What Is the Basic Structure and Function of the Embryo Sac?
The embryo sac is a vital structure in the reproductive process of flowering plants, serving as the site where fertilisation and seed development begin. Understanding its formation, structure, and functional roles is essential for Biology students, especially at the Class 12 level. This topic page will guide you through the embryo sac’s definition, development, significance, and real-world applications in agriculture and plant sciences.
What is an Embryo Sac? (Embryo Sac Definition)
The embryo sac is the female gametophyte found within the ovule of angiosperms (flowering plants). It functions as the central unit for female reproduction and fertilisation. The typical embryo sac consists of seven cells with eight nuclei and plays a pivotal role in double fertilisation, which leads to the formation of both the plant embryo and endosperm. This structure is essential for sexual reproduction in plants.
Key Stages of Embryo Sac Development
Embryo sac development starts with a process called megasporogenesis, which takes place inside the megasporangium of the ovule. Understanding these steps builds a solid foundation for plant reproduction studies and is often highlighted in embryo sac notes and MCQs.
- Formation of Megaspore Mother Cell: A hypodermal cell in the ovule's nucellus enlarges to become the megaspore mother cell (MMC).
- Meiosis in MMC: The MMC undergoes meiosis, resulting in four haploid megaspores arranged linearly.
- Degeneration: Three megaspores degenerate, leaving one functional megaspore at the chalazal end (monosporic development, often the Polygonum type).
- Mitosis: The surviving megaspore undergoes three mitotic divisions, creating an embryo sac with eight nuclei.
- Cellular Organisation: The eight nuclei arrange into seven cells—three at each end and two polar nuclei in the center—which finally fuse to form a diploid secondary nucleus.
During this sequence, only the functional megaspore matures into the complete embryo sac, which is crucial for egg apparatus formation and successful fertilisation in plants.
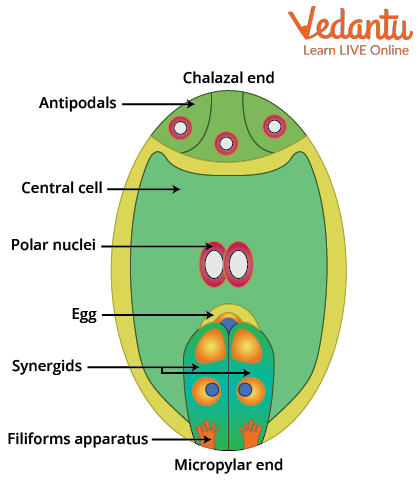
Structure of Embryo Sac
A mature embryo sac in angiosperms displays a unique organisation. It is often referred to as a 7-celled, 8-nucleate structure, which is commonly asked in embryo sac MCQs and questions. This arrangement ensures the efficient process of double fertilisation, a major difference between angiosperms and other plants.
- Egg Apparatus: Located at the micropylar end, it consists of one egg cell and two synergids. The synergids help direct the growing pollen tube during fertilisation.
- Central Cell: The largest cell in the centre contains two polar nuclei, which later fuse to form a diploid secondary nucleus (endosperm mother cell).
- Antipodal Cells: Three small cells at the chalazal end, which typically degenerate after fertilisation.
All these cells are surrounded by the embryo sac’s thin wall and play distinct roles during seed formation. The central cell ensures the development of nutritious endosperm for the growing embryo. For a comparison, check out the dicot embryo page to see how the embryo sac connects to further stages of development.
Role of Embryo Sac in Plant Reproduction
The embryo sac performs the key functions of female reproductive success in flowering plants. The process is a classic topic in embryo sac class 12 short notes and MCQs, as it highlights double fertilisation and its significance.
- Double Fertilisation: One male gamete fuses with the egg cell, forming the zygote (future embryo). The other male gamete fuses with the diploid central cell, forming the endosperm, which nourishes the embryo.
- Synergids: These regulate the pollen tube’s entry and discharge, ensuring the male gametes reach their correct targets.
- Antipodal Cells: Although their role is less clear, they may help in nutrient transfer or degeneration post-fertilisation.
The embryo sac’s ability to manage multiple fertilisation events distinguishes angiosperms. This process is not found in animals or gymnosperms. For deeper insight into plant reproductive systems, explore sexual reproduction in flowering plants on Vedantu.
Types of Embryo Sac Development
There are different types of embryo sac development, but the Polygonum type is the most common. In this monosporic development, only one megaspore out of four forms the complete embryo sac. The terminology and distinctions here make for excellent embryo sac MCQs and explain its widespread presence in plant reproduction.
- Monosporic (Polygonum type): Originates from a single megaspore (most common).
- Bisporic: Involves two nuclei from two different megaspores.
- Tetrasporic: Involves all four nuclei combining without walls separating them.
Understanding these types is important in advanced topics like megasporogenesis, which is the process by which the embryo sac forms inside the ovule. For more background, browse megasporogenesis and related reproductive processes on Vedantu.
Real-World Significance & Examples
The embryo sac is crucial in agriculture, plant breeding, and food production. By manipulating embryo sac development, scientists can increase seed yield in crops like rice, wheat, and maize. In environmental science, understanding the embryo sac’s function can help address climate-related challenges that impact seed viability. For more on plant science applications, see food science and life science.
- Example 1: Improving hybrid seed production in crops depends on precise embryo sac management.
- Example 2: Conservation efforts for endangered plants often involve studying the embryo sac to ensure successful reproduction.
- Example 3: Biotechnological advances allow for detection and correction of seed defects at the embryo sac stage.
In summary, the embryo sac’s study enhances food security, supports biodiversity, and is foundational in plant genetics and breeding.
Difference Between Ovule and Embryo Sac
| Feature | Ovule | Embryo Sac |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Structure inside ovary that develops into a seed | Female gametophyte inside the ovule |
| Components | Integuments, nucellus, embryo sac | Egg cell, synergids, antipodals, central cell |
| Role | Protects and nourishes female gametophyte | Site of fertilisation and endosperm formation |
While the ovule encloses and supports the embryo sac, the embryo sac itself is responsible for all the essential reproductive events leading to seed formation in flowering plants.
Quick Embryo Sac Short Notes
If you need rapid revision, these embryo sac short notes will help:
- Embryo sac = female gametophyte of angiosperms, usually 7-celled, 8-nucleate.
- Develops from a single functional megaspore after meiosis.
- Composed of egg apparatus (egg + two synergids), three antipodals, and a central cell with two polar nuclei.
- Central for double fertilisation—unique to angiosperms.
- Key topic for plant reproduction, genetics, and MCQs.
Downloadable Embryo Sac Resources
To master the topic, students can refer to Vedantu’s concise embryo sac notes, detailed diagrams, and topic-wise explanations relevant for Class 12 and entrance exams. For visual learners, try creating your own embryo sac diagram or organize an embryo sac ppt to summarize the steps and the key differences from other plant reproductive structures.
Practice Embryo Sac MCQs & Sample Questions
Boost your exam preparation by practising multiple choice questions (MCQs) and short-answer samples based on real-world and theoretical concepts about the embryo sac. Exploring these questions will improve your understanding of fertilisation, development, and structure-function relationships. For more MCQs and Class 12 biology resources, visit Vedantu’s biology sections and related reproductive biology pages.
In summary, the embryo sac is central to plant reproductive biology and food production, linking cell division, fertilisation, and seed formation. Mastery of this topic prepares students for higher studies and agricultural applications, as well as a deeper appreciation of plant life cycles and biodiversity. Vedantu’s expert, student-friendly content supports learning with easy-to-digest explanations and interactive revision materials.


FAQs on Embryo Sac in Biology: Definition, Structure and Role
1. What is an embryo sac?
The embryo sac is the female gametophyte in flowering plants (angiosperms), formed inside the ovule and responsible for fertilization and seed development. Key facts include:
- The embryo sac typically contains seven cells and eight nuclei.
- It develops through the process of megasporogenesis and megagametogenesis.
- The embryo sac includes egg cell, synergids, antipodals, and central cell with two polar nuclei.
2. How is the embryo sac formed in angiosperms?
The embryo sac forms through a two-step process: megasporogenesis and megagametogenesis. The main steps are:
- A megaspore mother cell undergoes meiosis to form four haploid megaspores.
- Usually, only one megaspore survives and develops into the embryo sac.
- The functional megaspore undergoes three mitotic divisions to produce eight nuclei, arranged as seven cells.
3. What are the components of the typical embryo sac in flowering plants?
The typical embryo sac in flowering plants contains seven cells arranged as follows:
- Three antipodal cells at the chalazal end
- Two synergids and one egg cell at the micropylar end
- One central cell with two polar nuclei in the center
4. What is the function of antipodal cells in the embryo sac?
Antipodal cells are located at the chalazal end of the embryo sac and play a supportive role. Their functions include:
- Nourishing the embryo sac during its development
- Facilitating the transport of nutrients from the ovule tissues
- Sometimes degenerating before or after fertilization
5. Describe the structure and importance of the egg apparatus in the embryo sac.
The egg apparatus in the embryo sac consists of one egg cell and two synergids at the micropylar end. Its importance:
- The egg cell is the female gamete that fuses with the sperm cell during fertilization.
- Synergids help guide the pollen tube toward the egg cell with the help of filiform apparatus.
6. What is double fertilization, and where does it occur in the embryo sac?
Double fertilization is a unique process in angiosperms that occurs inside the embryo sac. The steps include:
- One male gamete fuses with the egg cell to form the zygote (syngamy).
- Another male gamete fuses with the two polar nuclei to form the endosperm (triple fusion).
7. Explain the types of embryo sac development based on the number of megaspore nuclei that participate.
Embryo sac development is classified based on the number of megaspore nuclei involved:
- Monosporic (commonest): One megaspore forms the embryo sac (e.g., Polygonum type).
- Bisporic: Two megaspore nuclei participate.
- Tetrasporic: All four nuclei take part in forming the embryo sac.
8. What are synergids and what is their role in the embryo sac?
Synergids are two specialized cells at the micropylar end of the embryo sac, flanking the egg cell. Their roles include:
- Guiding the pollen tube into the embryo sac using the filiform apparatus.
- Participating in the fertilization process.
- Degenerating after the entry of the pollen tube.
9. How many cells and nuclei are present in a typical mature embryo sac?
A typical mature embryo sac (Polygonum type) contains:
- Seven cells (3 antipodal, 2 synergids, 1 egg cell, 1 central cell)
- Eight nuclei (each cell has one nucleus, central cell contains two polar nuclei)
10. Why is the central cell in the embryo sac important?
The central cell is the largest cell in the embryo sac and contains two polar nuclei. Its significance includes:
- Participating in triple fusion to form the primary endosperm nucleus.
- Providing nutrition to the developing embryo.










