Essential Biosphere Terms & Their Real-World Applications
From single-celled organisms to large animals, there are several different types of life on earth. All life forms exist in the zone of life which is called the biosphere. The biosphere is the fourth sphere where land, air, and water interact with each other to support all life forms. The biosphere includes the ground and the air and is characterised as that region of the earth where organisms live.
Eduard Suess was the first person to coin the term biosphere. He added the word Bio (life) with a sphere (shape of the earth) to refer to the areas on earth with all life forms. The biosphere is a narrow zone on the earth's surface where land, water, and air combine to sustain life. Life can only occur in this sphere.
The Biosphere
What is the Biosphere?
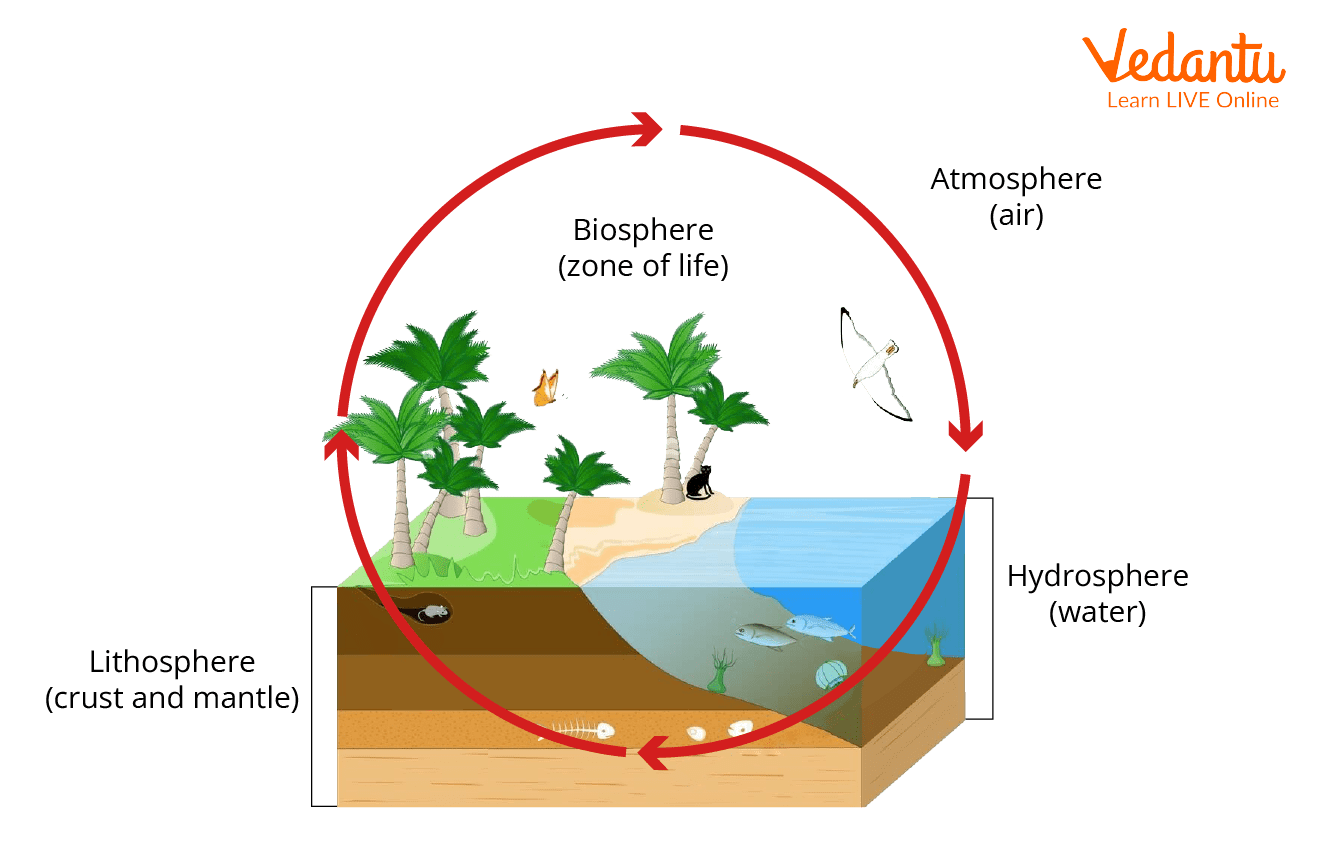
The biosphere is the zone where the lithosphere, the hydrosphere, and the atmosphere interact. The biosphere is defined as an area that contains all living organisms and the products of their activities. As a result, it plays a critical role in the maintenance of ecosystems. It is also known as the ecosphere and is the sum of all ecosystems.
The biosphere can also be termed the zone of life on Earth. The biosphere, atmosphere, geosphere, and hydrosphere are combined into a system to form the Ecosphere. Life forms in every part of the earth's biosphere even in the deepest trench (Mariana Trench). From polar ice caps to the equator, it features some form of life. Our biosphere is divided into several biomes. It is a large area inhabited by a community of plants and animals. For example, forest or tundra.
Components of Biosphere
From the highest mountains to the deepest ocean trenches, from the hottest deserts to the thickest jungles, life exists everywhere. The components of air, soil, water, and rocks are all parts of the biosphere.
The biosphere includes dead organic matter and all living organisms. The lithosphere, atmosphere, and hydrosphere all are included in the biosphere.
Lithosphere - It includes rocks and soil on earth.
Atmosphere - It includes all the gases that surround us. Carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and oxygen are important gases in the atmosphere. It is made up of several different layers.
Hydrosphere - It includes all the water on the earth in all forms. All living organisms need air, water, land, energy, and favourable temperature to survive on earth.
Biosphere Resources
There are different resources in the biosphere, that is Biotic and Abiotic Resources. All forms of life depend on these resources to sustain their life which include food, water, sunlight, land, and shelter. Biotic resources are living whereas abiotics are non-living. For example, plants and animals are biotic resources whereas rocks and sunlight are abiotic resources.
The biosphere is like a thin blanket of the Earth’s surface that supports life, reaching from a few kilometres into the atmosphere to deep-sea trenches. These resources have different impacts on the environment.
Importance of Biosphere
The biosphere is the interconnection between a healthy life and the interactions of living organisms. Even a minor change in the biosphere can cause a large impact on the lives of living organisms.
The biosphere promotes the life of the earth by adapting to various environmental changes, favourable climatic conditions, and a source of energy as food is the main importance of the biosphere.
To sustain life on earth, the biosphere also helps recycle nutrients like oxygen and nitrogen. The biosphere also provides food and raw material to different plants, animals, and human beings.
Features of Biosphere
The biosphere provides the ecosystem that is needed for the survival of organisms. It plays an important role in supporting life on the planet earth. It is a crucial element in climate regulation. Adaptation to the climate of the biosphere is expected for living organisms. The biosphere is the only source of food on Earth.
Safe areas for protecting plant and animal kingdoms are known as biosphere reserves. It also helps to protect and restore the tradition of tribals in the region. They preserve the biodiversity of a region. It covers all types of life as well as biomes.
The biosphere acts as the life support system of the earth, helping in the control of atmospheric composition, soil health, and the water cycle. It is the indicator of the contribution of a biome. The little change in the biosphere can cause a large impact on the lives of living organisms. It also helps in recycling nutrients, provides food and raw material, and promotes life on the earth. Adaptation to the biosphere can uphold life on earth.
Biosphere Examples
The biosphere, which includes the land and the air, is the region where organisms live. It is defined as the area where life exists on, above, and below the Earth’s surface. It is also known as the ecosphere.
It is the natural habitat of all living organisms. It is made up of the lithosphere, a lower portion of the atmosphere, and the hydrosphere.
It also provides resources to the humans through which man has evolved and changed the physical world as per the needs. For example, the soil becomes the basis for agriculture, and the river gives us water. It is important for the existence of living organisms.
The biosphere is the ecological system as a whole. It comprises all forms of life on Earth and all habitats capable of sustaining life. The biosphere also consists of biomes that have different climates, adaptations, vegetation, and wildlife. Photosynthesis is the main source of energy for ecosystem processes.
Conclusion
The biosphere is the narrow zone on the surface of the earth where land, water, and air interact to sustain life. Biotic and abiotic resources are the types of the biosphere. The Biosphere is divided into areas known as Biomes. Conservation by maintaining balance among elements of the biosphere is important. This can be achieved by various means like the concept of Biodiversity Conservation, the establishment of national parks, environmental impact assessment, afforestation, and adoption of SDGs.


FAQs on Biosphere: Explore Earth's Life Zone & Its Importance
1. What is the biosphere, and why is it called the 'zone of life'?
The biosphere is the part of the Earth where life exists. It is called the 'zone of life' because it represents the narrow region where the planet's land (lithosphere), water (hydrosphere), and air (atmosphere) interact and overlap, creating the specific conditions necessary to support all known living organisms, from the deepest oceans to high in the atmosphere.
2. What are the three main components that make up the biosphere?
The biosphere is composed of three primary components, which are essential for sustaining life:
The Lithosphere: This is the solid, outer part of the Earth, including the crust and upper mantle. It provides the soil, minerals, and physical foundation for terrestrial life.
The Hydrosphere: This includes all water on Earth in any form—oceans, seas, lakes, rivers, groundwater, ice caps, and glaciers. It is vital for all metabolic processes.
The Atmosphere: This is the layer of gases surrounding the Earth. It provides essential gases like oxygen for respiration and carbon dioxide for photosynthesis, and it protects life from harmful solar radiation.
3. How do the atmosphere, hydrosphere, and lithosphere interact to support life in the biosphere?
The interaction between the three spheres is crucial for life. The atmosphere provides gases that organisms breathe and protects them from the sun. The hydrosphere provides water, which is essential for all living cells and is a key part of climate regulation through the water cycle. The lithosphere provides nutrients from weathered rocks and a substrate for plants to anchor themselves. These components work together in cycles, like the carbon cycle and water cycle, to continuously circulate the elements necessary for life throughout the biosphere.
4. What is the difference between the biosphere and an ecosystem?
The key difference between the biosphere and an ecosystem is scale. The biosphere is the single, all-encompassing global system that includes every living thing and their environments on Earth. In contrast, an ecosystem is a much smaller, specific community of organisms interacting with their local physical environment. For example, a single forest, a coral reef, or a pond is an ecosystem. The biosphere is the sum of all ecosystems on the planet.
5. Why is the biosphere so important for the survival of living organisms?
The biosphere is fundamentally important as it provides all the necessary resources and conditions for life to exist and thrive. Its importance includes:
Providing essential elements like oxygen, carbon, and nitrogen through natural cycles.
Supplying food and water to all living organisms.
Regulating the Earth's climate and weather patterns.
Offering a habitat and physical space for countless species.
6. How does energy flow through the biosphere?
Energy flows through the biosphere in a one-way direction, primarily starting from the sun. Plants and other producers (autotrophs) capture this solar energy through photosynthesis and convert it into chemical energy. This energy is then transferred through the food chain as primary consumers (herbivores) eat the plants, and secondary or tertiary consumers (carnivores/omnivores) eat other animals. At each level, a significant amount of energy is lost as heat, which is why energy must be constantly supplied by the sun.
7. How do human activities impact the delicate balance of the biosphere?
Human activities can significantly disrupt the biosphere's balance. Key impacts include deforestation, which reduces biodiversity and affects the carbon cycle; the burning of fossil fuels, which increases greenhouse gases and leads to global warming; and pollution of the air, water, and soil, which harms organisms and their habitats. These actions can alter climates, lead to species extinction, and degrade the natural systems that support human life.
8. What is a Biosphere Reserve and why is it important for conservation?
A Biosphere Reserve is a protected area, part of a global network under UNESCO's Man and the Biosphere (MAB) Programme. It is important because its goal is not just to protect wildlife and plants but also to reconcile the conservation of biodiversity with its sustainable use. These reserves serve as living laboratories for testing and demonstrating integrated management of land, water, and biodiversity, promoting a balanced relationship between humans and nature.










