Persimmon Fruit Morphology and Economic Importance Explained
Welcome, young botanists and curious minds! Are you ready to explore a magical fruit tree that looks almost like something straight out of a fairy tale? Today, we’ll discover the secret world of the persimmon plant—how it grows, why it’s special, and how to tell it apart from other famous fruit trees. Let’s become plant detectives together, with Vedantu as your friendly guide!
Say Hello to the Persimmon Tree – Nature’s Orange Gem
What Is a Persimmon Plant?
The persimmon plant is a deciduous (leaf-shedding) tree with the scientific name Diospyros. It belongs to the Ebenaceae family, just like the ebony tree. Persimmon trees are well-known for their bright orange berries, which are not only pretty to look at but also delicious to eat when ripe. The most popular types are Diospyros kaki (Asian persimmon) and Diospyros virginiana (American persimmon).
Persimmons love mild to cool areas and are found in places like China, Japan, Korea, the USA, and even the hilly regions of India (like Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand). They can grow as small trees or become big enough to shade your whole garden!
Persimmon’s Family and Home
- Scientific Name: Diospyros spp.
- Family: Ebenaceae
- Grows In: Asia, North America, Mediterranean, Indian hills
- Tree Type: Deciduous (sheds leaves yearly)
Peek Inside: The Special Parts of Persimmon
Leaves, Flowers, and Fruit – Let’s Look Closely!
Just like every person is unique, so is each part of the persimmon plant! Here’s what you might notice if you meet this plant on your next nature walk:
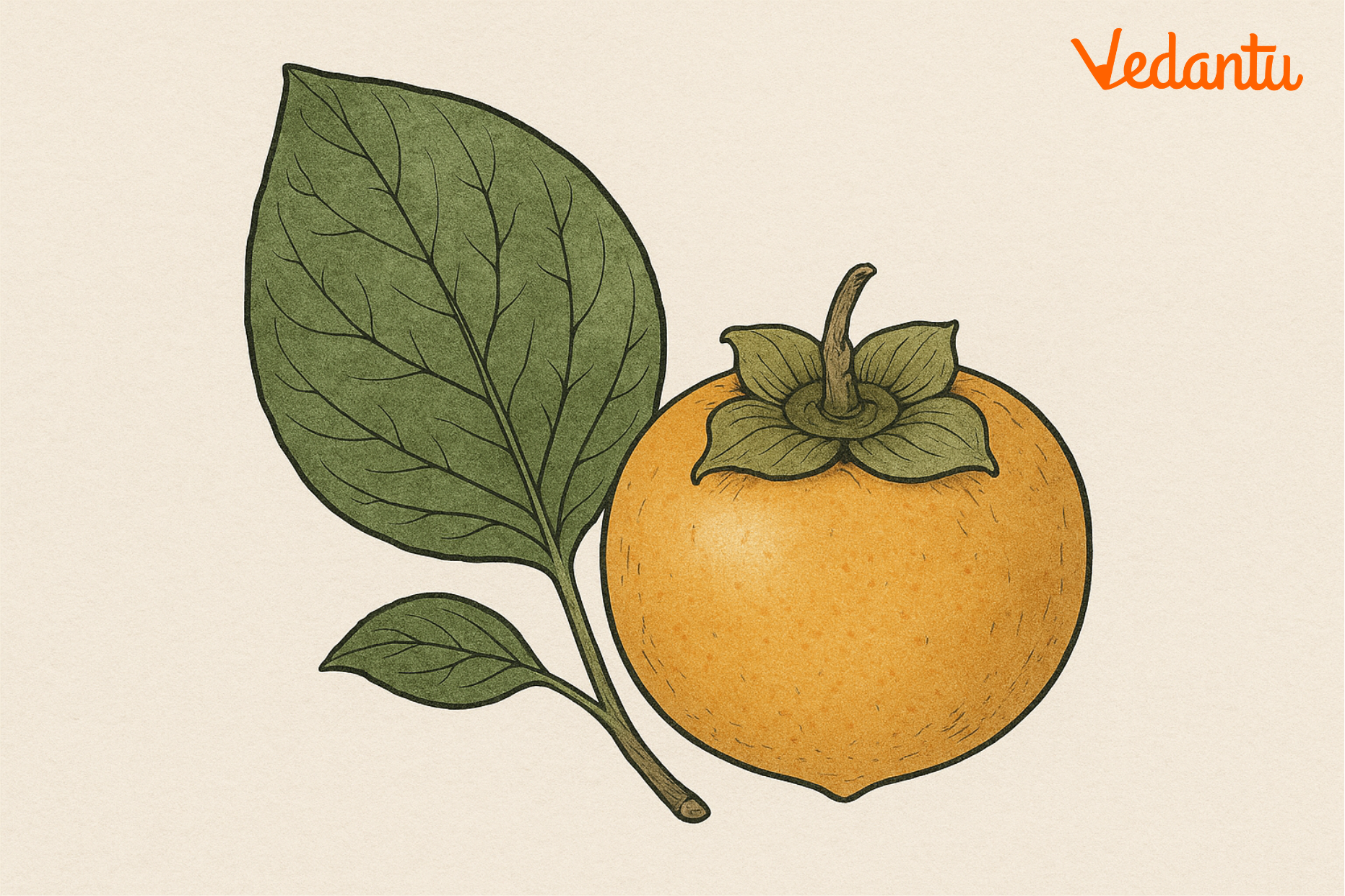
Leaves
- Simple (not divided), and arranged in an alternate pattern on branches
- Shiny dark green, oval-shaped, and a little leathery to touch
Flowers
- Small, creamy-white or yellow, shaped like tiny bells
- Boys and girls are on different trees! (That’s right—persimmons are usually dioecious.)
Fruit
- A real berry (botanically!), bright orange or red when ripe
- Edible and sweet, but only after it gets soft—otherwise, it can taste quite astringent
- Each fruit holds a handful of flat seeds inside
| Organ | Key Features |
|---|---|
| Leaf | Simple, alternate, smooth edge, shiny |
| Flower | Small, bell-shaped, separate male/female |
| Fruit | Berry, orange/red, 2–8 seeds, edible |
How Does a Persimmon Tree Grow Up?
Life Story: From Seed to Sweet Fruit
Persimmon trees begin life as little seeds or grafted plants. They need good soil, sunlight, and just enough water. It usually takes about three to five years before a persimmon tree gives its first yummy fruit!
- Persimmons use photosynthesis to make their own food, like other green plants
- They rely on wind or insects to help with pollination
- Seeds drop to the ground or get carried away and may sprout into new saplings
In colder places, the tree loses its leaves in autumn, showing off its orange fruits against bare branches – it looks like a natural ornament tree!
Super Survival Tricks
- Sturdy leaves save water during summer
- Fruit is astringent when unripe, keeping hungry animals away until seeds can be spread properly
Persimmons in Our Lives – More Than Just a Fruit!
Why People Grow and Love Persimmons
- Snack: Ripe fruit is sweet like candy and enjoyed as fresh slices, jams, or desserts.
- Medicine: Old remedies use persimmon for cough, blood pressure, digestion, and even to boost immunity (they are rich in vitamin C and A!).
- Wood: Some persimmon trees give strong wood used for sports equipment and fancy furniture.
- Gardens: Pretty fruits and colorful leaves make them a favorite in parks and home gardens.
Fun Around the World
- In Japan and China, persimmons are a traditional autumn treat
- In India, farmers grow them mainly in the Himalayan hills
- Birds and monkeys also love persimmon snacks!
| Use | Example |
|---|---|
| Food | Fresh/ dried fruit, puddings, jams |
| Traditional Medicine | Cough drops, digestion aid |
| Wood/ Timbers | Sports gear, ornaments |
Persimmon vs Mango vs Jackfruit – Spot the Differences!
It’s easy to mix up fruit trees! Here’s a handy comparison to keep things clear:
| Feature | Persimmon | Mango | Jackfruit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Leaf Arrangement | Simple, alternate | Simple, alternate | Simple, opposite |
| Fruit Type | Berry (true) | Drupe | Multiple fruit (syncarp) |
| Seeds Per Fruit | Multiple | One | Many |
Quick Facts Table – Persimmon at a Glance!
| Feature | What It Means | Fun to Know |
|---|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Diospyros kaki, D. virginiana | Also called ‘kaki’ or ‘American persimmon’ |
| Fruit Type | Berry | Looks like an orange tomato! |
| Tasty Part | The ripened fruit | Eaten fresh or in sweets |
| Where Grown | Asia, US, India hills | Loves mild hills and valleys |
| Harvest Time | Late autumn | Leaves fall, orange fruit shines |
Practice Like a Pro – Example Q&A
Q: Which family does persimmon belong to and what type of fruit does it produce?
Answer: The persimmon plant is from the Ebenaceae family and makes a true berry fruit with many seeds inside.
Try These Fun Questions!
- Why should you only eat ripe persimmons and not green ones?
- How can you tell a persimmon leaf from a mango leaf?
- What color are persimmon fruits when they are ready to eat?
Mistakes Kids Often Make – Let's Clear Them Up!
- Mix-up #1: Thinking all orange fruits are mangoes! (Check the fruit type and leaf shape!)
- Mix-up #2: Forgetting that Asian and American persimmons are different species but both called "persimmon"
- Mix-up #3: Confusing unripe fruit (which is very astringent!) with ripe, soft, and sweet ones
Bright Endings – What Makes Persimmon Special?
The persimmon plant brightens up forests, farms, and gardens around the world. Its sweet orange fruit is not only a treat for people but also important for wildlife. By learning to spot its special leaves, flowers, and berries, you’re one step closer to being a plant pro!
If you want to know more about fruit types and plant families, explore more fun topics like different fruit types or plant kingdoms on Vedantu, your learning buddy!
Keep exploring, keep asking questions, and remember—every great scientist started out just as curious as you!


FAQs on Persimmon Plant: Classification, Structure, and Key Uses
1. What is the persimmon plant and how is it classified?
The persimmon plant is a deciduous, fruit-bearing tree classified under the genus Diospyros in the family Ebenaceae. It is widely known for producing edible orange fruits and includes species such as Diospyros kaki (Oriental persimmon) and Diospyros virginiana (American persimmon).
Key classification:
- Kingdom: Plantae
- Family: Ebenaceae
- Genus: Diospyros
- Common species: D. kaki, D. virginiana
- Fruit type: True berry
2. How long does it take a persimmon tree to bear fruit?
A persimmon tree typically takes 3–5 years to bear fruit, depending on whether it is grown from a seed or a grafted plant.
- Grafted plants: Usually start fruiting in 2–3 years
- Seed-grown plants: May take 5 years or longer
3. Why are persimmons not sold in stores?
Persimmons are not commonly sold in stores because their fruit is delicate and has a short shelf-life.
- High perishability; bruises easily during transport
- Regional popularity in consumption
- Limited commercial cultivation in some countries
4. Where do persimmon trees grow best?
Persimmon trees grow best in temperate and subtropical regions with mild winters and well-drained soils.
- Common regions: China, Japan, Korea (Oriental persimmon), Eastern USA (American persimmon), and Indian hilly states (Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand)
- Ideal soil: Slightly acidic to neutral, well-drained
- Temperature: Require frost-free growing season for best fruiting
5. What are the main uses and economic importance of persimmon plants?
Persimmon plants have diverse uses, making them economically important.
- Culinary: Ripe fruit is eaten raw, in jams, puddings, and desserts.
- Medicinal: Fruits contain vitamin C, A, and antioxidants; used in traditional medicines.
- Timber: Some species provide hard wood (ebony) used in crafts and sports equipment.
- Ornamental: Attractive garden trees due to their colorful fruit and foliage.
6. What are the distinguishing morphological features of persimmon leaves and fruit?
Persimmon leaves are simple, alternate, and glossy with an ovate to elliptical shape, while the fruit is a true berry with a persistent calyx.
- Leaf: Simple, alternate arrangement, entire margin, leathery texture
- Flower: Small, unisexual, pale yellow/cream, axillary
- Fruit: Orange to red, edible, contains multiple seeds, persistent calyx
7. Can you eat fruit from a persimmon tree?
Yes, you can eat fruit from a persimmon tree; it is safe and nutritious when ripe.
- Ripe persimmons are sweet, soft, and rich in vitamins
- Unripe persimmons may be astringent and should be avoided as they contain tannins
- Fruits are used fresh or processed into jams, snacks, and desserts
8. How do you identify a wild persimmon tree?
A wild persimmon tree is identified by its simple, alternate leaves, blocky bark, and orange berry-like fruit with a persistent calyx.
- Leaves: Simple, alternate, broad, glossy texture
- Bark: Dark, square-patterned, resembling alligator skin (American persimmon)
- Fruit: Small, round/oval, orange, edible when ripe, multiple seeds
9. What is the botanical name and family of the persimmon plant?
The persimmon plant belongs to the genus Diospyros in the family Ebenaceae.
- Botanical name: Diospyros kaki (Oriental persimmon), Diospyros virginiana (American persimmon)
- Family: Ebenaceae
10. What are the medicinal properties of persimmon fruit?
Persimmon fruit offers several medicinal properties, making it valuable in traditional systems.
- Rich in vitamin C, vitamin A, and antioxidants
- Traditionally used in remedies for coughs and blood pressure management
- Contains dietary fiber for digestive health










