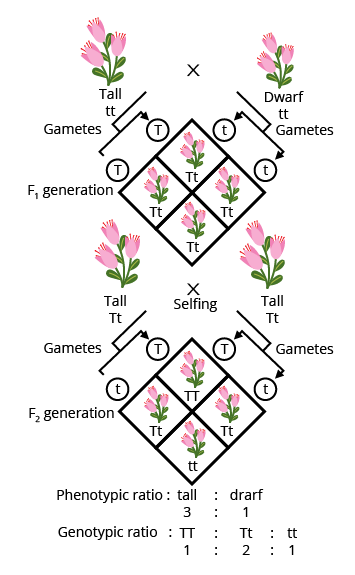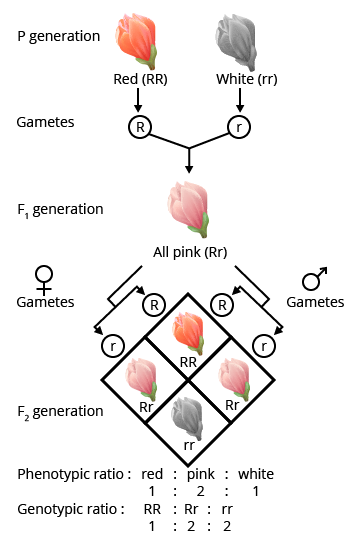Principles of Inheritance and Variation Class 12 important questions with answers PDF download


FAQs on Important Questions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 4 Principles of Inheritance and Variation - 2025-26
1. What are the most expected 3-mark questions for Principles of Inheritance and Variation in the CBSE Class 12 Biology exam?
Exam-focused 3-mark questions often include applications of Mendel’s laws, distinguishing between types of mutations, explaining test crosses with examples, and analyzing simple pedigree charts or inheritance patterns. Practice detailed explanations with examples as per CBSE 2025–26 marking scheme.
2. How does understanding important questions in Chapter 4 help improve exam performance in CBSE Class 12 Biology?
Focusing on important questions enables students to target frequently tested concepts, master high-weightage topics, and develop model answers matching the board’s expectations. This strategic preparation can result in higher accuracy and confidence during the exam.
3. What are the key differences between Mendelian and chromosomal disorders that can be asked as a board question?
- Mendelian disorders result from single gene mutations (e.g., sickle cell anaemia), follow predictable inheritance, and often appear in pedigree analysis questions.
- Chromosomal disorders arise from numerically or structurally abnormal chromosomes (e.g., Down syndrome), resulting in more complex or varied phenotypic effects. Board questions may require comparison with examples.
4. Which board trend questions are commonly repeated from Principles of Inheritance and Variation, and how should they be answered for maximum marks?
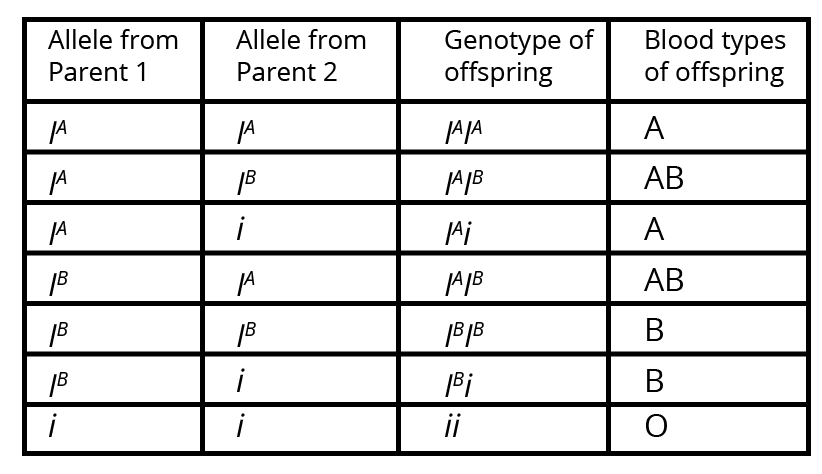
Questions on sex determination mechanisms, codominance vs incomplete dominance (with plant or blood group examples), and distinguishing Klinefelter’s and Turner’s syndromes have high recurrence. For maximum marks, write clear stepwise diagrams (if applicable), concise definitions, and 2–3 precise points per example as required by the marks allotted.
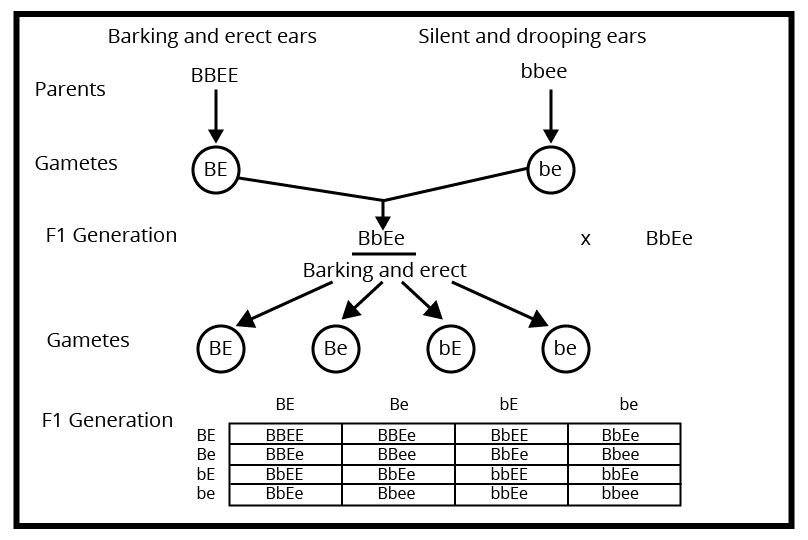
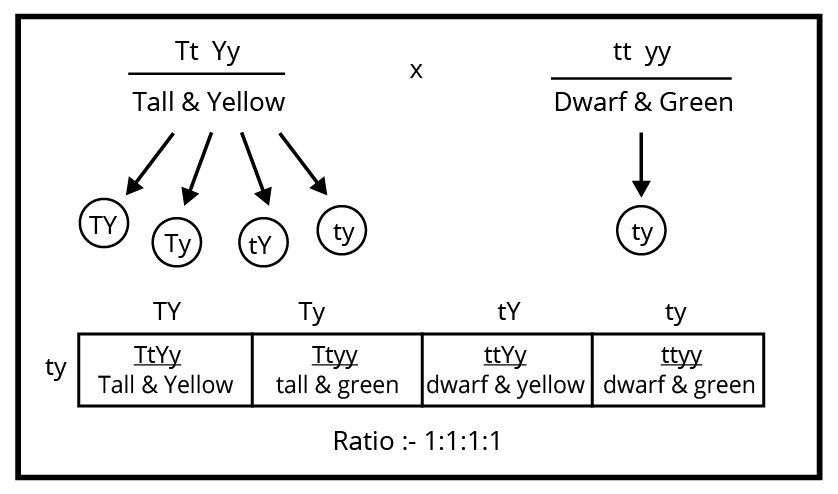
5. What is the exam strategy for attempting high-weightage questions on dihybrid crosses or genetic linkage?
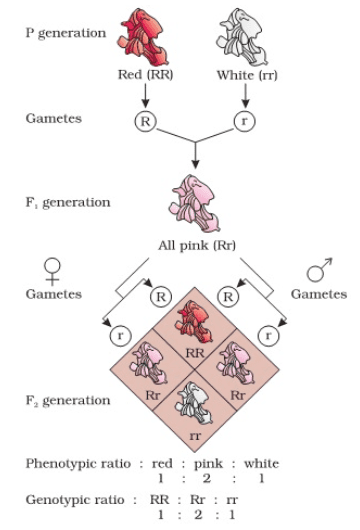
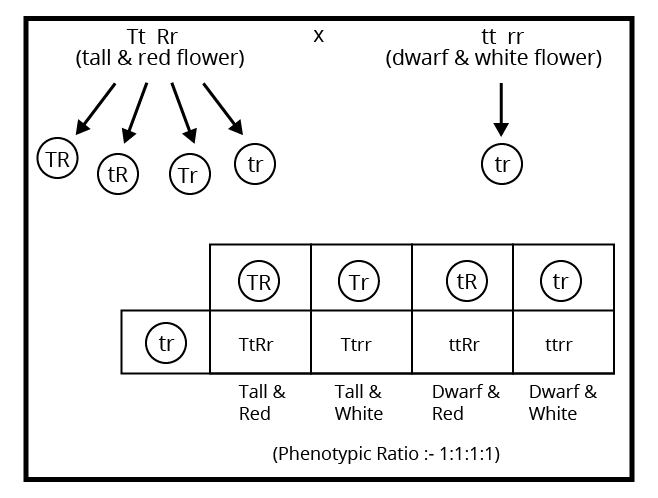
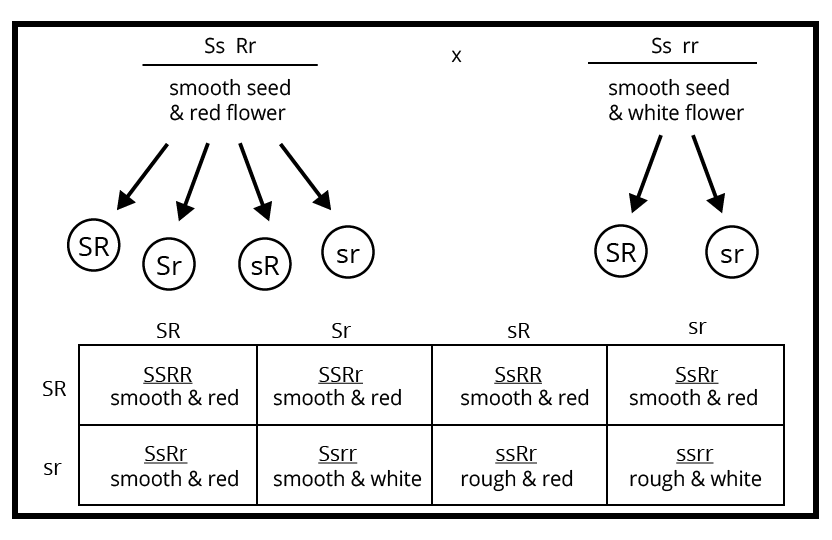
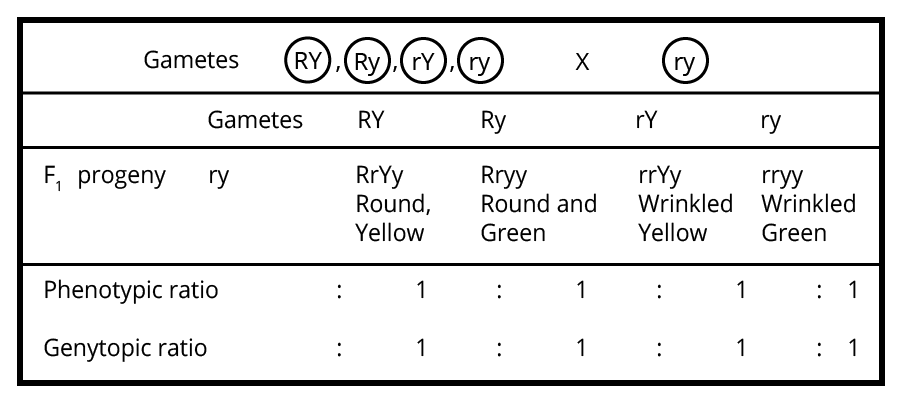
Start with a neat cross diagram, label all parental and F1, F2 generations, clearly state phenotypic and genotypic ratios, and briefly mention the principle illustrated (e.g., independent assortment). Highlight linkage effects or recombination if the question asks. Review marking guidelines to allocate time as per question value.
6. Why is it essential to practice both short and long answer important questions from this chapter before the board exam?
Short answer questions reinforce fundamental facts and definitions, while long answer questions develop concept application and reasoning skills. A balanced approach ensures readiness for all question types and maximizes scoring opportunities in line with the CBSE blueprint.
7. What are key conceptual traps students should avoid while answering inheritance and variation questions in the CBSE exam?
- Confusing codominance with incomplete dominance
- Incorrectly reporting phenotypic and genotypic ratios
- Forgetting to mention exceptions in sex-linked inheritance (e.g., criss-cross pattern)
- Misidentifying chromosomal constitutions in syndromes
8. How does the CBSE exam typically allocate marks for questions based on Punnett squares, pedigree analysis, or genetic disorders in Chapter 4?
Punnett square and cross-based problems are commonly 2–3 marks, requiring stepwise solution and interpretations. Pedigree analysis can range from 3 to 5 marks depending on analysis depth. Genetic disorder differentiation and explanation are usually asked for 3 marks, focusing on causes, symptoms, and inheritance pattern. Refer to latest CBSE sample papers for specific distribution.
9. Why do important questions on human genetic disorders such as haemophilia or sickle cell anaemia carry conceptual weightage in board papers?
These disorders test the ability to apply inheritance principles to real-life scenarios, analyze pedigree, recognize types of mutations (point or frameshift), and recall medical relevance. Answering well demonstrates both factual knowledge and applied understanding, meeting key board evaluation criteria.
10. What should students focus on when revising high-order thinking important questions for Principles of Inheritance and Variation?
Target questions that require comparison (e.g., between disorders or inheritance patterns), critical reasoning (why certain crosses yield specific ratios), and analytical application (solving unfamiliar pedigree or gene mapping problems). Practice writing structured, logically sequenced answers with key terms highlighted to align with CBSE evaluation rubrics.