What Happens During Encystation in Amoeba and Entamoeba?
Encystation is the formation of a layered hard crust or a cyst around to protect itself from unfavourable conditions. Organisms go through encystation for protection and reproduction. However, the morphology of cyst walls depends on the genus and species. The cysts are immotile and metabolically idle yet are innately fit for vegetation by shedding their cyst coating.
Encystation is just a defensive feature taken by the cell to survive the pressure forced by an adverse climate. We can observe encystations in many organisms like Amoeba, Entamoeba, etc. but it is studied deeply in Amoeba only.
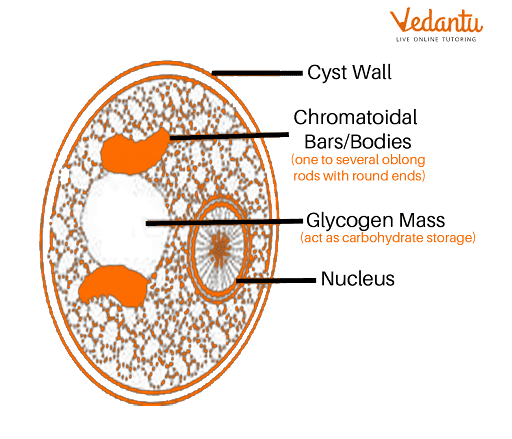
Cyst Structure
Encystation in Amoeba
Amoeba is a protozoan which possesses pseudopodia for mobility and traps its food for nutrition. It reproduces by binary or multiple fission. It shows endocytosis and exocytosis for taking in food and secreting out waste, respectively.
Encystation: During the adverse environmental conditions, it withdraws its pseudopodia and forms a shell-like structure having hard layers around itself called a cyst. It shows no movement or nutrition but is vegetatively active inside the cyst.
Morphologically, cyst in amoeba has two layers of walls. The ectocyst is the external layer, and the endocyst, which is formed after the ectocyst, is the internal fibrillar layer. These layers are composed of acid-insoluble proteins and cellulose but the exact composition is not well known.
Some scientists suggested that cellulose was the only compound present in both layers of the cyst wall but later this was disapproved and recently it has been shown that the endocyst is thinner and fibrillar than the ectocyst which resembles the cellulose structure found in plant cell walls.
When this cyst matures and conditions are favourable, the cyst bursts open and releases many cells which divide multiple fission. These daughter cells of amoeba possess pseudopodia and are fit for survival and reproduction.
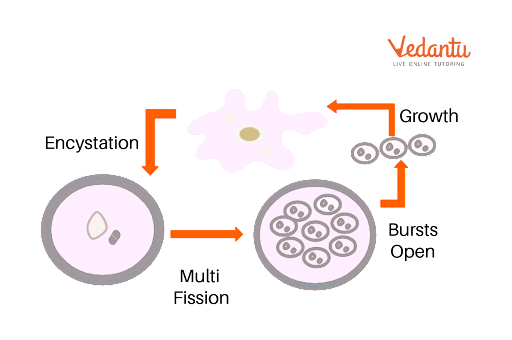
Cyst Formation in Amoeba
Encystation in Entamoeba Histolytica
Entamoeba histolytica is a parasitic protozoan which can cause amoebic dysentery affecting approximately 90 million people each year worldwide. It is transmitted through ingestion of food and water contaminated with the cyst form, which undergoes excystation in the small intestine to the trophozoite form that colonises the large intestine. They show encystation outside the host body and when they enter they start to reproduce after rupturing out from the cyst.
From this article, we can conclude that the sole purpose of encystation is reproduction and spreading the disease. Morphologically entamoeba has one layered cyst composed of chitin and encystation-specific chitin-binding lectins that cross-link chitin, degrade chitin, or self-aggregate that makes cyst walls impenetrable to small molecules, acids or other substances.
Encystment and Excystment
The formation of cyst is known as encystment. It occurs during unfavourable conditions. When the environment is favourable after encystment, the wall of the cyst ruptures this is called as excystation. This happens under favourable conditions and to prevent diseases caused by this protozoan (e.g., Amoeba), the process excystment should be blocked. It can be done by taking steps to interrupt their life cycles.
Important Questions
What does excystation mean?
Ans: When favourable conditions arrive, the protozoans tend to reproduce. They rupture their cyst wall and burst open with many cells divided by multiple fission. This is called an excystation.
Which organisms undergo encystation?
Ans: Protozoans like euglena, amoeba, and entamoeba histolytica undergo the process of encystation. They tend to become dormant during adverse conditions like high temperature, acidic environment, or high pressure and survive this by forming hard shell-like cyst around them.
Practice Questions
1. Histolytica does not show ________________.
Budding
Excystation
2. Sporulation in Amoeba mainly occurs during ___________.
Favourable conditions
Unfavourable conditions
The time of germination
Answers: 1(b) 2(a)
Key Features
The formation of cyst is an integral part of the life cycle of many protozoans. This allows these organisms to become dormant and survive adverse environmental conditions.
When the favourable conditions arrive, they may reproduce or spread the diseases in the host body.
Encystation can be studied and observed deeply in amoeba only and to our knowledge, no research and investigations have yet been performed to determine the survival capacities in other protozoan cysts.


FAQs on Encystation Explained: Steps, Examples & Significance
1. What is encystation in biology?
Encystation is a biological survival mechanism where an organism forms a resilient, multi-layered outer wall, or cyst, around itself. This process is a response to unfavourable environmental conditions, enabling the organism to enter a dormant, low-metabolic state until conditions become suitable for life again.
2. What is the primary purpose of encystation for an organism?
The primary purpose of encystation is survival during adverse conditions. It protects the organism from a range of environmental threats, including:
- Lack of food or water (desiccation)
- Extreme temperatures (both hot and cold)
- Harmful changes in pH or salinity
- Presence of toxins or lack of oxygen
By forming a cyst, the organism can endure these stresses and resume its active state when the environment improves.
3. What are the key differences between encystation and excystation?
Encystation and excystation are two opposite phases in the life cycle of many protists.
- Encystation is the process of forming a cyst in response to unfavourable or harsh environmental conditions. It is a move towards a dormant, protected state.
- Excystation is the process of emerging from the cyst when environmental conditions become favourable again. It marks the return to an active, metabolising, and often reproductive state (known as the trophozoite stage).
4. Describe the process of encystation in Amoeba as per the CBSE syllabus.
In Amoeba, encystation occurs as a direct response to adverse conditions. The process involves the following steps:
1. The Amoeba first stops moving and withdraws its pseudopodia, becoming spherical in shape.
2. It reduces its metabolic activity by losing most of its internal water.
3. The organism then secretes a tough, protective, three-layered chitinous wall around its cell membrane, forming the cyst.
This encysted Amoeba can remain dormant for extended periods, surviving harsh environments.
5. What environmental factors typically trigger the process of encystation?
Encystation is not a random event; it is triggered by specific environmental stressors that signal a threat to the organism's survival. The most common triggers include:
- Nutritional Deprivation: A lack of available food is a primary signal.
- Desiccation: The drying up of the surrounding aquatic habitat.
- Temperature Extremes: Both excessively high and freezing temperatures can initiate the process.
- pH and Oxygen Fluctuations: Significant changes in the acidity or a lack of oxygen in the environment.
6. How does encystation differ from sporulation?
While both are survival strategies, encystation and sporulation are fundamentally different processes.
- Encystation: The entire organism transforms into a single, dormant cyst. Its primary function is protection and defence for that individual organism.
- Sporulation: This is a method of asexual reproduction where the parent organism produces numerous, tiny, resistant structures called spores. Each spore can later germinate into a new individual. Therefore, sporulation serves the dual purpose of protection and population dispersal.
7. Is the cyst formed during encystation considered a reproductive structure?
Fundamentally, a cyst is a protective, dormant structure, not a reproductive one. However, the process of encystation can facilitate reproduction. In organisms like Amoeba, while inside the cyst, the nucleus can undergo multiple fission to create many minute daughter amoebae. When excystation occurs, the cyst ruptures and releases these new individuals. In this way, encystation provides the safe environment needed for this form of asexual reproduction.
8. Besides Amoeba, what are some other important examples of organisms that exhibit encystation?
Encystation is a widespread survival strategy in the microbial world. Other important organisms that undergo encystation include:
- Protozoan Parasites: Such as Entamoeba histolytica (causes amoebic dysentery) and Giardia lamblia (causes giardiasis). The cyst stage is crucial for their transmission between hosts.
- Algae: Certain types of unicellular algae form cysts to survive harsh winters or dry periods.
- Slime Molds: These organisms form cysts to endure periods of drought or food scarcity.










