How Single Cell Protein Transforms Nutrition and Food Security
With the constant rise in the global population, the need for protein-rich food has become more urgent. Single cell protein (SCP) offers a novel solution by using microbial biomass to supplement or replace conventional protein sources. If you are wondering what a single-cell protein is, it simply refers to the protein content extracted from the cells of microorganisms such as bacteria, yeast, algae, or fungi. These microorganisms can be cultivated using low-cost materials, including agricultural waste, thereby providing a sustainable approach to address protein deficiency.
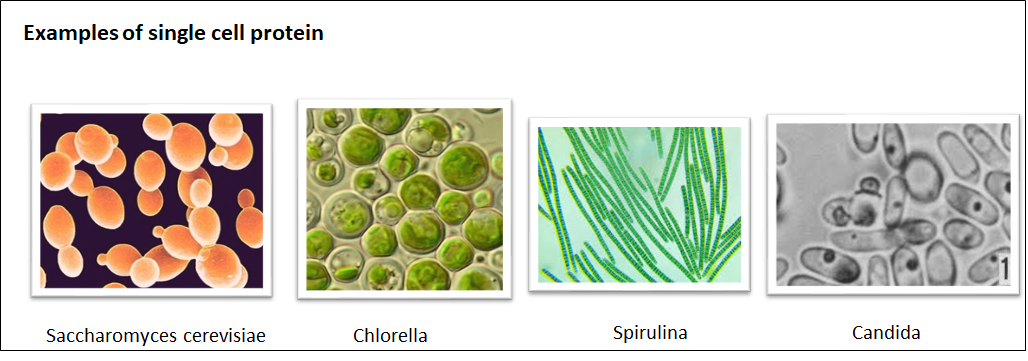
Sources of Single-Cell Protein
A single-cell protein example can come from any single celled microorganism or the collective biomass of these microbes. Commonly used microorganisms include:
Fungi: Aspergillus niger, Aspergillus fumigatus, Rhizopus cyclopean
Yeast: Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Candida utilis, Candida tropicalis
Algae: Spirulina, Chlorella pyrenoidosa, Chondrus crispus
Bacteria: Pseudomonas fluorescens, Lactobacillus species, Bacillus megaterium
Each type has its growth requirements and nutritional advantages, making them important contributors to single-cell protein.
Also Read:
Composition of Single Cell Protein
The composition of single cell protein can vary with the type of microorganism used. On a dry-weight basis, the approximate ranges are:
These values show that microorganisms can be rich sources of protein, often surpassing many traditional protein foods.
Single Cell Protein Production
Single cell protein production generally follows these steps:
Selection of Microorganism: A suitable strain is chosen based on its growth rate, protein yield, substrate compatibility, and nutritional profile.
Preparation of Substrate: Microbes utilise inexpensive or waste materials as substrates. These can include agricultural by-products (e.g., corn cobs, wood shavings) or even animal and human waste in certain specialised systems.
Fermentation: Microorganisms are grown in a controlled environment with optimal nutrients, pH, temperature, and oxygen supply. Most SCP processes are aerobic (except certain algal fermentation).
Harvesting: Once sufficient microbial growth has occurred, the biomass is separated from the medium (often by centrifugation or filtration).
Post-harvest Treatment: The harvested biomass is treated to remove any impurities and reduce nucleic acid levels.
Processing for Consumption: The final product can be dried or refined to make it safe and palatable as a protein supplement.
Advantages of Single Cell Protein
The advantages of single cell protein are quite significant, especially in addressing protein shortages:
Rapid Growth: Microorganisms multiply fast, yielding large amounts of biomass in less time compared to conventional livestock.
Nutritional Enhancement: Genetic modification can tailor amino acid composition to meet specific dietary needs.
Waste Utilisation: Production can use low-cost, abundant substrates, helping reduce pollution and manage waste effectively.
Climate Independence: SCP can be produced year-round without reliance on specific weather or soil conditions.
Disadvantages of Single Cell Protein
When discussing the advantages and disadvantages of single-cell protein, certain limitations must be considered:
High Nucleic Acid Content: Excess nucleic acids may lead to health issues, such as elevated uric acid levels and potential kidney stones if consumed in large quantities.
Allergic Reactions: Some individuals may develop allergies if their digestive system recognises the microbial proteins as foreign.
Possible Toxic Metabolites: Improperly processed biomass might contain secondary metabolites, causing hypersensitivity or other adverse effects.
Capital-Intensive Production: Setting up and maintaining fermentation facilities with strict sterile conditions can be costly.
Applications of Single Cell Protein
Despite these challenges, single cell protein has a wide range of applications:
Food Supplement: SCP can be added to diets for instant energy and to combat malnutrition. It is especially helpful for undernourished children.
Nutritional Benefits: It provides essential amino acids, vitamins, minerals, and crude fibres.
Therapeutic Uses:
Helps control obesity
Regulates blood sugar in diabetic patients
Reduces cholesterol and stress levels
Cosmetic Products: Microbial proteins are used in certain herbal creams, lotions, and hair care products.
Animal and Poultry Feed: SCP serves as an excellent protein source to improve the diet of livestock, poultry, and fish.
Quick Quiz
Test your understanding of single cell protein with these questions:
1. Which microorganisms are commonly used for single cell protein production?
A. Fungi
B. Bacteria
C. Yeast
D. All of the above
2. What is one of the main advantages of using single cell protein?
A. Slow production rate
B. Low protein content
C. Ability to use waste materials as substrates
D. None of the above
3. Why does high nucleic acid content in SCP pose a problem?
A. May cause elevated uric acid
B. Improves digestion
C. Reduces energy levels
D. Enhances taste
Answers:
D
C
A
Related Topics


FAQs on Single Cell Protein: Meaning, Production, and Key Advantages
1. What is Single Cell Protein (SCP) as defined in the context of biology?
Single Cell Protein (SCP) refers to the dried cells of microorganisms, such as algae, fungi, yeast, and bacteria, that are grown in large quantities for use as a protein-rich supplement for humans and animals. These microorganisms have a very high protein content in their biomass, making them a valuable alternative protein source.
2. What are the main steps involved in the large-scale production of Single Cell Protein?
The commercial production of SCP involves a series of controlled steps. It begins with the selection of a suitable microbial strain and a low-cost substrate (like agricultural waste). The microbe is then grown in a large container called a fermenter or bioreactor under optimal conditions of temperature, pH, and oxygen. After sufficient growth, the microbial biomass is harvested, separated from the medium, washed, dried, and processed to create the final SCP product.
3. What are some common examples of microorganisms used for SCP production?
Several types of microorganisms are used for SCP production due to their high protein content and rapid growth. Key examples include:
- Algae: Spirulina and Chlorella are widely used, especially in health supplements.
- Fungi: Yeast, such as Saccharomyces cerevisiae (baker's yeast), and filamentous fungi are common.
- Bacteria: Species like Methylophilus methylotrophus can produce large amounts of biomass very quickly.
4. What are the key advantages of using SCP over traditional protein sources?
SCP offers several important advantages:
- Rapid Production: Microorganisms grow much faster than plants or animals, allowing for a high yield in a short time.
- Reduced Land Use: SCP production requires significantly less land and water compared to conventional agriculture.
- Waste Utilisation: It can be grown on a variety of low-cost substrates, including industrial and agricultural waste, which helps in reducing pollution.
- Climate Independence: Production can be carried out year-round, as it is independent of seasonal or climatic variations.
5. Why is the high nucleic acid content in SCP a health concern, and how is this problem managed?
The high nucleic acid (DNA and RNA) content in microbial biomass is a concern because its breakdown in the human body produces uric acid. Elevated levels of uric acid can lead to health issues like gout and kidney stones. To make SCP safe for consumption, the nucleic acid content is reduced through post-harvest processing techniques, such as enzymatic treatment (using ribonucleases) or heat shock, which break down the nucleic acids without significantly damaging the protein.
6. How does the nutritional profile of SCP compare to that of conventional proteins like soy or meat?
SCP is nutritionally comparable and often superior in certain aspects. It has a very high protein content (typically 40-80% of its dry weight), which is higher than most conventional sources like soy (around 40%) or meat (around 20-30%). It is also a good source of vitamins (especially B-complex), minerals, and essential amino acids. However, the specific amino acid profile can vary, and it is sometimes deficient in sulphur-containing amino acids like methionine, which can be addressed through supplementation.
7. Beyond human food supplements, what are the other significant applications of Single Cell Protein?
While SCP is well-known as a human nutritional supplement, its applications extend to several other industries. A major use is in animal feed, particularly for aquaculture (fish farming), poultry, and pigs, where it serves as a protein-rich ingredient. It is also used in the cosmetics industry for skincare products and as a source for extracting valuable biochemicals like enzymes and vitamins for various industrial processes.
8. Can SCP completely replace traditional agricultural proteins in the global food supply? Explain the practical challenges.
While SCP has immense potential, it is unlikely to completely replace traditional proteins in the near future due to several practical challenges. These include:
- Consumer Acceptance: There can be a cultural or psychological barrier to consuming food derived from microbes.
- Digestive Issues: Some people may experience allergic reactions or digestive problems.
- Processing Costs: The technology required for large-scale fermentation and purification, especially nucleic acid reduction, can be expensive.
- Flavour and Texture: The taste and mouthfeel of SCP often need to be improved to match conventional foods.










