Biology Notes for Chapter 10 Biotechnology And Its Applications Class 12 - FREE PDF Download


FAQs on CBSE Notes Class 12 Biology Chapter 10 - Biotechnology And Its Applications - 2025-26
1. What are the key concepts summarised in the Class 12 Biotechnology and Its Applications revision notes as per the 2025–26 CBSE syllabus?
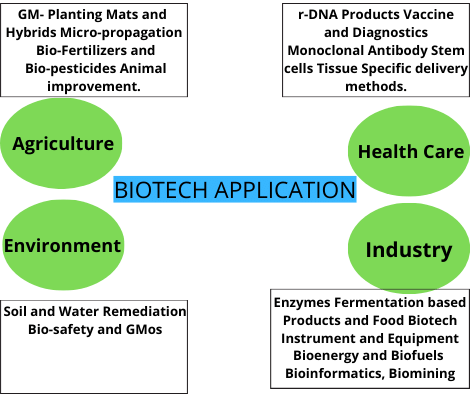
The revision notes focus on biotechnology applications in agriculture (such as genetic engineering, pest-resistant crops, and improved nutritional values), medical advances (including gene therapy, molecular diagnostics, insulin production), production of transgenic organisms, and ethical and legal issues like biopiracy and biopatents. Each concept is linked to aid clear, quick revision for CBSE Class 12 Biology.
2. How can students use revision notes effectively for quick study and last-minute exam revision in Biotechnology and Its Applications?
Students should focus on highlighted key terms, concise definitions, and concept maps provided in the notes. Regular revision of diagrams, flowcharts, and processes like genetic engineering helps consolidate memory, while summarised points enable efficient recall during exams.
3. How do the revision notes connect concepts like genetic engineering, transgenic organisms, and ethical concerns for systematic revision?
The notes are structured to show progression from biotechnology basics to genetic engineering techniques, leading to applications in agriculture and medicine, followed by the creation and use of GMOs and transgenic animals, and concluding with social and ethical issues such as biosafety and the role of regulatory bodies like GEAC. This conceptual flow helps students form a comprehensive understanding.
4. What revision strategies are suggested in the notes to master key terms and concepts for CBSE Biology Class 12?
Revision notes recommend the following strategies:
- Regularly revising key definitions and terms
- Using diagrams and flowcharts for visual memory
- Summarising topics in your own words
- Practising conceptual and application-based questions
- Organising information in tables for comparison
5. Why is it essential to understand molecular diagnostic techniques like ELISA and PCR in the context of this chapter's revision notes?
ELISA and PCR are highlighted as crucial techniques for early and accurate disease detection. Understanding their working principles and applications helps students answer exam questions on modern medical biotechnology and improves conceptual clarity as required by the CBSE syllabus.
6. How do Biotechnology and Its Applications revision notes differentiate between biopiracy and biopatents for exam preparation?
The notes clearly distinguish that biopiracy is the unauthorised use of bio-resources without due permission or compensation, while a biopatent grants legal rights for innovations based on biological materials. Recognising this difference is key for handling legal and ethical questions in CBSE board exams.
7. What is the importance of understanding ethical concerns and regulatory bodies like GEAC, as emphasised in the notes?
Understanding ethical concerns equips students to write balanced answers on the risks and benefits of GMOs. The role of the Genetic Engineering Approval Committee (GEAC) is discussed to show how government oversight ensures biosafety and addresses societal implications of biotechnology.
8. What types of questions should students focus on practising after revising this chapter using the notes?
After revising, students should practise
- Conceptual MCQs
- Short answer questions
- Diagram-based questions
- Application-based case studies
- Reasoning and differentiation questions, especially on processes and ethical issues
9. How do the revision notes aid with understanding and recalling the mechanisms behind pest-resistant crops like Bt cotton?
The notes provide simple explanations and diagrams to clarify how the Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) gene is inserted into cotton plants, making them withstand insect pests. Summarised key facts and mechanisms make it easier to remember for application or reasoning-based questions in the CBSE exam.
10. In what ways do the notes suggest integrating diagrams and definitions for efficient Biology revision?
The notes suggest combining labeled diagrams with clear definitions to strengthen understanding of core processes like gene transfer or recombinant DNA technology. This integration aids visual learning and ensures answers are complete and exam-ready.
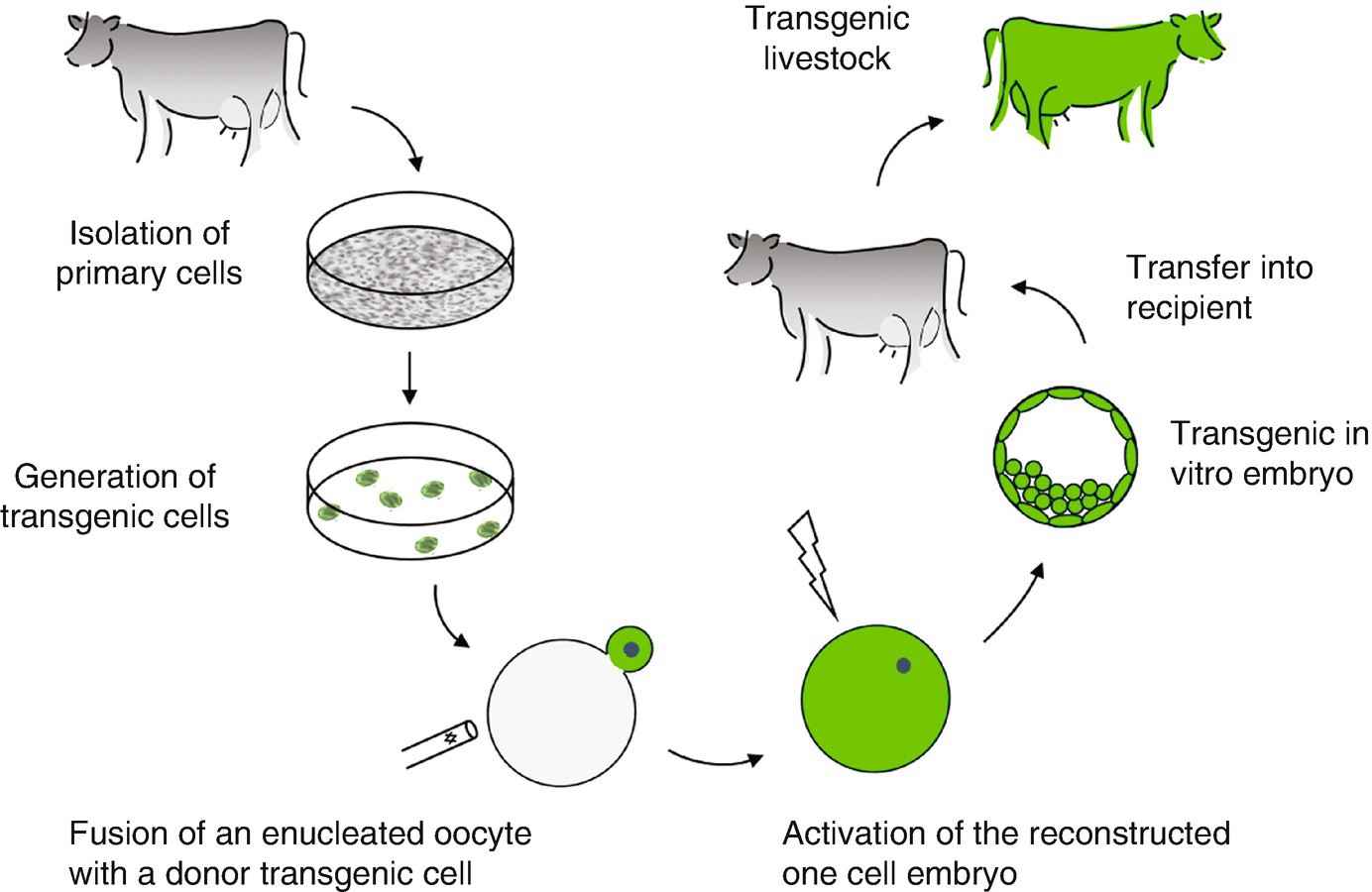
11. What role do transgenic animals play, according to the summary provided in the revision notes?
Transgenic animals are described as essential for research on gene function, the modelling of human diseases, and the production of pharmaceutical proteins (e.g., human insulin or protein-rich milk). Their study is important for application-based and reasoned answers in Class 12 Biology as per the CBSE 2025–26 syllabus.
12. How do concept maps in the notes help students organise and connect different parts of the chapter for effective revision?
Concept maps visually link major ideas like biotechnology basics, techniques, applications, and ethical issues. This structure helps students quickly navigate and systematically revise the chapter, supporting holistic learning for the Biology exam.