What Are the Symptoms and Causes of High Bilirubin?
Bilirubin may be a dark yellow material that's primarily created once the body breaks down Hb, that is, the supermolecule in red blood cells that carries chemical elements. Bilirubin is found in gall, which is fluid in your liver that's concerned with digesting food. Most bilirubin is eliminated within the BM or excrement.
The bilirubin takes a look and checks the health of your liver by measuring the number of bilirubin in your blood or in your excrement.
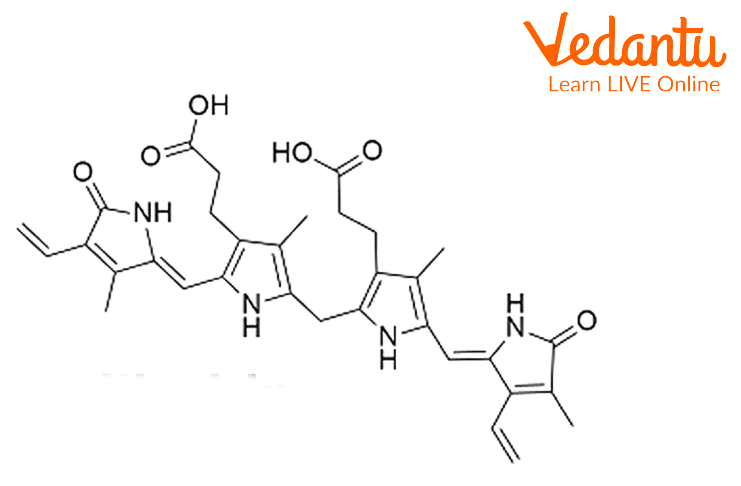
Bilirubin Structure
Definition of Bilirubin
Substance fashioned once red blood cells are dampened. Bilirubin is a component of the digestive juice that is created within the liver and is held on within the vesica. The abnormal buildup of bilirubin causes jaundice.
The amount of bilirubin factory-made relates to the number of blood cells destroyed. About 0.5 to a pair of grams square measure made daily. It's not a famous performance and may be venomous to the foetal brain.
Bilirubin within the blood is sometimes in an exceedingly free, or unconjugated, state; it's connected to simple protein, a protein because it is transported. Once within the liver, it conjugates with glucuronic acid made of the sugar aldohexose. It's then targeted to concerning,1000 times the strength found in plasm.
In humans, bilirubin is believed to be unconjugated till it reaches the liver. In dogs, sheep, and rats, there's no bilirubin within the blood, although it's a gift within the liver.
Direct and Indirect Bilirubin
What is Direct Bilirubin?
Direct bilirubin, additionally referred to as conjugated bilirubin, is the changed sort of merchandise obtained once the dissimilation of Hb.
The indirect bilirubin is conjugated with glucuronic acid by the accelerator glucuronyltransferase. This conjugation makes the direct bilirubin less venomous and simple to egest. Direct bilirubin is soluble in water.
The total bilirubin of our body is the addition of direct and indirect bilirubin. The bilirubin’s normal range or traditional bilirubin values for adults are:
Total bilirubin: zero.3 to 1.9 mg/dL
Direct bilirubin: zero.0 to 0.3 mg/dL.
What is Indirect Bilirubin?
Indirect bilirubin, additionally called unconjugated haematoidin, is the direct product of the breakdown of Hb. The unconjugated bilirubin binds to albumin, facilitating straightforward transport from blood to the liver. However, this manner of indirect bilirubin is very toxic; thus, it's reborn to direct bilirubin within the liver with the assistance of enzymes, which is a smaller amount cytotoxic.
Indirect bilirubin is very soluble in lipids and is oleophilic. It is, however, insoluble in water. If you have got high bilirubin, your symptoms can depend upon the underlying cause. you'll be able to have gently high bilirubin and haven't any symptoms in any respect. With moderately high bilirubin, you'll solely have jaundice, which may be a yellow colour to your eyes and skin. Jaundice is the main sign of high bilirubin levels.
Symptoms of High Bilirubin
Abdominal pain or swelling
Chills
Fever
Chest pain
Weakness
Lightheadedness
Higher levels of bilirubin are caused because of many reasons like, hemolytic anaemia, which is maybe a condition wherever our body starts obtaining too many RBCs.
Genetic bad
Gallstones
Gilbert’s syndrome
Hepatitis
Bilirubin Blood Test
A bilirubin biopsy measures the amount of bilirubin in your blood. If your liver is healthy, it'll take away most of the bilirubin from your body. If your liver is broken, bilirubin will break off your liver and into your blood. Once an excessive amount of bilirubin gets into the blood, it will cause jaundice, a condition that causes your skin and eyes to show yellow.
Need for a Bilirubin Check
Your physician might order a bilirubin blood test:
If you have got symptoms like jaundice, dark urine, or abdomen pain. These might be symptoms of liver disease, cirrhosis, or different liver diseases. they will even be signs of vesica unwellness.
To find out if there's a blockage within the gall ducts, the tubes that carry gall from your liver.
To check on existing disease or disorder.
To diagnose disorders associated with issues with breaking down red blood cells. High bilirubin levels in the blood are also a symptom of a condition known as hemolytic anaemia. During this condition, the body destroys red blood cells quicker than it makes them.
Interesting Facts
Kernicterus (Bilirubin Encephalopathy)
Lipid-soluble, unconjugated, indirect bilirubin fraction is venomous to the developing central system, particularly once indirect bilirubin concentrations are high and exceed the binding capability of albumin.
Important Questions
What is the most important supply of bilirubin?
Ans: Roughly, eighty percent of bilirubin is formed from the breakdown of hemoprotein in old red blood cells, and untimely destroyed erythroid cells within the bone marrow. The rest originates from the turnover of varied heme-containing proteins found in alternative tissues, primarily the liver and muscles.
Is bilirubin affected by lights?
Ans: Bilirubin may be a substance absorbing light within the colour spectrum, and it's well recognised to endure each isomerisation and oxidation reaction in serum exposed to visible radiation, leading to reduced measured bilirubin values.
Conclusion
Serum bilirubin could be a yellow pigment found in gall, a fluid created by the liver. Bilirubin may also be measured with a piddle check. Direct bilirubin, conjointly called conjugated bilirubin, is the changed style of the merchandise obtained when the biological process of bilirubin. The indirect haematoidin is conjugated with glucuronic acid by the protein glucuronyltransferase. This conjugation makes the direct bilirubin less cyanogenic and simple to expel.


FAQs on Bilirubin: Meaning, Types & Role in the Body
1. What is bilirubin and where does it come from in the body?
Bilirubin is a yellowish pigment that is formed as a natural byproduct of the breakdown of old or damaged red blood cells (RBCs). Specifically, it originates from the non-iron part of heme, a component of haemoglobin. This process primarily occurs in the spleen, liver, and bone marrow.
2. How is bilirubin processed and metabolised by the liver?
Once produced, bilirubin is initially in an insoluble form (unconjugated). It travels through the bloodstream bound to a protein called albumin to the liver. In the liver, it is combined with glucuronic acid in a process called conjugation, which makes it water-soluble. This conjugated bilirubin is then secreted into the bile, which flows into the small intestine to help with digestion and is eventually eliminated from the body primarily through faeces.
3. What is the difference between conjugated (direct) and unconjugated (indirect) bilirubin?
The primary difference lies in their solubility and processing by the liver.
- Unconjugated (Indirect) Bilirubin: This is the initial form of bilirubin produced from heme breakdown. It is fat-soluble and not water-soluble, which is why it needs to bind to albumin to be transported in the blood.
- Conjugated (Direct) Bilirubin: This is the form of bilirubin after it has been processed by the liver. It is water-soluble, allowing it to be excreted into the bile and eliminated from the body. High levels of specific types can indicate different health issues.
4. What are the main causes of high bilirubin levels (hyperbilirubinemia)?
High bilirubin levels, a condition known as hyperbilirubinemia, can be caused by three main types of issues:
- Pre-hepatic causes: An excessive breakdown of red blood cells (hemolysis), as seen in conditions like sickle cell anaemia or malaria, which produces bilirubin faster than the liver can process it.
- Hepatic causes: Liver damage or disease, such as hepatitis or cirrhosis, impairs the liver's ability to conjugate and excrete bilirubin. Genetic conditions like Gilbert's syndrome also fall in this category.
- Post-hepatic causes: A blockage in the bile ducts (e.g., from gallstones or a tumour) prevents conjugated bilirubin from being drained from the liver, causing it to leak back into the bloodstream.
5. How does an elevated level of bilirubin in the blood lead to jaundice?
Jaundice is the clinical sign of high bilirubin levels. Because bilirubin is a yellow pigment, its accumulation in the bloodstream leads to it being deposited in various tissues. This causes the characteristic yellowing of the skin, the whites of the eyes (sclera), and mucous membranes. It is not a disease itself but a symptom of an underlying problem with bilirubin metabolism or excretion.
6. What is a bilirubin test and what are the typical normal ranges in adults?
A bilirubin test is a blood test that measures the amount of bilirubin in your bloodstream. It helps assess liver function and diagnose conditions related to red blood cell destruction. The test measures total, direct (conjugated), and indirect (unconjugated) bilirubin. For adults, a typical normal range for total bilirubin is about 0.1 to 1.2 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). Normal ranges can vary slightly between laboratories.
7. Why is it particularly important to monitor bilirubin levels in newborn infants?
Newborns often have higher bilirubin levels because their liver is still maturing and may not be efficient at conjugation. While mild jaundice is common and often resolves on its own, extremely high levels of unconjugated bilirubin are a major concern. This form can cross the blood-brain barrier and deposit in the brain, leading to a serious condition called kernicterus, which can cause permanent brain damage and developmental issues. Therefore, monitoring is crucial to intervene with treatments like phototherapy if levels become dangerously high.
8. How does the body's elimination of bilirubin compare to the excretion of urea?
The excretion pathways for bilirubin and urea are fundamentally different, reflecting their origins and the organs involved.
- Bilirubin: It is a waste product of heme breakdown, processed by the liver, made water-soluble, and excreted primarily into the digestive tract via bile, giving stool its colour. A very small amount is excreted via the kidneys.
- Urea: It is the main waste product of protein and amino acid metabolism, formed in the liver through the urea cycle. Unlike bilirubin, it is transported to the kidneys and is the primary nitrogenous compound excreted in urine.
9. Apart from being a waste product, does bilirubin have any beneficial functions in the body?
Yes, despite being a waste product, recent studies show that bilirubin has significant biological functions. At normal physiological concentrations, it acts as a potent antioxidant. It helps protect cells from damage caused by free radicals and oxidative stress. This antioxidant capacity is believed to play a protective role against certain cardiovascular and inflammatory diseases. However, this benefit is lost when its levels become excessively high and toxic.
10. What does the presence of bilirubin in urine (bilirubinuria) signify?
The presence of bilirubin in urine is not normal and is a significant clinical finding. Only conjugated (direct) bilirubin is water-soluble and can be filtered by the kidneys into urine. Unconjugated bilirubin cannot. Therefore, bilirubinuria indicates that there are elevated levels of conjugated bilirubin in the blood, which points towards a problem occurring after the liver has processed it. This is typically a sign of liver disease (like hepatitis) or a blockage of the bile ducts (obstructive jaundice), which prevents the bilirubin from being eliminated through the intestines.










