Stages of Evolution: From Simple to Complex Life Explained
The concept of evolution by stages is essential in biology and helps explain real-world biological processes and exam-level questions effectively.
Understanding Evolution by Stages
Evolution by stages refers to the gradual and stepwise development of living organisms over time, through a series of distinct, intermediate steps. Instead of huge changes happening all at once, evolution happens in small, gradual shifts. This idea is especially important for understanding complex traits and how they develop. Evolution by stages connects concepts such as natural selection, adaptation, and the existence of variation in living organisms.
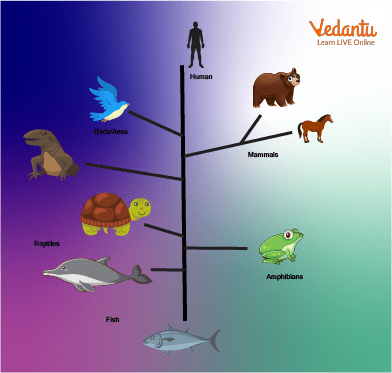
Stages of Evolution Explained
The process of evolution by stages includes a series of key steps that lead to the formation of new features and species. These steps create a logical timeline showing how life forms become more complex:
- Variation – Changes in genetic information occur naturally in populations.
- Natural Selection – Individuals with favorable variations are more likely to survive and reproduce.
- Adaptation – Populations gradually become better suited to their environments.
- Speciation – New species arise as groups become reproductively isolated.
- Extinction – Species unable to adapt may disappear.
Stage-wise Example: Evolution of Man
Studying evolution by stages is especially clear in the case of human evolution. Here are the major stages in the evolution of modern humans:
| Stage | Details | Special Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Dryopithecus | Ape-like ancestors found in forests (herbivores) | Quadrupedal, tree-dwellers |
| Australopithecus | Early hominids, walked upright, used stones | Bipedalism, simple tool use |
| Homo erectus | Used fire, made tools, lived in caves | Large brain, social living |
| Homo sapiens neanderthalensis | Strong, skilled hunters, early art | Ritual burial, advanced tools |
| Homo sapiens sapiens (Modern Man) | Developed language, culture, advanced technology | Art, agriculture, civilizations |
Other Examples of Evolution by Stages
- Evolution of the vertebrate eye: from light-sensitive spots to complex camera eyes.
- Evolution of whales: transition from land-dwelling mammals to fully aquatic animals.
- Development of bird wings: from arms used for climbing to organs of flight.
Quick Revision Table: Main Stages and Their Roles
| Stage | Description | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Variation | Genetic differences within a population | Raw material for evolution |
| Natural Selection | Survival of the fittest traits | Favorable traits passed on |
| Adaptation | Population becomes better suited | Increased fitness |
| Speciation | Formation of new species | Biodiversity increases |
| Extinction | Loss of unsuccessful species | Removal of unfit forms |
Class 10 Board Focus
Evolution by stages is a key topic in class 10 biology. In board exams, students should write in a stepwise flow, include diagrams, and use keywords such as variation, selection, adaptation, and speciation. Draw tables and timelines for quick revision. Use NCERT phrases for higher scores.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Confusing types of evolution (like convergent, divergent) with stages of evolution.
- Skipping intermediate stages while describing evolution in board answers.
- Not using labeled diagrams or clear tables for revision.
Real-World Applications
The concept of evolution by stages is important in medicine (tracing disease origins), agriculture (developing better crops), and environmental science (conservation of species). Vedantu helps connect these real-life examples to classroom learning for better understanding.
In this article, we explored evolution by stages, its key processes, real-life significance, and how to solve questions based on it. To learn more and build confidence, keep practicing with Vedantu.
Explore Related Topics
- Evolution of Life on Earth – Understand early life and timelines.
- Theory of Evolution – Learn Darwin’s principles and natural selection.
- Human Evolution Progress – Stepwise human lineage with diagrams.
- Heredity and Evolution – Role of inheritance in evolutionary changes.
- Significance of Genetics in the Process of Evolution – How genes drive evolutionary steps.
- Speciation – How new species are formed as a stage in evolution.
- Variations – Base for all staged evolutionary changes.
- Origin and Evolution of Man – Human evolution explained simply.
- Genetics and Evolution – Connecting genetics to stepwise changes.
- Adaptive Radiation Evolution – A process involving sequential evolutionary stages.
- Natural Selection – A major stage and mechanism of evolution.


FAQs on Evolution by Stages: Step-by-Step Guide with Diagrams
1. What is evolution by stages?
Evolution by stages is the biological process where organisms develop gradually through a series of distinct phases. Each stage marks a clear change in structure or function, illustrating how complex life forms evolved step-by-step from simpler ancestors over time.
2. How many stages are there in human evolution?
The stages of human evolution are commonly classified into about 5 to 7 major phases, including genera such as Dryopithecus, Australopithecus, Homo erectus, Homo neanderthalensis, and Homo sapiens. Each stage represents significant anatomical and behavioral changes leading up to modern humans.
3. What are the five main stages of evolution?
The five principal stages in evolution by stages generally include: Variation, where genetic differences arise; Natural Selection, favoring beneficial traits; Adaptation, the adjustment to environment; Speciation, emergence of new species; and finally Extinction, where species unable to adapt perish.
4. How is evolution by stages explained in class 10 Biology?
In Class 10 Biology, evolution by stages is taught as a gradual process where organisms undergo sequential changes over generations. The textbook emphasizes the stepwise progression with examples like human evolution, focusing on clear definitions, diagrams, and key milestones aligned with NCERT syllabus requirements for exams.
5. What is the difference between types and stages of evolution?
The types of evolution (such as convergent, divergent, and parallel evolution) describe different evolutionary patterns or mechanisms. In contrast, stages of evolution refer to the sequential phases an organism or species passes through during its evolutionary history, outlining a timeline of change.
6. Can you give examples of evolution by stages?
Examples of evolution by stages include: the development of the human species from apelike ancestors, the formation of the eye from simple light-sensitive cells to complex organs, and the transition of land mammals into aquatic whales through intermediate forms.
7. Why can stages of evolution vary in number across textbooks?
The number of evolutionary stages varies because different textbooks and scientists classify the timeline based on their focus and available fossil evidence. Some prefer broad stages, while others outline more detailed phases, reflecting new discoveries and varying educational scopes.
8. Do all organisms go through the same stages during evolution?
No, different organisms follow unique evolutionary paths depending on their environment and genetic makeup. While fundamental processes like variation and natural selection are universal, the specific stages and traits evolved vary widely across species.
9. Why is “evolution by stages” confused with evolutionary types (like convergent evolution)?
The confusion arises because terms like types of evolution describe methods or patterns of evolutionary change, whereas stages of evolution denote the chronological phases within a lineage. Clarifying context and definitions prevents this mix-up among students.
10. Are terms like “stages of computer evolution” or “stages of Pokémon evolution” related to biology?
No, terms such as stages of computer evolution or Pokémon evolution relate to technology or entertainment contexts and are not biological. In biology, evolution by stages specifically refers to the gradual development of living organisms over time.
11. Why are diagrams important when revising stages of evolution for exams?
Diagrams help students visually understand and memorize the chronological progression and differences at each evolutionary stage. They simplify complex information, aiding in quick revision and higher board exam scores.
12. What are the key evidences supporting evolution by stages?
Key evidences supporting evolution by stages include:
- Fossil records showing gradual morphological changes.
- Transitional forms linking ancestral and derived species.
- Comparative anatomy demonstrating homologous structures.
- Genetic studies revealing stepwise DNA mutations across species.










