Key Advantages and Disadvantages of Aeroponics in Biology
Aeroponics simply means, "growing in the air". In an aeroponic system, there is no medium since the plant's roots are suspended freely in an open root-zone environment. The growth chamber of an aeroponics system receives the ideal amounts of water, nutrients and air. The practice of growing plants in the absence of soil, in the presence of air or a mist, is known as aeroponics.
What is Aeroponics?
Aeroponic comes from the Latin words "aero" (air) and "ponic" (labour) (work). This is an alternate technique for soil-free cultivation in conditions that regulate development.
Aeroponics is the practice of growing plants in an atmosphere of mist or air without the need for soil or by spraying the roots with hydroponic solutions that are floating in the atmosphere. It doesn't make use of soil or aggregate media. A nutrient-dense fluid is sprayed on the plant roots at predetermined intervals while the plant roots are suspended in a dark container in an aeroponic system. With this technique, nutrients are delivered extremely precisely, and since roots receive enough oxygen, growth may occur more quickly. This system may have clogging problems since relatively small holes are used for spraying.
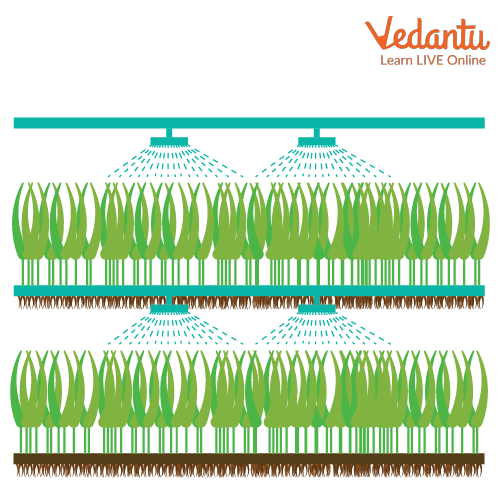

Aeroponics’ Diagram
Aeroponic Farming
Aeroponics is a method of growing plants that do not require soil. Roots are suspended in the air and irrigated with a nutrient-dense mist instead. This is in contrast to hydroponic systems, in which plant roots are submerged in a nutrient-rich solution on a regular basis. The plant you want to grow is suspended in an atmosphere that is typically fully or partially closed in an aeroponics system. In order to manage the amount of light, air and nutrient-rich water spray delivered to the plant, it is best to carry out this procedure in a closed, controlled environment.
Since they receive more oxygen to carry out their food-producing activity and are less vulnerable to pests and diseases, plants typically flourish in misty and airy environments. By spraying the plant's lower stem and dangling roots with a nutrient-rich water solution that helps them absorb the nutrients they need to generate nutrient-rich food to be consumed later, the necessary nutrients are delivered.
The plant's lower stem area is covered with biodegradable foams, which is then connected to or inserted into the aeroponics chamber apertures. The nutrient-rich liquid is dispersed in aeroponics chambers, where the time of the spraying is automated. For this system to work well, it is crucial to maintain a proper temperature and make sure that the necessary amount of nutrient-rich mist is available.
Aeroponics System
In this aeroponics system, there are primarily two live components:
Roots: The architecture of the plant that supports it neatly divides the roots underneath.
Canopy: The canopy refers to the leaves and crown that are frequently higher than the plant's structural supports.
In order to meet this requirement, aeroponics relies on hydroponics. This is because there is a requirement to have a backup system for supplying the necessary nutrients for the plants in the event that the aeroponics system fails. A high-pressure (80 psi) diaphragm pump is used in high-pressure aeroponics to supply nutrients to the roots through 20-50 mm mist heads.
Advantages of Aeroponics
Productive and Sustainable: Compared to soil-based farming, this sustainable method of food production uses 80-90% less water. If you aim to go fully commercial in this field, you can grow more food, healthier types and also more profitably because you can use height and air as a growing place.
Air Exposure Promotes Healthy and Rapid Plant Growth: As aeroponics is used to grow plants in the air with tiny drops of water, it is ideally suited to promote rapid plant growth in virtually any species. As a result, compared to soil-based farming, more plants can be grown in less time.
It Can Be Cultivated without Land: If you have a place in your tiny garden or on the roof, you may use it right now to grow your food, which fully eliminates the need for you to have a huge amount of land under cultivation. To experience the beauty of aeroponics and to meet your daily food needs, you can even build small aeroponics units in your living room or balcony.
Photosynthesis is Promoted via Aeroponics: This feature makes it environmentally friendly too. By removing a considerable amount of carbon dioxide from the environment and managing its concentration inside the system, aeroponics has an impact on how rapidly plants produce oxygen in their leaves.
Disadvantages of Aeroponics
Along with the associated costs, proper expertise and training are necessary to get going. If one is going to start using aeroponics, they need to be thoroughly trained in how to keep the system clean. The caretaker of this system must always upgrade their abilities because it is a scientific system supported by technology that is still developing.
It entails difficulties in sustaining the tangible elements. Numerous components make up this system, some of which, if improperly maintained, could cause a system failure.
Maintaining the proper supply of light and supply of air for the exposed part of the plant, in the closed or indoor methodology of aeroponics farming can occasionally be challenging, especially when vertical farming in the air is the way to produce more. This is where artificial lighting becomes important.
Aeroponic Plants
Any type of plant may now be grown with aeroponics. However, this method is best suited for green leaves, herbs, marijuana, strawberries, tomatoes and cucumbers.
Although root and tuber crops are less common in this system, you can still cultivate them if you have access to the most advanced infrastructure. However, doing so can be expensive.
Aeroponic Vertical Farming
It is a farming technique that involves growing crops in layers that are piled vertically. It is carried out in a controlled environment utilising soilless growing methods such as aquaponics, hydroponics and aeroponics. Vertical farming may be used to meet the expanding food demands of the world because there is a growing population and not enough usable farmland to go around.
Hydroponic Farming Methods: Techniques
Without the use of soil, plants can be grown using hydroponics. Here, magnesium, nitrogen, potassium, calcium etc. are submerged in the roots of the plants. These remedies assist roots, increasing the likelihood of a bigger production and decreasing reliance on water. According to studies, the production was 11 times higher than on conventional farms, while using 13 times less water. Therefore, the most popular vertical farming technique is hydroponics.
Aquaponics
Aquaponics is a little more sophisticated technology than hydroponics that combines the production of plants with that of aquatic organisms in a closed-loop system that mimics nature.
Aeroponics and Hydroponics
Although the concepts of aeroponics and hydroponics are similar, the two systems' mechanics are very dissimilar. Both systems are equally efficient and sustainable. Both systems demand different types and quantities of resources.
Hydroponic systems need water. Their water usage is naturally higher than that of aeroponic systems. A hydroponic system's water usage, however, might be recycled and utilised again. System maintenance is the second crucial component. Both hydroponic and aeroponic systems require hands-on training and experience for installation, upkeep, cleaning and sanitising. However, a hydroponic system is simpler than an aeroponic one.
Contrary to hydroponic systems, which can be created at home using PVC pipes and easily accessible basic supplies, aeroponic systems are more challenging to build. A good system is necessary for it to function fully and successfully. For precisely this reason, aeroponics is less economically viable.
The rapidly expanding hydroponics agricultural sector in India tremendously benefits urban farming. Many Indian cities use aeroponics. The properties of hydroponic and aeroponic systems are compared in light of this.
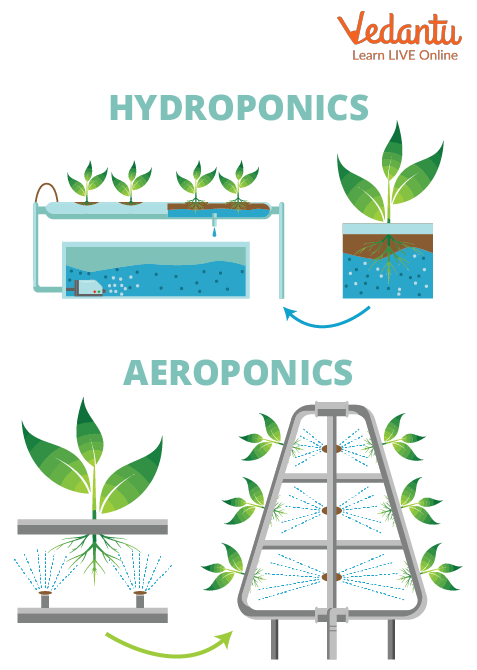
Hydroponics and Aeroponics Concept
Aeroponic Tower
Agronomy is Europe's first vertical garden that employs aeroponic towers to grow food naturally, while conserving 95 per cent of the water used in normal organic farming. These aeroponic towers also produce vegetables, fruits and herbs with 35 to 60 per cent more nutrients than soil-grown competitors.

Aeroponic Tower
Conclusion
An optional tool for soil-less cultivation in climate-controlled settings like greenhouses is the aeroponic culture technique. The root system is enclosed in a dim space using this technique, which also includes the use of a nutritional solution misting system.


FAQs on Aeroponics: Structure, Function & Benefits
1. What is aeroponics?
Aeroponics is an advanced method of soilless agriculture where plants are grown with their roots suspended in the air within a closed or semi-closed environment. The name originates from the Greek words 'aer' (air) and 'ponos' (labour). Instead of soil or water, a fine, nutrient-rich mist is periodically sprayed directly onto the roots, providing the necessary moisture and minerals for growth.
2. How does an aeroponic system function?
An aeroponic system functions by housing plants in a framework that holds them in place while their roots hang freely in a dark, enclosed chamber. A high-pressure pump connected to a reservoir of nutrient solution delivers this solution to mist nozzles. At regular, timed intervals, the nozzles spray a fine, atomised mist over the roots, ensuring they receive water and nutrients. The high level of oxygen exposure in the air-filled chamber significantly boosts plant growth and health.
3. What are the main components that make up an aeroponic structure?
A typical aeroponic structure consists of several key components working together:
Reservoir: A tank that holds the water and nutrient solution.
Pump: A high-pressure pump to move the nutrient solution from the reservoir to the misting nozzles.
Timer: A device that controls the pump, regulating the frequency and duration of the misting cycles.
Mist Nozzles: Sprayers that atomise the nutrient solution into a fine mist for the roots to absorb.
Root Chamber: An enclosed, light-proof container where the plant roots are suspended.
Plant Support Structure: A platform, often with small pots or collars, that holds the plants securely above the root chamber.
4. What are the key benefits of aeroponics compared to traditional farming?
Aeroponics offers several significant benefits over traditional soil-based agriculture:
Water Conservation: It uses up to 95% less water as the nutrient solution is recirculated.
Faster Growth Rate: Enhanced oxygen availability to the roots can lead to up to three times faster growth.
Higher Yields: The optimised environment often results in greater crop yields in a smaller space.
Reduced Land Usage: Systems can be stacked vertically, making it ideal for urban farming.
Disease Control: The absence of soil eliminates soil-borne diseases and reduces the need for pesticides.
5. Which types of plants are best suited for growing with aeroponics?
Aeroponics is versatile and can support a wide variety of plants. It is especially effective for leafy greens like lettuce, spinach, and kale; herbs such as basil, mint, and cilantro; and vining plants like tomatoes, cucumbers, and strawberries. Even some root vegetables, including potatoes and radishes, have been successfully grown using this method, as the unhindered root growth is highly beneficial.
6. How does aeroponics fundamentally differ from hydroponics?
The primary difference between aeroponics and hydroponics lies in how water, nutrients, and oxygen are delivered to the roots. In hydroponics, plant roots are submerged in or frequently flooded with a nutrient-rich water solution. In aeroponics, the roots are suspended in the air and receive nutrients from a fine mist. This key difference gives aeroponics an advantage in providing superior root oxygenation, which often leads to faster plant growth.
7. Why is the absence of a growing medium a major advantage in aeroponics?
The absence of a growing medium like soil or coir is a significant advantage because it provides the plant roots with unparalleled access to oxygen. This direct exposure to air accelerates respiration and metabolic rates, leading to faster nutrient absorption and more rapid growth. Furthermore, it eliminates the risk of soil-borne pathogens and pests, reduces the physical labour of handling substrates, and allows for cleaner and more controlled harvesting.
8. What environmental conditions must be precisely controlled in an aeroponic chamber for optimal results?
For optimal results, an aeroponic chamber requires precise control over several environmental factors. These include the nutrient concentration (EC) and pH of the water solution, the temperature and humidity within the root chamber, the duration and frequency of misting cycles, and the amount of light the plant receives. This level of control allows growers to create the perfect environment tailored to a specific plant's needs, which is a major reason for its high efficiency.










