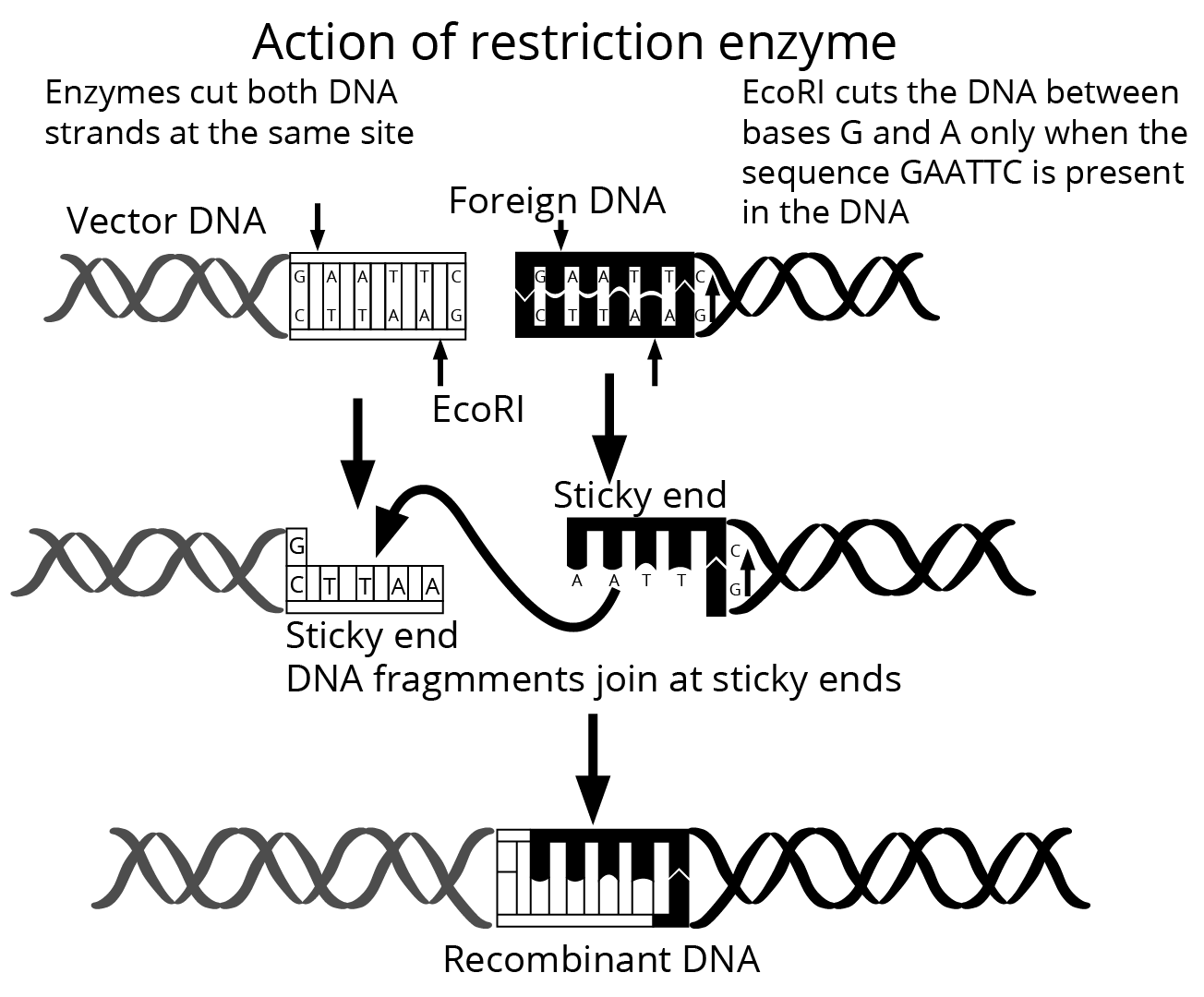Biotechnology: Principles and Processes Class 12 important questions with answers PDF download
FAQs on Important Questions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 9 Biotechnology: Principles and Processes - 2025-26
1. What are the key principles of biotechnology discussed in Class 12 Chapter 9 Important Questions for CBSE 2025–26?
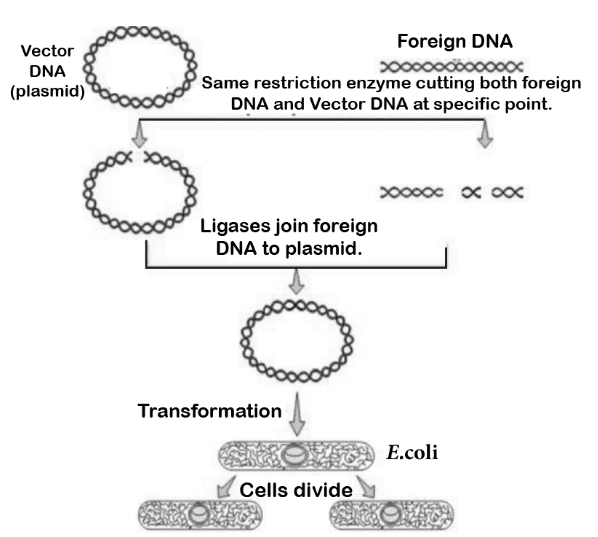
- Genetic engineering — manipulating genetic material using techniques such as recombinant DNA technology.
- Use of enzymes — including restriction enzymes (molecular scissors) and ligases for cutting and joining DNA.
- Vectors and cloning — employing plasmids, bacteriophages, and Ti plasmids for transferring genes.
- Screening and selection — identifying transformants with selectable markers and using downstream processing to purify products.
2. According to CBSE Class 12 Biology, what are three important properties of an ideal cloning vector in biotechnology?
- Origin of replication (Ori): Ensures independent replication within the host.
- Selectable marker: Such as antibiotic resistance or lacZ gene, enables identification of transformed cells.
- Unique recognition/cloning site: Allows insertion of foreign DNA at a specific location.
3. Differentiate between plasmid DNA and chromosomal DNA as per important questions for Class 12 Biotechnology: Principles and Processes.
- Plasmid DNA: Small, circular, extra-chromosomal DNA, present in bacteria, used as a vector in genetic engineering.
- Chromosomal DNA: Large, linear (in eukaryotes), contains essential genes, found in the nucleus or nucleoid.
4. Explain the role of Agrobacterium tumefaciens in plant genetic engineering based on CBSE 2025–26 Important Questions.
Agrobacterium tumefaciens uses its Ti (tumor-inducing) plasmid to naturally transfer T-DNA into plant genomes, making it an effective vector for introducing desired genes in dicot plants ("natural genetic engineer").
5. What are the main steps of polymerase chain reaction (PCR), and why is the Taq polymerase enzyme critical?
- Denaturation: Separates DNA strands by heating.
- Annealing: Primers bind to target DNA at a lower temperature.
- Extension: Taq polymerase synthesizes new DNA strands at high temperature. Taq polymerase (from Thermus aquaticus) is heat-stable and allows for repeated cycles without enzyme degradation.
6. Why are restriction enzymes known as molecular scissors, and what is their significance in biotechnology practical questions?
Restriction enzymes cut DNA at specific sites, producing defined fragments. This enables precise insertion or removal of genes, which is fundamental for recombinant DNA technology.
7. High-Order Thinking: How does insertional inactivation help identify recombinant bacteria as per CBSE important questions for Class 12?
Insertional inactivation disables a marker gene (e.g., lacZ). Only bacteria with disrupted (inactivated) marker genes (those that received the insert) do not show marker activity (such as blue-white screening), allowing easy identification of true recombinants.
8. What are two basic techniques in modern biotechnology highlighted in Class 12 important questions?
- Genetic Engineering: Modifies genetic material for desired traits.
- Bioprocess Engineering: Involves maintaining sterile conditions to cultivate and multiply genetically engineered cells or organisms for mass production of products.
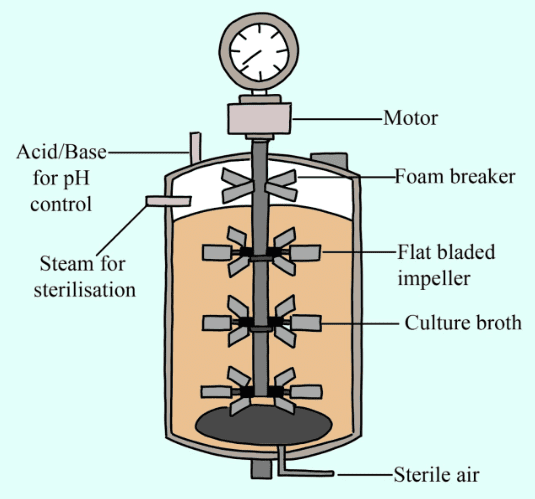
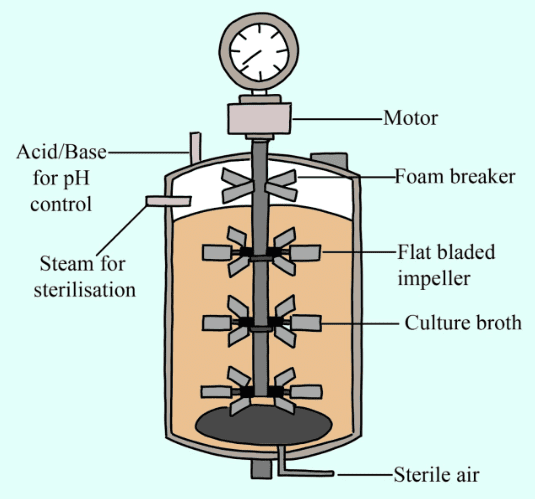
9. Application-Based: Why is a bioreactor preferred over a shake flask for large-scale production, as per Class 12 Biotechnology Important Questions?
- Bioreactors offer precise control over growth conditions (temperature, pH, oxygen, substrate concentration),
- Allow for aseptic sampling and agitation,
- Enable higher yield and quality of product compared to unregulated shake flasks.
10. What are three common vector-less methods for delivering recombinant DNA to host cells in CBSE Class 12 exams?
- Microinjection: Direct injection of DNA into the nucleus of animal cells.
- Gene gun (biolistics): High-speed bombardment of DNA-coated particles into plant cells.
- Transformation: Uptake of naked DNA by competent bacterial cells, often enhanced by calcium ions and heat shock.
11. CBSE Conceptual: How do exonucleases and endonucleases differ, and what is the significance of this distinction in biotechnology as per recent exam trends?
- Exonucleases: Remove nucleotides from DNA ends.
- Endonucleases: Cut within the DNA molecule at specific sequences (e.g., restriction enzymes).
- This specificity allows endonucleases to precisely excise or insert genes, a key operation in genetic engineering.
12. FUQ: What key feature allows sticky ends from a restriction enzyme digest to facilitate recombinant DNA formation?
Sticky ends have complementary single-stranded overhangs that hydrogen bond with foreign DNA cut with the same enzyme, making ligation (joining) efficient and specific during cloning.
13. What is the significance of selectable markers in genetic engineering, and give an example relevant to CBSE Class 12 board questions?
Selectable markers (e.g., antibiotic resistance genes like ampicillin resistance) help identify cells that have taken up the vector, enabling the selection of successful transformants for further study or production.
14. HOTS: In gel electrophoresis, why does DNA migrate towards the anode, and what is the practical implication for biotechnology labs?
DNA is negatively charged due to its phosphate backbone, so it migrates toward the positive anode when a current is applied. This property is utilized to separate DNA fragments by size for further analysis or purification.
15. High-Order: Discuss bioconversion and its importance in sustainable biotechnology based on CBSE Important Questions.
Bioconversion refers to transforming raw materials into useful products using biological agents (microbes, plant, or animal cells). It is crucial for developing sustainable biofuels, pharmaceuticals, and bioplastics, reducing reliance on chemical processes.