Physics Notes for Chapter 3 Current Electricity Class 12 - FREE PDF Download



FAQs on CBSE Notes Class 12 Physics Chapter 3 - Current Electricity - 2025-26
1. What are the key concepts students should revise first from Class 12 Physics Chapter 3 Current Electricity?
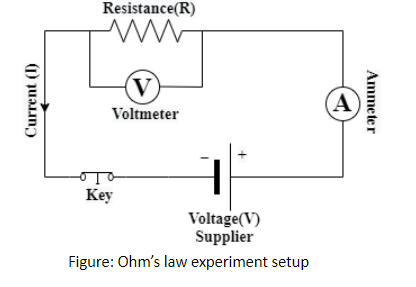
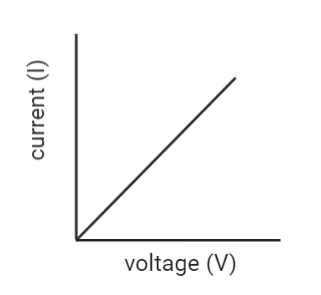
Begin your revision with Ohm’s Law, Kirchhoff’s Rules, the definitions of resistance and resistivity, and the behaviour of series and parallel circuits. Next, focus on the effects of temperature on resistance, drift velocity, mobility, and electrical power formulas. Ensure you can explain each concept clearly for good exam performance.
2. How can a concept map help when revising Current Electricity in Class 12 Physics?
A concept map allows you to visually connect formulas, definitions, and laws. For Current Electricity, map out the links between electric current, Ohm’s Law, circuit rules, and types of materials, which helps in quick recall and understanding how each topic interrelates during your final revision.
3. What summary points should you focus on for exam-oriented revision of current electricity?
When revising, summarize:
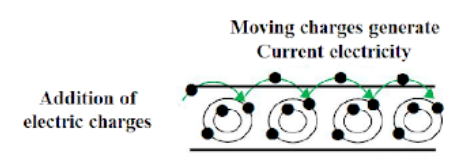
- The meaning of electric current (charge flow per time)
- Ohm's Law and the factors affecting resistance
- Drift velocity and its connection with current
- Series and parallel circuit behaviour
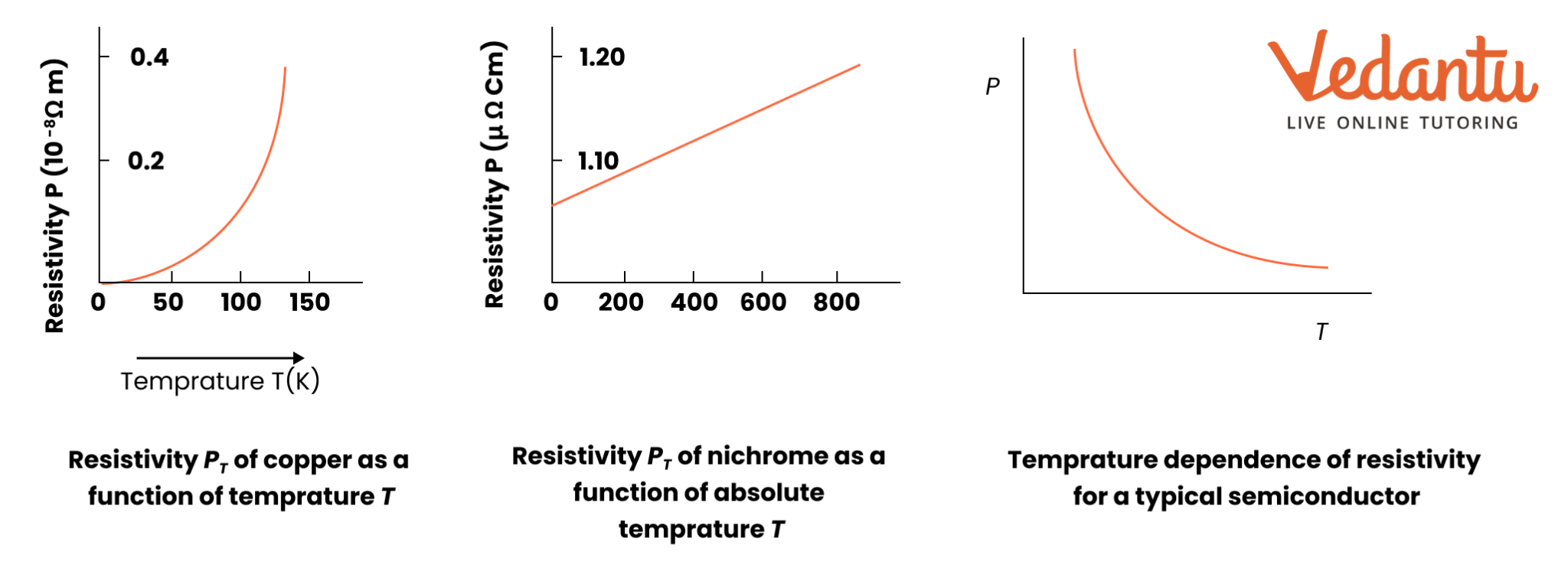
- Temperature dependence of resistivity for metals and semiconductors
- The concept of electromotive force (EMF) and internal resistance
4. How should students approach formula revision for Class 12 Current Electricity?
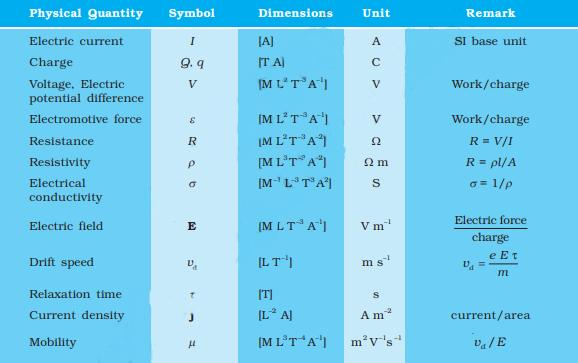
List all key formulas such as V = IR, P = VI, R = \(\rho \frac{L}{A}\), and resistivity-temperature relationships. Write these formulas with units and variable meanings. Practicing problems involving each ensures you remember when and how to apply them, which is crucial for board exams.
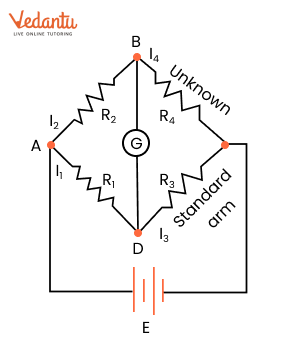
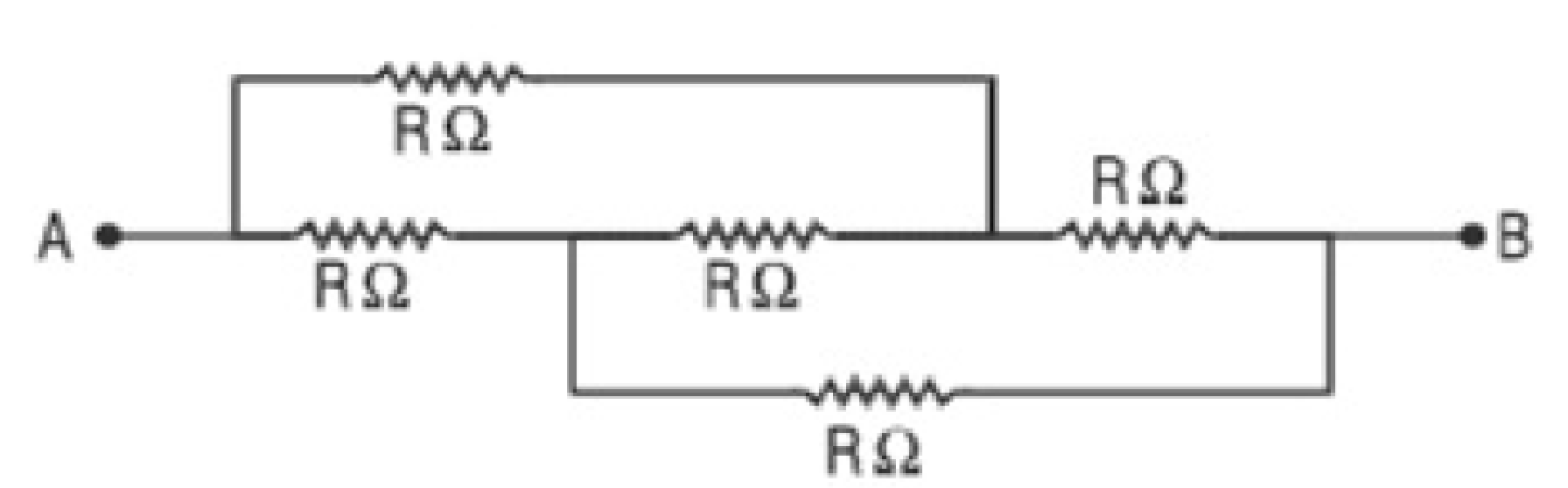
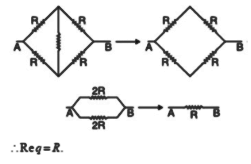
5. What is the best revision strategy for complex concepts like Kirchhoff’s Laws or the Wheatstone Bridge?
Start with the statement and mathematical expression of each law. Practice drawing and labelling circuit diagrams. Summarize steps to solve numerical problems using these laws, and solve representative questions to reinforce understanding and approach.
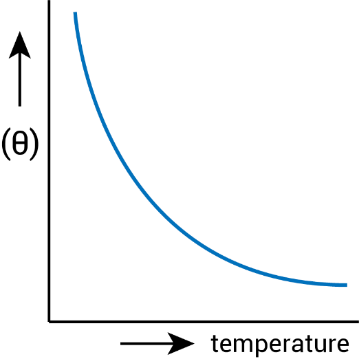
6. Why is understanding resistivity and its temperature dependence essential in Class 12 Current Electricity revisions?
Resistivity influences how easily current flows through materials, so its understanding is vital for comparing conductors, insulators, and semiconductors. Knowing how resistivity changes with temperature helps in explaining device performance and is commonly tested in CBSE exams.
7. How can students avoid common mistakes when revising the derivations in Current Electricity?
Review each derivation stepwise, stating all assumptions and definitions upfront. Use proper units throughout, and relate the derived result back to physical meaning. Practicing these with past exam questions helps avoid missing important steps in the answer.
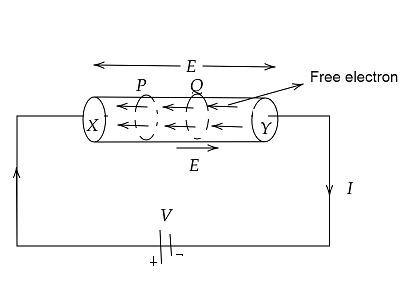
8. What role does understanding the difference between drift velocity and mobility play during revision?
Drift velocity is the average velocity acquired by electrons due to an electric field, while mobility measures how quickly charge carriers move under unit field. Recognizing this difference aids in correct application of relationships and clearer explanations in both theory and numerical questions.
9. Why should students focus on the applications of Current Electricity concepts in daily life during revision?
Applying concepts like Ohm’s Law, heating effect, or power transmission to real life (e.g., electrical appliances, fuses, household wiring) boosts understanding and helps write better answers in value-based or application-based questions in CBSE exams.
10. What is the ideal order to revise the subtopics in Class 12 Physics Current Electricity for quick and effective preparation?
Begin with basics of electric current, then move to drift of electrons, Ohm’s Law and resistance, series and parallel circuits, Kirchhoff’s Laws, heating effects of current, and finish with EMF, internal resistance, and Wheatstone bridge. This order reflects logical progression and helps consolidate underlying principles efficiently.
11. How do revision notes help in mastering numerical problem-solving for Current Electricity in board exams?
Well-structured revision notes distill the problem-solving steps, highlight key equations, and provide solved examples. This enables quick referencing, troubleshooting errors, and developing speed and accuracy for marks-oriented numerical questions.
12. What common misconceptions should be clarified while reviewing Current Electricity concepts?
Clear up misconceptions such as:
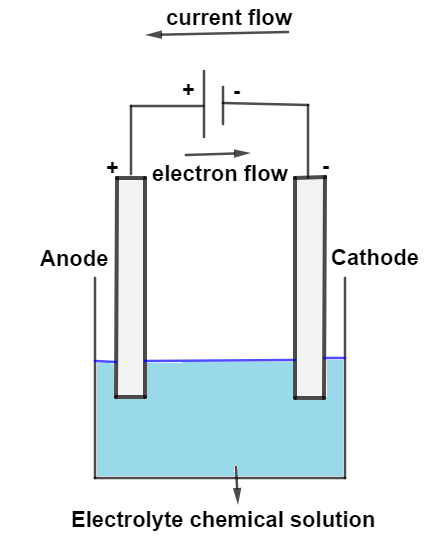
- Direction of current vs. electron flow
- Resistivity and resistance being the same (they are not)
- Effect of heating on resistivity for metals vs. semiconductors
- Assuming Ohm’s Law applies to all materials (it does not)
13. What are some effective ways to revise and retain circuit analysis methods for Current Electricity?
Practice drawing clear circuit diagrams, labelling all components, and writing out the steps for solving using Kirchhoff’s Rules or equivalent resistance formulas. Reviewing example problems helps reinforce these methods and boosts retention.
14. How should students approach the revision of different types of materials based on resistivity in this chapter?
Compare properties of conductors, insulators, and semiconductors by their typical resistivity values, temperature dependence, and applications. Understanding these differences is vital for both MCQ and reasoning questions as per CBSE 2025–26 syllabus.
15. What are the most important tips for quick last-minute revision of Current Electricity before the board exam?
- Review all summaries and boxed formulas
- Go through circuit diagrams and basic laws
- Recall main definitions and units
- Practice one or two representative numericals
- Clarify the key differences between resistivity, resistance, and conductivity