Understanding Number, Biomass, and Energy Pyramids in Biology
An ecological pyramid is a graphical representation that illustrates how different groups of organisms (producers, consumers, and decomposers) are structured and how energy or biomass flows across various trophic levels in an ecosystem.
The idea of representing these relationships in a pyramid shape dates back to the work of Charles Elton, who first introduced the concept of the pyramid of numbers. Later, scientists such as G. Evelyn Hutchinson and Raymond Lindeman contributed valuable insights into the flow of energy, leading to the development of the pyramid of energy.
Also Read: Ecology
Types of Ecological Pyramid
There are three major types of ecological pyramids commonly studied in biology:
Pyramid of Number
Pyramid of Biomass
Pyramid of Energy
Pyramid of Number
A pyramid of numbers focuses on the count of individual organisms at each trophic level. Typically:
The base (the widest level) is occupied by producers (like plants or algae), which are often extremely numerous.
The next level is formed by primary consumers (herbivores), followed by secondary and tertiary consumers.
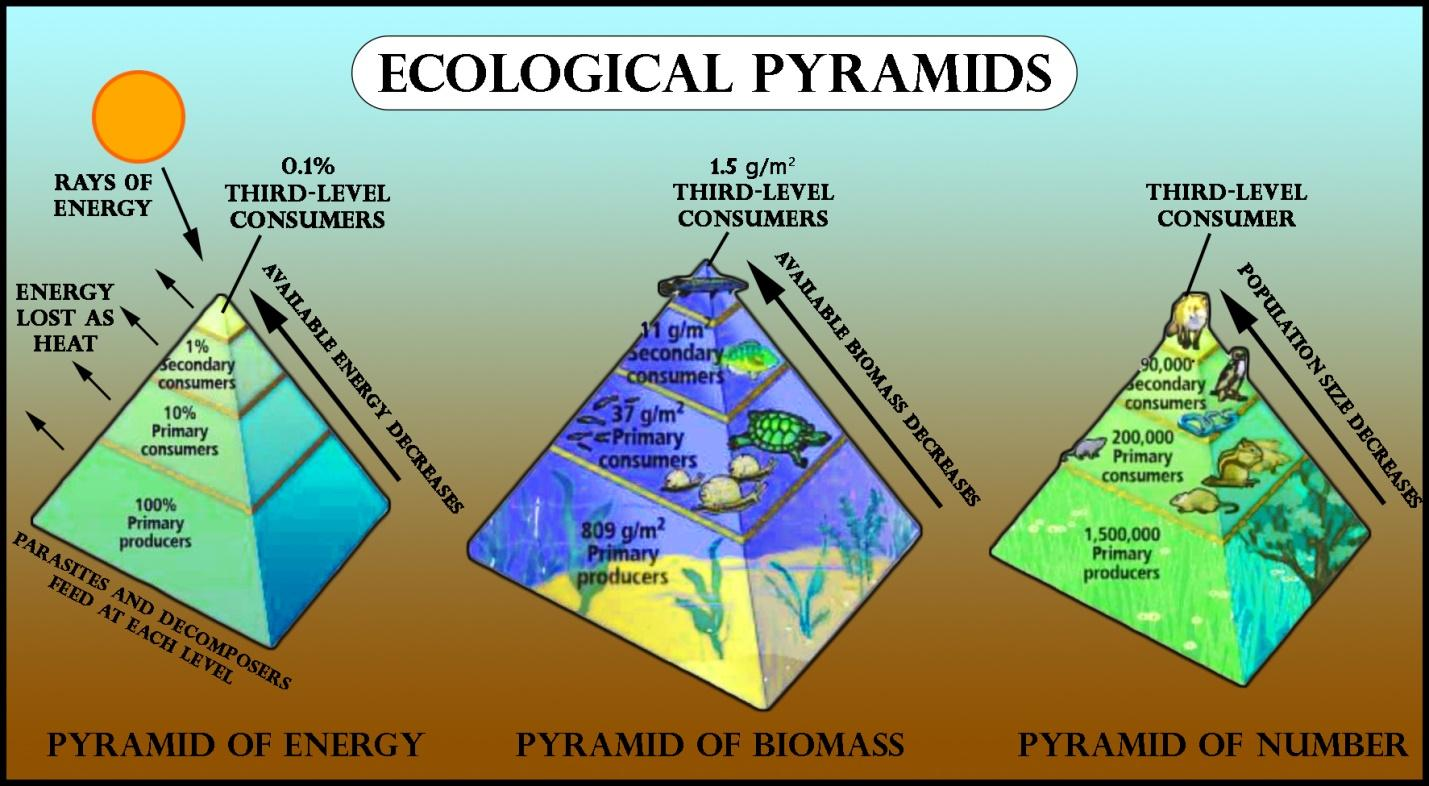
Most of the time, a pyramid of numbers is upright because there tend to be more producers than consumers in healthy ecosystems. However, certain ecosystems—such as those dominated by trees, or detritus-based food chains—may show inverted or partially inverted pyramids. For instance, a single large tree can support numerous insects, creating a top-heavy shape.
Pyramid of Biomass
The pyramid of biomass compares the total dry weight (or living organic matter) of organisms at each trophic level. Here:
Producers usually form the heaviest bulk of living matter in an ecosystem, so they create a broad base.
Consumers tend to have less total biomass at higher trophic levels.
Like the pyramid of numbers, the pyramid of biomass is often upright. However, in certain marine ecosystems, you might find an inverted shape. This happens when a smaller mass of phytoplankton (the producers) supports a much larger mass of zooplankton (the primary consumers) at any given moment. Over time, the high turnover rate of phytoplankton still sustains the food chain, even though their “snapshot” biomass is relatively small.
Pyramid of Energy
A pyramid of energy shows the flow of energy at different trophic levels within a specified period, often measured in kilocalories (kcal) or joules (J). This is the only type of ecological pyramid that is always upright because energy flows in a single direction—from producers up to various levels of consumers—and at each transfer, some energy is lost as heat.
First Trophic Level (Producers): They capture energy from the sun (via photosynthesis) or chemicals (via chemosynthesis).
Higher Trophic Levels (Consumers): Herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores derive energy by feeding on organisms at lower levels. At each step, around 10% (the “10% law” described by Raymond Lindeman) of the energy is passed on to the next level, while the rest is lost primarily as heat or through metabolic processes.
Energy Pyramid Examples
To clarify how energy decreases at each step, here are a couple of common energy pyramid examples:
Grassland Ecosystem
Producers: Grasses and small shrubs capturing sunlight
Primary Consumers: Grasshoppers, rabbits
Secondary Consumers: Snakes, foxes
Tertiary Consumers: Hawks or eagles
At each level, the available energy becomes progressively smaller.
Aquatic Ecosystem
Producers: Phytoplankton (microscopic algae)
Primary Consumers: Zooplankton
Secondary Consumers: Small fish
Tertiary Consumers: Large predatory fish (e.g., tuna), and sometimes apex predators like sharks
Again, the flow of energy follows a unidirectional path, with most energy lost as heat at every step.
Importance of Ecological Pyramids in the Ecosystem
Studying ecological pyramids in the ecosystem is vital for the following reasons:
Clear Visualisation: They offer a quick and clear way to understand the structure of food chains and the distribution of energy or biomass.
Ecosystem Health Monitoring: Changes in the shape or stability of these pyramids can indicate ecosystem imbalances (e.g., overfishing, and deforestation).
Energy Transfer Efficiency: The 10% law and the shape of the pyramid of energy highlight how little energy is transferred from one level to the next.
Conservation & Management: By understanding which trophic levels are most vulnerable, conservationists can intervene more effectively to preserve biodiversity.
Read More: Conservation of Biodiversituy
Limitations of the Ecological Pyramid
Although ecological pyramids are a powerful tool for visualising trophic relationships, there are a few limitations of the ecological pyramid approach:
Complex Food Webs: Natural ecosystems rarely form simple chains. They consist of interconnected food webs. A single species can occupy multiple trophic levels (e.g., omnivores).
Exclusion of Decomposers: Decomposers or saprophytes are often left out of the classic pyramid model, even though they play an essential role in recycling nutrients.
No Seasonal or Climatic Variations: Pyramids typically offer a “snapshot” view and may not account for seasonal fluctuations or climate changes.
Inverted or Partially Inverted Pyramids: Some ecosystems (e.g., aquatic systems) may have an inverted pyramid of biomass, confusing one-size-fits-all diagrams.
Quantification Challenges: Measuring biomass and energy flow accurately can be difficult, leading to data gaps or high margins of error.
Additional Insights & Quick Facts
Raymond Lindeman’s 10% Law: This principle states that only about 10% of energy is transferred to each successive trophic level. This underpins why the pyramid of energy always narrows sharply.
Productivity vs. Standing Crop: While the pyramid of biomass measures “standing crop” at a given time, a pyramid of productivity (a variation of the energy pyramid) measures the rate at which biomass is produced over time.
Human Impact: Overharvesting at higher trophic levels (like large fish in oceans) can disrupt the natural shape of the pyramid, threatening ecosystem stability.
Omnivores & Mixed Diets: Humans, bears, and some other animals can feed at multiple trophic levels, illustrating how complex real-world food webs can be.
By including these additional details, you gain a more accurate picture of how ecological pyramids in the ecosystem behave in real-world scenarios.
Also Check:


FAQs on Ecological Pyramids: Types and Examples for Easy Learning
1. What is an ecological pyramid?
An ecological pyramid is a graphical representation designed to show the relationship between different organisms at various trophic levels in an ecosystem. It illustrates how parameters like the number of individuals, biomass, or energy flow from the producers at the bottom to the consumers at the top.
2. What are the three main types of ecological pyramids studied in Biology?
The three major types of ecological pyramids are:
- Pyramid of Numbers: This shows the total count of individual organisms at each trophic level.
- Pyramid of Biomass: This represents the total dry weight (or living organic matter) of all organisms at each level.
- Pyramid of Energy: This illustrates the rate of energy flow from one trophic level to the next, and it is always upright.
3. What do the different levels in an ecological pyramid represent?
Each level in an ecological pyramid represents a specific trophic level, or a step in the food chain. The broad base is the first trophic level, occupied by producers (e.g., plants). The subsequent levels are occupied by consumers: primary consumers (herbivores), followed by secondary and tertiary consumers (carnivores or omnivores).
4. Why is the pyramid of energy always upright?
A pyramid of energy is always upright because energy transfer between trophic levels is highly inefficient. Following the 10% Law, only about 10% of the energy from a lower trophic level is converted into biomass at the next level. The rest is lost, primarily as heat during metabolic activities, ensuring that energy always decreases as it moves up the food chain.
5. Can a pyramid of biomass be inverted? Explain with an example.
Yes, a pyramid of biomass can be inverted, especially in certain aquatic ecosystems. For instance, a small standing crop of producers like phytoplankton (which reproduce very quickly) can support a much larger biomass of primary consumers like zooplankton at any single point in time, creating an inverted shape.
6. What is the significance of the 10% Law in an energy pyramid?
The 10% Law, introduced by Raymond Lindeman, is a fundamental principle explaining why energy pyramids have a wide base and a narrow top. It states that only about 10% of the energy consumed at one trophic level is stored and transferred to the next. This law highlights the massive energy loss at each step and explains why food chains are typically limited to four or five levels.
7. How do ecological pyramids help in understanding the health of an ecosystem?
Ecological pyramids serve as a vital tool for monitoring ecosystem health. A stable, upright pyramid generally indicates a balanced ecosystem. Any significant change in its shape, such as a shrinking base or a bulging middle level, can signal an environmental issue like pollution, disease, or the impact of invasive species, helping ecologists identify and address these problems.
8. Why are decomposers not placed in a standard ecological pyramid?
Decomposers, like bacteria and fungi, are a critical part of any ecosystem but are generally excluded from standard ecological pyramids. This is because they derive their energy from dead organic matter from all trophic levels (dead producers, consumers, etc.). Placing them on a single, specific level would be inaccurate and would overcomplicate the pyramid's purpose of showing a linear flow of energy through feeding levels.
9. How can human activities like overfishing impact an ecological pyramid?
Human activities can severely disrupt the natural structure of ecological pyramids. For example, overfishing removes large quantities of top predators (tertiary consumers) from marine ecosystems. This can cause the top level of the pyramid to shrink drastically, leading to an overpopulation of their prey (secondary consumers) and creating a cascading effect that unbalances the entire food web.










