Biology Notes for Chapter 9 Biotechnology Principles And Processes Class 12 - FREE PDF Download
FAQs on CBSE Notes Class 12 Biology Chapter 9 - Biotechnology Principles And Processes - 2025-26
1. How do these revision notes for Biotechnology: Principles and Processes help in preparing for the Class 12 board exams?
These notes provide a quick and focused summary of all key topics from Chapter 9. They are designed to help you revise important concepts, definitions, and processes like recombinant DNA technology without having to read the entire textbook, making your exam preparation more efficient.
2. What are the major topics covered in these Class 12 Biology revision notes?
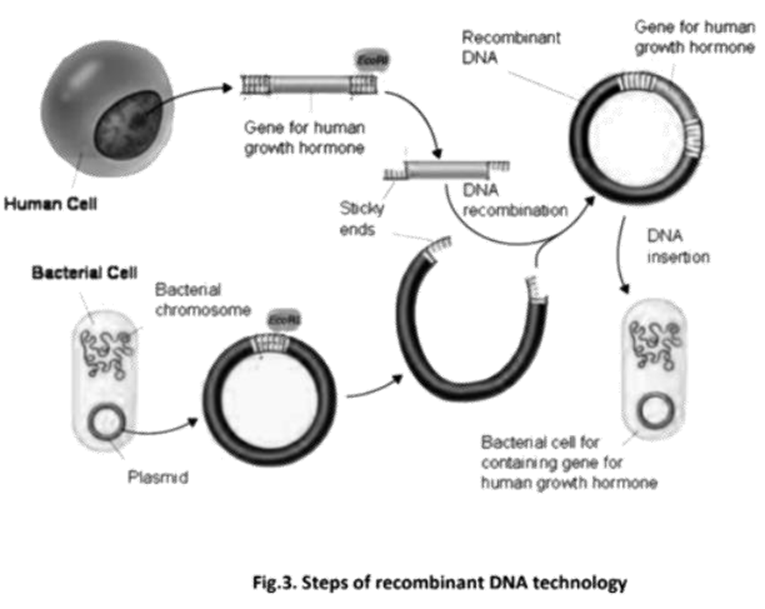
These notes summarise the core principles of biotechnology, including:
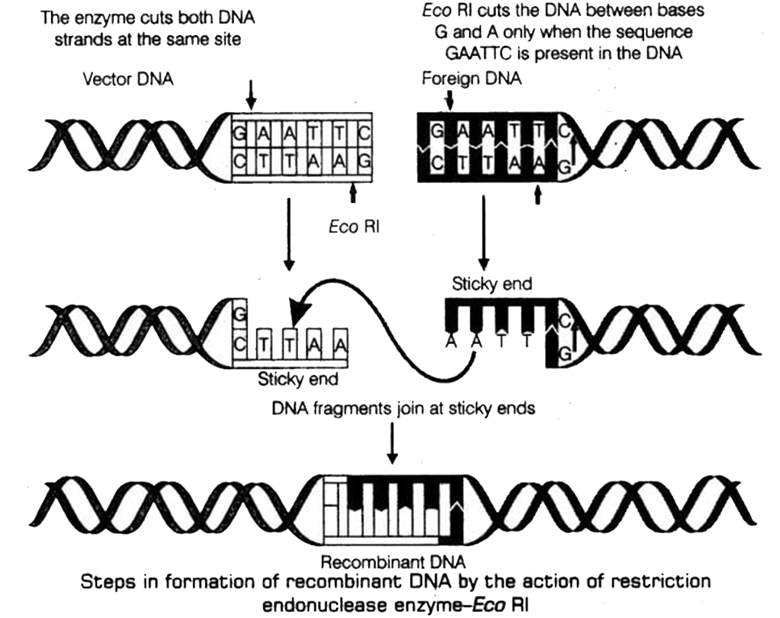
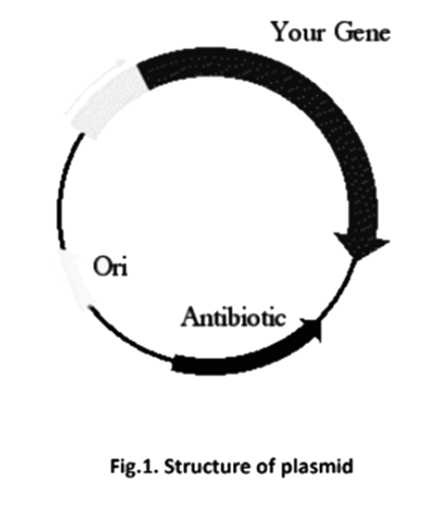
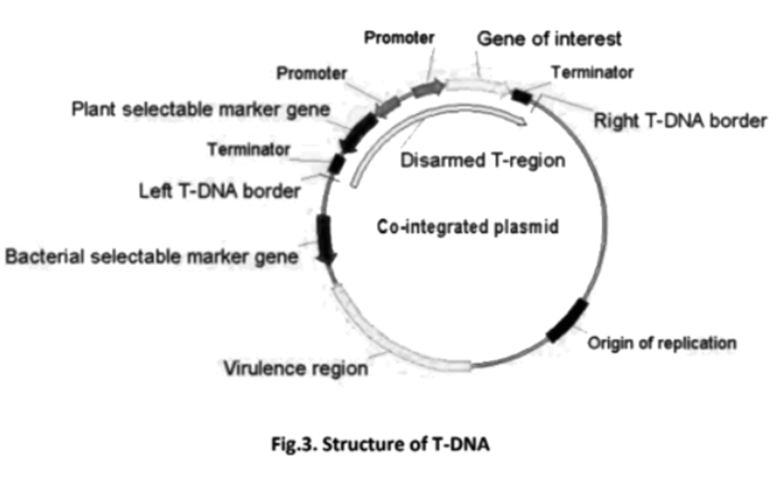
- The tools of Recombinant DNA Technology (like restriction enzymes, ligases, and vectors).
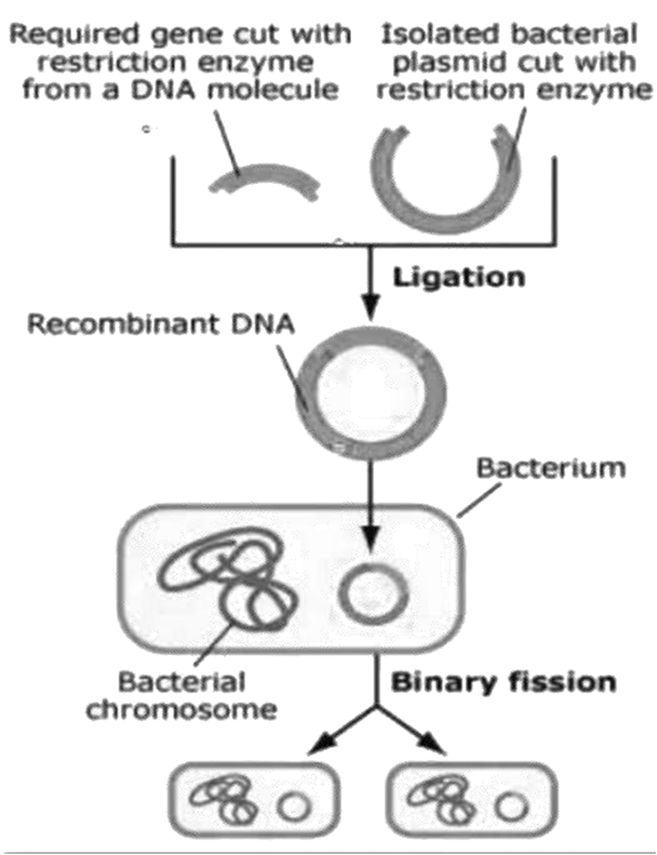
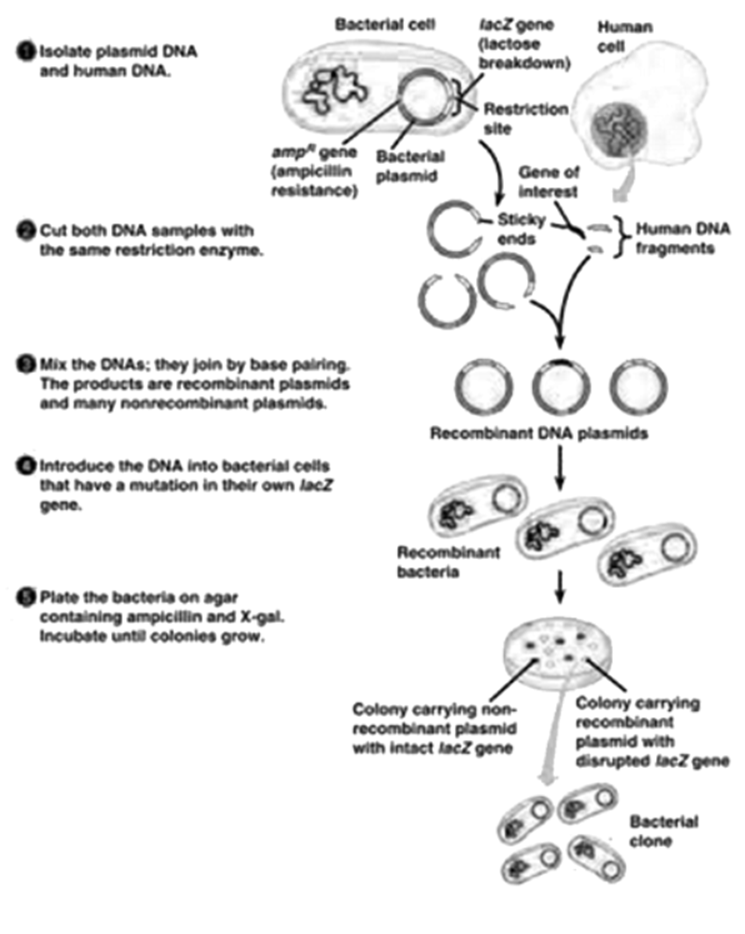
- The process of creating recombinant DNA.
- The steps involved in gene cloning and gene transfer.
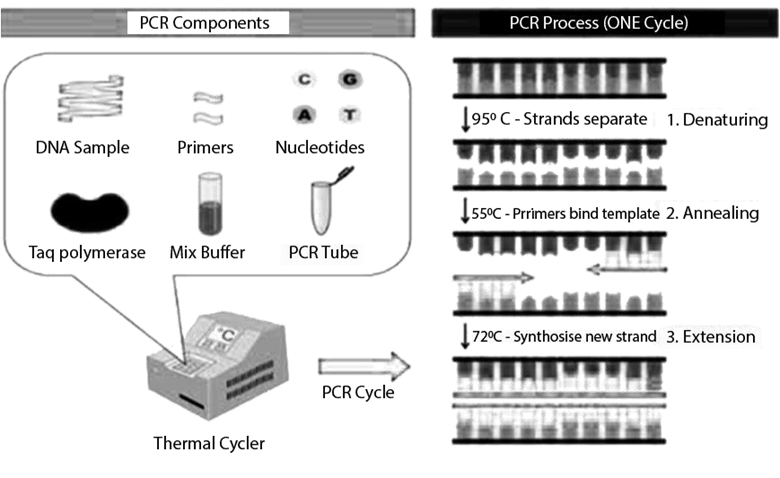
- An overview of key processes like PCR and bioreactors.
3. How can I use these notes to quickly revise the steps of the PCR process?
The notes break down the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) into its three main steps: Denaturation, Annealing, and Extension. They provide a concise summary of what happens at each stage and the temperatures required, which is perfect for a quick recap before an exam.
4. What is the best way to use these notes for last-minute revision?
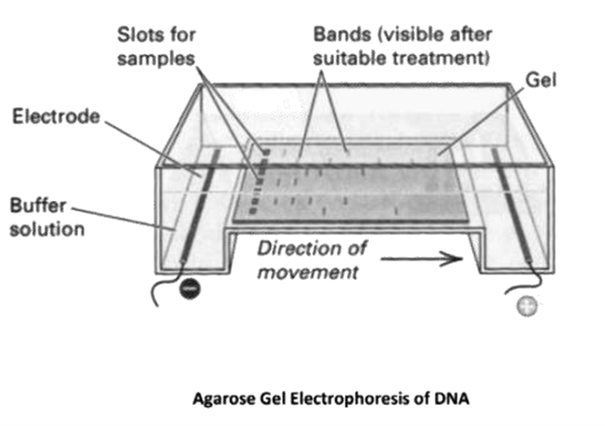
For last-minute revision, focus on the key definitions, flowcharts, and diagrams summarised in the notes. Pay special attention to the tools of rDNA technology and the sequence of steps in the overall process. This helps reinforce the main concepts quickly.
5. While revising, why is it important to understand the role of a 'selectable marker'?
Understanding the 'selectable marker' is crucial because it helps you grasp how scientists identify and select transformed cells from non-transformed ones. These notes clarify that selectable markers, like antibiotic resistance genes, are essential for ensuring that only cells with the desired recombinant DNA are grown.
6. How do these notes help differentiate between the various tools of genetic engineering?
The notes clearly define and explain the specific function of each tool. For example, they distinguish restriction enzymes as 'molecular scissors' that cut DNA and ligases as the 'glue' that joins DNA fragments. This helps avoid confusion during revision.
7. Why is 'downstream processing' mentioned as the final step in these revision notes?
Downstream processing is included as the final stage because it's a critical part of creating a finished product in biotechnology. These notes explain that after the recombinant protein is produced in a bioreactor, it must be separated, purified, and formulated, which are all part of downstream processing. This completes the entire biotechnological process.
8. How do the concepts in these notes, like cloning vectors, lay the foundation for the next chapter on Biotechnology and its Applications?
These notes on principles are fundamental because they explain the 'how' of genetic engineering. By understanding how a cloning vector like a plasmid is used to carry a gene of interest, you can better appreciate how this technique is applied to create things like pest-resistant plants or insulin, which are discussed in the next chapter.