Comparative Table: Spermatogenesis vs Oogenesis (Easy Explanation)
The process of gamete formation is essential to human reproduction and genetic continuity. Two vital processes—spermatogenesis and oogenesis—are responsible for producing the male (sperm) and female (ovum) gametes, respectively. Understanding how these processes differ is crucial for students, educators, and parents alike in the study of reproductive biology.
Write Four Differences Between Spermatogenesis and Oogenesis
Spermatogenesis and oogenesis each play unique roles in forming male and female gametes. While both are types of gametogenesis, they differ in location, process, timing, and outcomes. Below is a simple tabular comparison outlining four fundamental differences between the two processes, as referenced in leading educational resources.
| Point of Difference | Spermatogenesis | Oogenesis |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Site of Occurrence | Takes place in the testes of males. | Occurs in the ovaries of females. |
| 2. Number of Gametes Produced | From each primary spermatocyte, four functional sperm cells are formed. | From each primary oocyte, only one functional ovum is produced, along with polar bodies. |
| 3. Timing and Continuity | A continuous process starting at puberty, continuing throughout life. | A discontinuous process that begins before birth, pauses, and completes only after fertilisation. |
| 4. Division of Cytoplasm | Cytokinesis is equal — resulting in four similar sized sperm cells. | Cytokinesis is unequal — resulting in one large ovum and smaller polar bodies. |
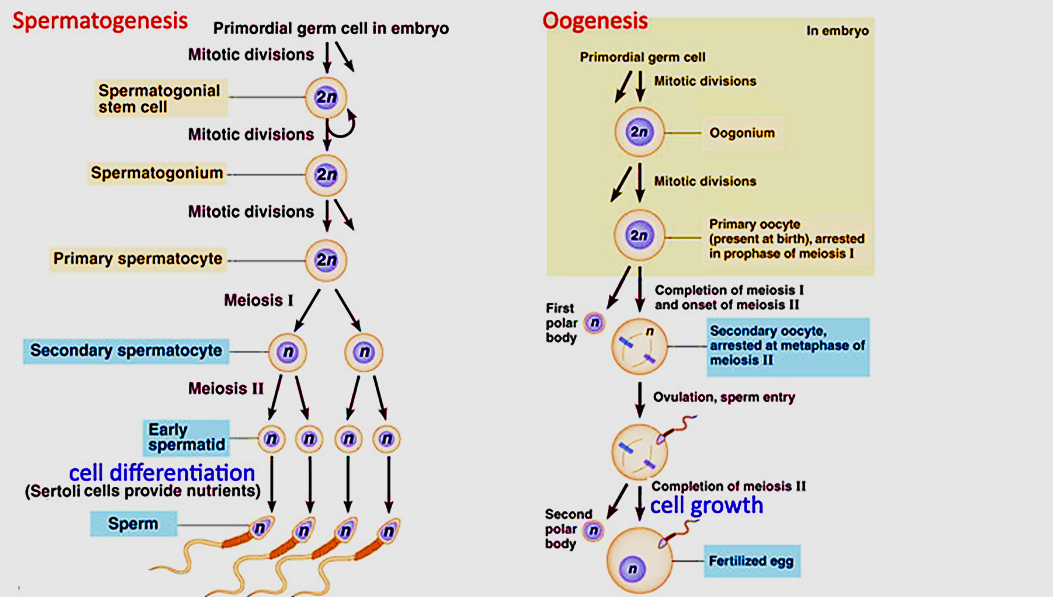
Explanation with Examples
Spermatogenesis ensures that millions of motile sperm are produced continuously in males, maintaining fertility throughout the reproductive years. For example, in a healthy male, spermatogenesis generates several million sperm every day, all of which are capable of fertilizing an ovum.
Oogenesis, in contrast, produces one mature ovum per menstrual cycle. The process starts before the birth of a female, with primary oocytes getting arrested until puberty. Upon ovulation, usually only one ovum completes the process and is available for fertilisation—thus, far fewer ova are produced compared to sperm.
Step-by-Step Breakdown of Each Process
Spermatogenesis:
- Occurs in the seminiferous tubules of the testes.
- Begins with spermatogonia (male germ cells) multiplying by mitosis.
- Primary spermatocytes undergo meiosis, leading to four haploid spermatids per cycle.
- Spermatids differentiate into mature, motile sperm.
Oogenesis:
- Occurs in the ovary, starting before a female is born.
- Oogonia divide mitotically and form primary oocytes, which arrest in meiosis until puberty.
- After puberty, each menstrual cycle, usually one oocyte resumes meiosis and forms a secondary oocyte and polar body.
- Meiosis completes only upon fertilisation, yielding a single ovum and additional polar bodies.
Key Definitions and Biological Significance
Spermatogenesis is the formation process of sperm cells in the male reproductive system. It ensures continuous availability of male gametes for fertilisation.
Oogenesis is the formation process of ova in the female reproductive system, essential for providing the cytoplasm and nutrients the early embryo needs. The formation of only one large ovum ensures that the resulting zygote has sufficient resources for early development.
Further Vedantu Resources
Practice Questions
- List four differences between spermatogenesis and oogenesis.
- Why does oogenesis produce only one ovum, while spermatogenesis produces four sperm?
- Explain the significance of unequal cytokinesis in oogenesis.
- Draw the process of oogenesis and label each stage.
Understanding these differences in gamete formation helps clarify many concepts in reproductive biology and is foundational knowledge for advanced studies and exams.


FAQs on Difference Between Spermatogenesis and Oogenesis (With Diagram & Table)
1. What are four main differences between spermatogenesis and oogenesis?
Spermatogenesis and oogenesis differ in the following key ways:
- Location: Spermatogenesis occurs in the seminiferous tubules of testes; oogenesis takes place in the ovarian cortex.
- Timing: Spermatogenesis starts at puberty and continues throughout life; oogenesis begins before birth, pauses, and completes after fertilization.
- Gamete production: One primary spermatocyte forms four sperm; one primary oocyte forms one ovum and three polar bodies.
- Cytoplasmic division: Spermatogenesis has equal division; oogenesis involves unequal division, resulting in a larger ovum and smaller polar bodies.
2. What is the major difference between spermatogenesis and oogenesis?
The major difference is that spermatogenesis produces four equal and functional sperm cells from each precursor cell, while oogenesis produces only one functional ovum and three non-functional polar bodies from each precursor cell, due to unequal cytoplasmic division during meiosis.
3. Write three differences between oogenesis and spermatogenesis.
Three key differences:
- Onset: Spermatogenesis starts at puberty; oogenesis starts during fetal development.
- Number of functional gametes: Spermatogenesis yields four sperm per precursor; oogenesis yields one ovum per precursor.
- Completion: Spermatogenesis is continuous; oogenesis is arrested till puberty and completes after fertilization.
4. Why does oogenesis result in only one functional ovum?
Oogenesis results in one functional ovum because meiosis involves unequal cytoplasmic divisions. Most cytoplasm is retained in the ovum to support early embryonic development, while the three polar bodies receive minimal cytoplasm and degenerate.
5. Describe the process of spermatogenesis with stages.
Spermatogenesis process:
- Begins with diploid spermatogonia in seminiferous tubules
- Spermatogonia undergo mitosis to form primary spermatocytes
- Primary spermatocyte performs meiosis I, producing two secondary spermatocytes (haploid)
- Each secondary spermatocyte undergoes meiosis II, forming two spermatids (total of four per primary spermatocyte)
- Spermatids undergo spermiogenesis to become motile spermatozoa
6. What are the similarities between spermatogenesis and oogenesis?
Similarities:
- Both are gametogenesis processes producing haploid gametes from diploid germ cells
- Involve mitosis, growth phase, two meiotic divisions, and differentiation
- Controlled by hormones such as FSH and LH
- Essential for sexual reproduction and genetic variation
7. In which organ does oogenesis occur and when does it start?
Oogenesis occurs in the ovaries, specifically within the ovarian cortex. It starts during fetal life, before a female is born, with primary oocytes getting arrested at prophase I until puberty.
8. How is cytoplasmic division different in oogenesis and spermatogenesis?
In spermatogenesis, cytoplasmic division is equal, producing four small, similar sperm cells. In oogenesis, division is unequal; most cytoplasm remains in the ovum, while the smaller polar bodies receive little and eventually degenerate.
9. How many gametes are produced from one primary spermatocyte and one primary oocyte?
From one primary spermatocyte (male), four functional sperm are produced. From one primary oocyte (female), only one functional ovum and three polar bodies are produced.
10. What is the significance of polar bodies in oogenesis?
Polar bodies eliminate extra sets of chromosomes and maintain correct chromosome numbers. They do not participate in fertilization and help ensure that the ovum retains most of the cytoplasm for embryo development.
11. Why is spermatogenesis considered a continuous process while oogenesis is discontinuous?
Spermatogenesis is continuous because it starts at puberty and continues throughout a male’s life. Oogenesis is discontinuous as it begins before birth, pauses at prophase I, resumes at puberty, and completes only after fertilization.
12. What role do FSH and LH play in spermatogenesis and oogenesis?
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and Luteinizing hormone (LH) regulate both processes. FSH stimulates gamete production, while LH triggers ovulation in females and testosterone production (supporting spermatogenesis) in males.










