links:


FAQs on Food Webs Made Simple: Diagrams, Examples & Energy Flow
1. What is a food web and how does it represent energy flow in an ecosystem?
A food web is a detailed model that illustrates the complex network of interconnected food chains within an ecosystem. Unlike a simple, linear food chain, it shows how multiple organisms feed on various other organisms, representing a more realistic flow of energy. The arrows in a food web diagram point from the organism being eaten to the organism that eats it, mapping the pathway of energy transfer from producers up through various consumer levels.
2. What are the primary components, or trophic levels, of a typical food web?
A food web consists of several key components organised into trophic levels, which are positions in the food chain:
- Producers: Autotrophs, like plants and algae, that produce their own food using sunlight. They form the base of the food web.
- Primary Consumers: Herbivores that feed directly on producers.
- Secondary Consumers: Carnivores or omnivores that feed on primary consumers.
- Tertiary Consumers: Carnivores or omnivores that feed on secondary consumers, often at the top of the food web.
- Decomposers: Organisms like bacteria and fungi that break down dead organic matter from all levels, recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem.
3. What is the main difference between a food chain and a food web?
The primary difference is one of complexity and scope. A food chain illustrates a single, linear pathway of energy transfer (e.g., grass → deer → tiger). In contrast, a food web is a complex network of multiple interconnected food chains, showing that most organisms have diverse diets and are part of several energy pathways. A food web provides a more holistic and accurate representation of the feeding relationships in an ecosystem.
4. Why is the energy transfer between trophic levels in a food web only about 10% efficient?
The transfer of energy between trophic levels is inefficient due to the Second Law of Thermodynamics. Only about 10% of the energy from one level is incorporated into the biomass of the next. The remaining 90% is lost primarily as metabolic heat during respiration, used for life processes like movement and reproduction, or is unavailable in parts of the organism that are not consumed. This 10% rule explains why food webs have a limited number of trophic levels.
5. Can you provide an example of a simple terrestrial and an aquatic food web?
Certainly. Here are two simplified examples of food webs:
- Terrestrial (Forest) Food Web: Plants (producers) are eaten by rabbits (primary consumers) and insects (primary consumers). The insects are eaten by frogs (secondary consumers), and both rabbits and frogs are eaten by foxes (tertiary consumers).
- Aquatic (Pond) Food Web: Algae (producers) are consumed by small fish (primary consumers) and zooplankton (primary consumers). The zooplankton is eaten by small fish, and both are eaten by larger fish (secondary consumers), which are then eaten by birds like herons (tertiary consumers).
6. How would the removal of a keystone species, like a top predator, impact the stability of its entire food web?
Removing a keystone species causes a disproportionately large disruption, often leading to a trophic cascade. For example, if a top predator like a wolf is removed, its primary prey (e.g., deer) may overpopulate. This leads to overgrazing of plants (producers), which can degrade the habitat and negatively affect other species that depend on those plants for food or shelter. This single change can destabilise the entire food web's structure and function.
7. Why are decomposers considered a critical component of a food web?
Decomposers are critical because they are responsible for nutrient cycling. They break down dead organic material from all trophic levels—dead plants, animals, and waste products—and return essential nutrients like carbon and nitrogen to the soil and water. These nutrients are then available for producers to use, thus completing the ecosystem's energy and nutrient loops. Without decomposers, the flow of nutrients would halt, and the ecosystem would collapse.
8. What are the two main types of food chains that form a food web?
Every food web is formed by the interconnection of two primary types of food chains:
- Grazing Food Chain (GFC): This is the type most commonly depicted. It starts with producers (e.g., green plants) and moves to herbivores and then carnivores.
- Detritus Food Chain (DFC): This chain begins with dead organic matter, called detritus. It is consumed by decomposers and detritivores (like earthworms or fungi), which are then eaten by other organisms. In many ecosystems, a larger fraction of energy flows through the detritus pathway.
9. What is the role of humans in a global food web, and how do our dietary choices affect its structure?
Humans act as omnivores and occupy multiple trophic levels. Our role is significant because our dietary choices have large-scale ecological impacts. A diet high in meat (consuming primary or secondary consumers) requires far more energy and land resources from the producer level compared to a plant-based diet. Therefore, widespread dietary patterns can alter the structure of agricultural and natural food webs, impacting biodiversity and resource availability globally.
10. Are the top carnivores in a food web the most important organisms in an ecosystem?
No, while top carnivores are vital for regulating populations, they are not the most important. The producers (plants, algae) are the most crucial component. They form the foundational trophic level by converting solar energy into chemical energy, supporting the entire food web. Without a massive and healthy producer base, no other trophic levels could exist, making them the true cornerstone of any ecosystem.










