Economics Class 12 Chapter 1 Questions and Answers - Free PDF Download
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Economics Chapter 1 Introduction To Micro Economics - 2025-26
1. What are the three central problems of an economy, as explained in the NCERT Class 12 Microeconomics textbook?
According to the NCERT solutions for the 2025-26 syllabus, every economy faces three central problems due to the scarcity of resources. The correct method to answer this involves detailing each problem:
- What to produce and in what quantities? This problem involves choosing which goods and services to produce (e.g., consumer goods vs. capital goods) and deciding the quantity of each, as resources are limited.
- How to produce? This refers to the choice of production technique. An economy must decide whether to use labour-intensive techniques (more labour, less capital) or capital-intensive techniques (more capital, less labour), depending on resource availability.
- For whom to produce? This problem concerns the distribution of the final goods and services among the population. It addresses how the national product is shared among different households and factors of production (land, labour, capital, entrepreneur).
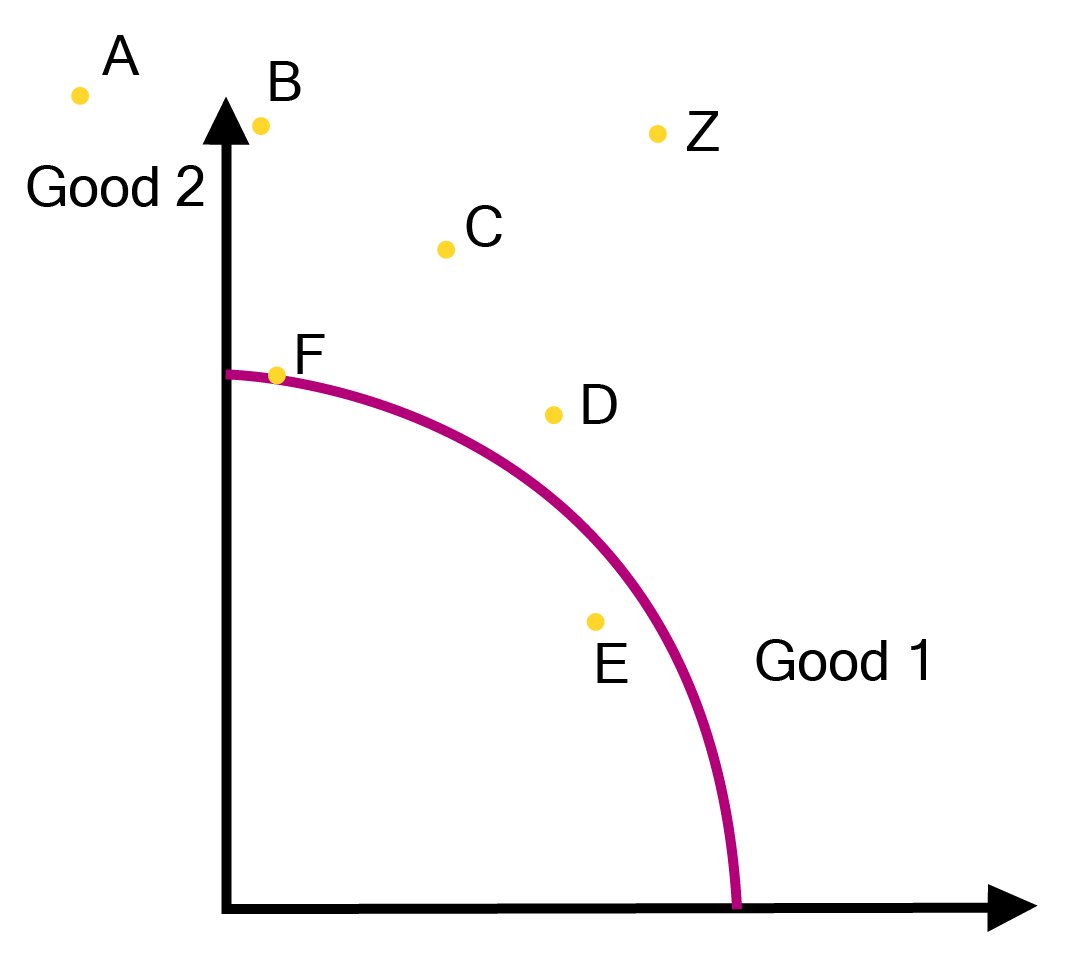
2. How should a student explain the Production Possibility Frontier (PPF) with a diagram for board exams?
To correctly explain the Production Possibility Frontier (PPF), or Production Possibility Curve (PPC), you should follow these steps:
First, define the PPF as a graphical representation showing all possible combinations of two goods that can be produced with available resources and technology, assuming full and efficient utilisation. It is also called a Transformation Curve.
Next, draw a diagram with two axes (Good X and Good Y). The curve should be downward sloping and concave to the origin.
Finally, explain the key points on the diagram:
- Points on the curve: Represent efficient and full utilisation of resources.
- Points inside the curve: Indicate underutilisation or inefficient use of resources.
- Points outside the curve: Are unattainable with the current level of resources and technology.
The downward slope signifies that to produce more of one good, some units of the other good must be sacrificed.
3. What is the correct method to distinguish between a Centrally Planned Economy and a Market Economy?
As per the NCERT solutions, the correct method to distinguish between these two economic systems is by comparing their core features in a structured manner:
- Ownership of Resources: In a centrally planned economy, resources are collectively owned by the government. In a market economy, resources are predominantly owned by private individuals.
- Economic Decisions: Decisions regarding production, consumption, and investment are made by a central authority or the government in a planned economy. In a market economy, these decisions are driven by the forces of supply and demand.
- Motive: The primary motive in a planned economy is social welfare. In a market economy, the main motive is profit maximisation.
- Role of Government: The government plays a comprehensive role in all economic activities in a planned economy. In a market economy, the government's role is generally limited to maintaining law and order.
4. Why is a Production Possibility Curve (PPC) typically concave to the origin?
A Production Possibility Curve (PPC) is concave to the origin because of the increasing marginal opportunity cost (MOC) or Marginal Rate of Transformation (MRT). This means that to produce one additional unit of a good, an increasing amount of the other good has to be sacrificed. This happens because resources are not equally efficient in the production of all goods. When resources are transferred from the production of one good to another, their productivity decreases, leading to a higher rate of sacrifice.
5. How does the concept of 'opportunity cost' relate to the central problem of 'what to produce'?
The concept of opportunity cost is fundamental to solving the central problem of 'what to produce'. Opportunity cost is the value of the next-best alternative that is given up when making a choice. Since resources are scarce and have alternative uses, an economy cannot produce everything it wants. When it decides to produce more of one good (e.g., wheat), it must divert resources from the production of another good (e.g., cloth). The amount of cloth that is sacrificed is the opportunity cost of producing more wheat. Therefore, the decision of 'what to produce' is always made by evaluating the opportunity cost involved.
6. What do 'Positive' and 'Normative' economic analyses mean, and how are they approached differently?
The NCERT solution distinguishes between Positive and Normative economic analyses based on their approach to economic issues:
- Positive Economic Analysis: This focuses on 'what is'. It deals with factual statements and cause-and-effect relationships that can be tested and verified with data. For example, stating "An increase in the price of a good leads to a decrease in its quantity demanded" is a positive statement. The approach is objective and descriptive.
- Normative Economic Analysis: This focuses on 'what ought to be'. It involves value judgements, opinions, and deals with how economic problems should be solved. For example, stating "The government should increase the minimum wage to reduce poverty" is a normative statement. The approach is subjective and prescriptive, and its conclusions cannot be empirically tested.
7. According to NCERT, what is the fundamental difference between Microeconomics and Macroeconomics?
The fundamental difference lies in the scope of study:
- Microeconomics is the study of economic behaviour at the level of individual units, such as a single consumer, a household, a firm, or a specific market. It deals with how prices of individual commodities and factors of production are determined. It is also known as Price Theory.
- Macroeconomics is the study of the economy as a whole. It deals with aggregate variables like national income, aggregate demand, aggregate supply, unemployment, and inflation. It is also known as the Theory of Income and Employment.
Essentially, microeconomics looks at the individual trees, while macroeconomics looks at the entire forest.
8. What key topics are covered in the NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Microeconomics, Chapter 1: Introduction to Microeconomics?
The NCERT solutions for this introductory chapter focus on the foundational concepts of economics. The key topics you need to solve and understand are:
- The meaning of an economy and why economic problems arise (scarcity, choice).
- The three central problems of an economy: what, how, and for whom to produce.
- The concepts of Opportunity Cost and the Production Possibility Frontier (PPF).
- The distinction between Microeconomics and Macroeconomics.
- The difference between Positive and Normative Economics.
- An introduction to different types of economies, mainly Centrally Planned, Market, and Mixed Economies.