Steps and Diagram of Megasporogenesis in Plants
Megasporogenesis is a critical process in plant reproduction that leads to the formation of the female spores (megaspores) within the ovules of flowering plants. Understanding megasporogenesis is essential for mastering topics in plant biology, genetics, and embryology. This page presents a comprehensive explanation, types, step-by-step process, key examples, diagrams, and relevant notes for students and educators alike.
What is Megasporogenesis? (Definition & Overview)
Megasporogenesis definition: Megasporogenesis is the biological process by which a diploid megaspore mother cell (also called megasporocyte) located inside the ovule undergoes meiosis to produce four haploid megaspores. Generally, only one of these becomes the functional megaspore that develops into the embryo sac or female gametophyte.
Steps Involved in Megasporogenesis
- Selection of Megaspore Mother Cell: Within the ovule’s nucellus, a cell differentiates into the diploid megaspore mother cell.
- Meiosis I: The megaspore mother cell undergoes the first meiotic division, producing two haploid cells.
- Meiosis II: Each haploid cell divides again, resulting in a linear tetrad of four haploid megaspores.
- Degeneration: Typically, three megaspores (the micropylar end ones) degenerate, while one (the chalazal end) survives as the functional megaspore.
This single functional megaspore gives rise to the embryo sac through a subsequent process called megagametogenesis. Learn more about cellular division and its variations here.
Types of Megasporogenesis
Megasporogenesis can occur in three main types, based on the timing and pattern of cell division and cytokinesis:
- Monosporic Megasporogenesis: Only one of the four haploid megaspores survives (common in >70% of angiosperms; e.g., Polygonum type in wheat, rice).
- Bisporic Megasporogenesis: Cytokinesis occurs after the first meiotic division, resulting in two megaspores – one continues as the functional cell (e.g., Allium type).
- Tetrasporic Megasporogenesis: All four nuclei remain together (no cytokinesis); they contribute to forming the embryo sac (e.g., Fritillaria/Lilium types).
These types lead to different structural outcomes in the female gametophyte, adding diversity among flowering plant species.
Megasporogenesis Diagram
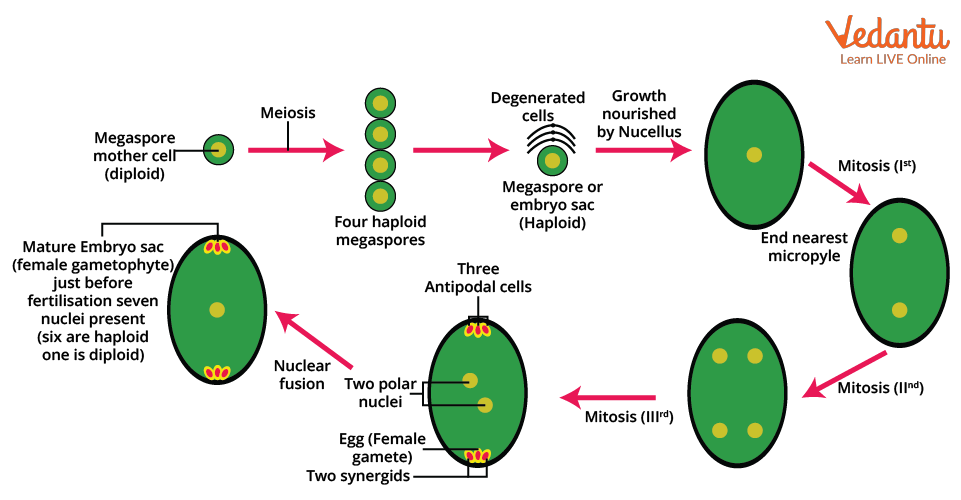
This diagram visually demonstrates the series of changes from the megaspore mother cell through meiosis, resulting in four megaspores, and the selection of the functional megaspore.
Examples of Megasporogenesis in Plants
- Wheat & Rice: Both exhibit typical monosporic megasporogenesis, leading to a Polygonum-type embryo sac.
- Lilium (Lily): Shows tetrasporic megasporogenesis, with all four nuclei participating in embryo sac formation.
- Allium (Onion): A classic example of bisporic megasporogenesis.
These megasporogenesis examples are central to reproductive strategies used in many crop and wild plants. Learn more about reproduction in plants at this Vedantu resource.
Significance and Applications of Megasporogenesis
Megasporogenesis is vital for seed formation and genetic variation in plants. It ensures the transfer of genetic material through female gametes, directly impacting crop yield and plant breeding. Research into megasporogenesis supports advances in agriculture, biotechnology, and food security. The process also relates to environmental studies, such as plant responses to climate change (learn more).
Comparison: Megasporogenesis vs. Microsporogenesis
| Features | Megasporogenesis | Microsporogenesis |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Inside ovules (ovary) | Inside anthers (stamen) |
| Cell Involved | Megaspore mother cell (megasporecyte) | Microspore mother cell (microsporocyte) |
| Product | 4 megaspores (1 functional) | 4 microspores (all functional) |
| Develops Into | Embryo sac (female gametophyte) | Pollen grains (male gametophytes) |
This table highlights the differences between these two essential reproductive processes. For further detail on plant gametogenesis, visit this link.
Short Notes and Key Points on Megasporogenesis
- Megasporogenesis produces female gametes in most flowering plants.
- It begins with a single megaspore mother cell per ovule undergoing two meiotic divisions.
- The process is essential for embryo sac and thus seed development.
- Common types: monosporic (most widespread), bisporic, tetrasporic.
- Understanding this process helps in plant breeding, hybridizing, and crop improvement.
Common Questions on Megasporogenesis (Practice and MCQs)
- At which stage is the functional megaspore selected?
After the tetrad of four megaspores forms, three degenerate; one remains functional. - How does megasporogenesis differ from microsporogenesis?
Megasporogenesis is female (in ovule); microsporogenesis is male (in anther). - Which type is most common among angiosperms?
Monosporic megasporogenesis, often Polygonum type.
Try more questions on related topics at Vedantu’s MCQ resource here.
Download Megasporogenesis Notes and PPT
Comprehensive megasporogenesis notes, explanations, and diagrams are available on Vedantu. These resources provide valuable revision material for class 12 biology, NEET, and other competitive exams. Integration with diagrams and well-structured short notes makes learning easy. You can explore more detailed topic explanations within the Plant Reproductive System section on Vedantu.
Real-World Importance
Understanding megasporogenesis helps agriculture scientists improve crop varieties. It also aids in conservation of genetic diversity and supports sustainable food production. The topic helps in research on stress, fertilization failures, and advances in genetic engineering. Knowledge of plant reproduction underpins breakthroughs in medicine, environmental management, and biotechnology.
Megasporogenesis is a fundamental topic in plant reproduction that connects cell biology, genetics, and ecology. By grasping its stages, types, examples, and significance, students gain deeper insights into how plants reproduce and adapt. This knowledge is vital for success in academics and practical applications across biology, agriculture, and environmental science.


FAQs on What is Megasporogenesis?
1. What is megasporogenesis?
Megasporogenesis is the process of formation of a megaspore from a megaspore mother cell (MMC) inside the ovule of flowering plants.
Key points:
- Occurs inside the nucellus of the ovule
- MMC undergoes meiosis to produce four haploid megaspores
- Only one megaspore typically survives and forms the embryo sac
- Essential for female gametophyte development in plants
2. What are the steps of megasporogenesis?
Megasporogenesis involves the following key steps:
- The megaspore mother cell (MMC) enlarges inside the ovule
- MMC undergoes meiosis I and II to produce four haploid megaspores
- Usually, only one megaspore (usually the chalazal one) survives
- The remaining three megaspores degenerate
3. What is the difference between megasporogenesis and microsporogenesis?
Megasporogenesis forms female megaspores in the ovule, while microsporogenesis forms male microspores in the anther.
Main differences:
- Megasporogenesis occurs in the ovary; microsporogenesis occurs in the anther
- Megasporogenesis produces 1 functional megaspore; microsporogenesis produces 4 functional microspores
- Involved in female vs. male gametophyte development
4. Define the megaspore mother cell. Where is it located?
A megaspore mother cell (MMC) is a large, diploid cell inside the nucellus of the ovule that undergoes meiosis to form megaspores.
- Located deeply within the ovule's nucellus
- Undergoes meiotic division to produce four haploid megaspores
- Key for starting female gametophyte formation
5. What is the fate of megaspores produced during megasporogenesis?
Of the four megaspores formed from the MMC, only one usually survives while the other three degenerate.
Details:
- The surviving megaspore becomes the functional megaspore
- This functional megaspore develops into the embryo sac
6. Explain the role of meiosis in megasporogenesis.
Meiosis in megasporogenesis reduces the chromosome number by half, producing haploid megaspores from a diploid mother cell.
Importance:
- Ensures genetic variation
- Prepares formation of the female gametophyte (embryo sac)
- Maintains the haploid-diploid cycle in plants
7. What is the significance of megasporogenesis in plants?
Megasporogenesis is vital because it gives rise to the female gametophyte that ultimately develops into the egg cell for fertilization.
Main Points:
- Initiates the process leading to seed production
- Crucial for sexual reproduction in flowering plants
- Ensures genetic diversity through recombination
8. What are the types of embryo sac development after megasporogenesis?
After megasporogenesis, there are three main types of embryo sac development:
- Monosporic – only one megaspore (commonly the chalazal one) participates, e.g., Polygonum type
- Bisporic – two nuclei participate in embryo sac formation
- Tetrasporic – all four nuclei take part without wall formation between them
9. What is the difference between monosporic, bisporic, and tetrasporic embryo sacs?
The main difference lies in the number of megaspores that contribute to the embryo sac's formation:
- Monosporic: Only one megaspore forms the embryo sac (e.g., Polygonum type, commonest)
- Bisporic: Two nuclei form the embryo sac (e.g., Allium type)
- Tetrasporic: All four nuclei remain in one cell to form the embryo sac (e.g., Fritillaria type)
10. In which part of the ovule does megasporogenesis take place?
Megasporogenesis takes place in the nucellus of the ovule, usually at the micropylar end.
Key facts:
- The megaspore mother cell is situated in the nucellus
- Ovule is present inside the ovary of a flower
11. Write a short note on the importance of megasporogenesis in plant reproduction.
Megasporogenesis is crucial as it leads to the formation of the egg cell required for fertilization in flowering plants.
- Initiates the embryo sac formation
- Enables sexual reproduction and seed formation
- Ensures genetic continuity and variation in plants
12. What changes occur in the megaspore mother cell during megasporogenesis?
During megasporogenesis, the megaspore mother cell:
- Enlarges and becomes highly active
- Undergoes meiotic division to produce four haploid megaspores
- Only one megaspore survives, while others degenerate










