What Is the Structure and Role of the Lac Operon in E. coli?
The lac operon is a classic example of gene regulation found in bacteria, especially E. coli. It helps the cell efficiently manage energy by turning genes on or off based on the presence of lactose. Understanding the lac operon is important for students studying genetics, molecular biology, and biotechnology, especially those preparing for class 12 biology or competitive exams.
What is Lac Operon?
The lac operon definition describes a group of genes in bacteria that control the digestion of lactose—a sugar found in milk. The operon includes three main structural genes, a promoter, and an operator. The lac operon acts as an on/off switch, enabling bacteria to use lactose only when it is available. This regulatory system conserves energy and is a fundamental concept covered in lac operon class 12 topics.
Structure of the Lac Operon
The lac operon consists of several essential parts. Each component plays a specific role in gene regulation and lactose metabolism, making it a popular topic for biology diagrams and lac operon explanations.
- Regulatory Gene (lacI): Codes for the lac repressor protein.
- Promoter (P): The binding site for RNA polymerase to initiate transcription.
- Operator (O): The segment where the repressor binds to block transcription.
- Structural Genes:
- lacZ: Encodes β-galactosidase, which breaks lactose into glucose and galactose.
- lacY: Encodes permease, facilitating lactose entry into the cell.
- lacA: Encodes transacetylase, involved in detoxification.
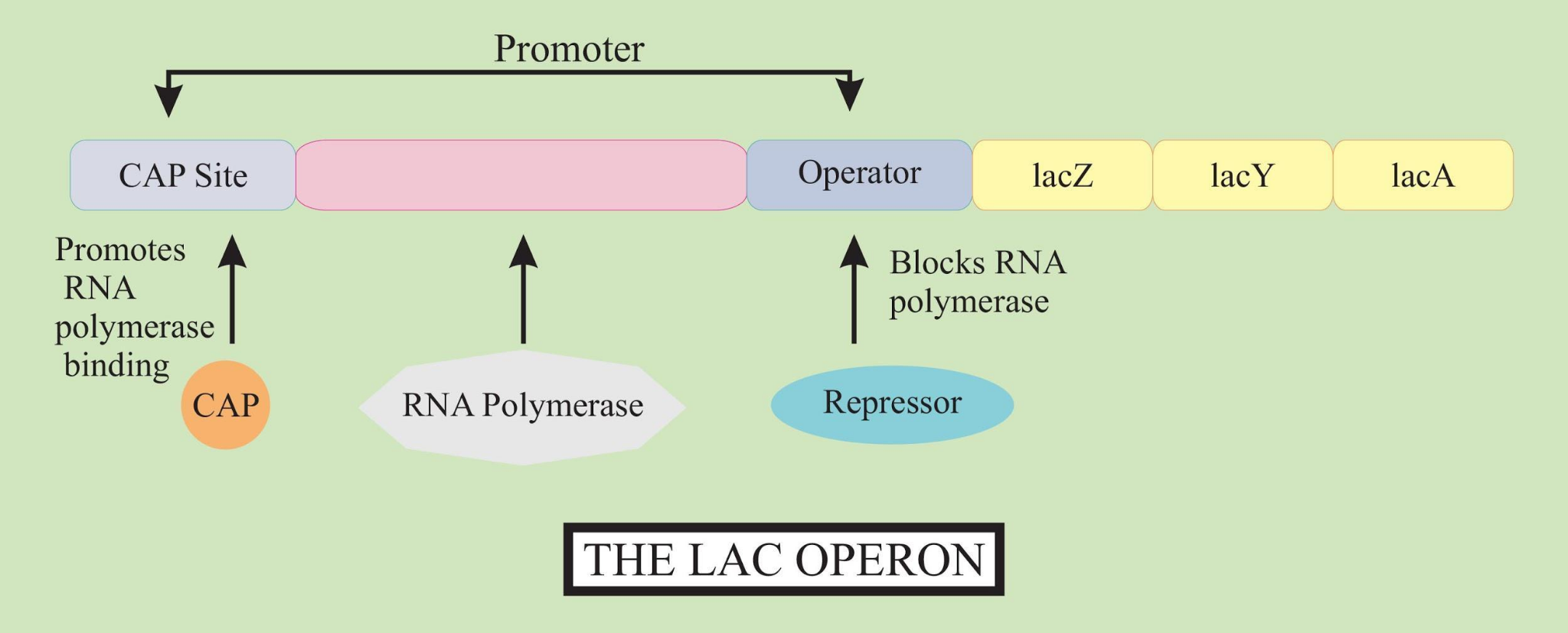
This structure allows bacteria to respond quickly to environmental changes, linking gene expression with nutrient availability.
How the Lac Operon Works: Mechanism and Regulation
The lac operon is a tightly regulated system. It responds to the presence or absence of lactose using a combination of repressors, inducers, and the components mentioned above. This mechanism demonstrates complex cellular responses and provides an excellent lac operon explanation for students.
Lac Operon Regulation: Turned Off (No Lactose)
When there is no lactose in the environment:
- The lacI gene produces a repressor protein.
- This repressor binds to the operator region.
- RNA polymerase cannot proceed to transcribe the structural genes.
- No enzymes for lactose metabolism are produced.
Lac Operon Regulation: Turned On (Lactose Present)
When lactose is present in the environment:
- Lactose (allolactose) acts as an inducer by binding to the repressor protein.
- This binding changes the shape of the repressor, causing it to detach from the operator.
- RNA polymerase can now transcribe the structural genes.
- Enzymes required to digest lactose are produced only when needed.
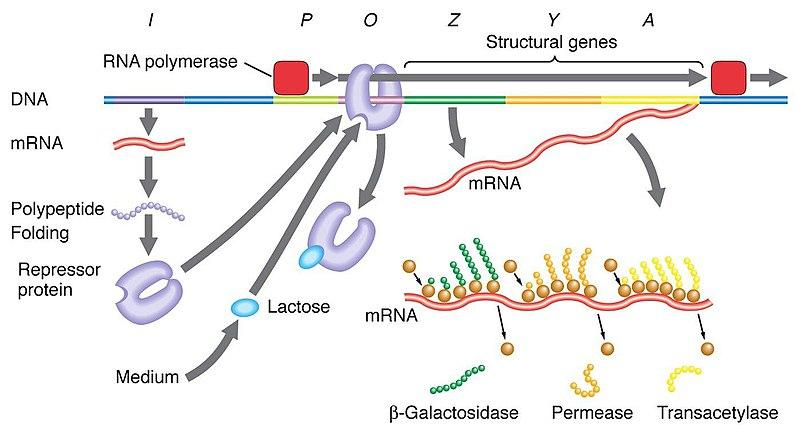
This efficient system is a model example for regulating metabolic pathways in bacteria. Other topics like inherited traits and gene regulation build on this concept.
Lac Operon Diagram and Labelled Model
A lac operon diagram visually explains gene positions and regulatory controls. It shows the sequence of promoter, operator, and genes. In class 12 biology, labelled diagrams help clarify how the transcriptional machinery and regulatory proteins interact.
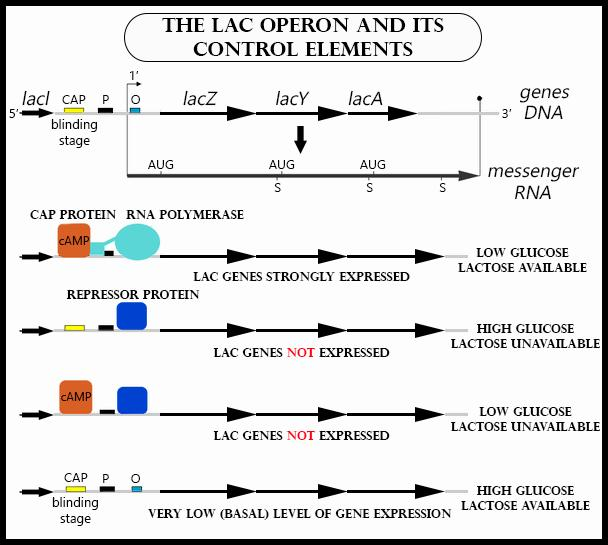
A labelled diagram is often used in lac operon ppt presentations in class or for self-study. Drawing this diagram is a common exam question and aids in understanding genetic control.
Significance and Applications of Lac Operon
Studying the lac operon has advanced our understanding of molecular genetics. Real-world applications include:
- Genetic Engineering: The lac operon is used as a genetic switch in recombinant DNA technology and for protein production in bacteria.
- Medical Research: Understanding gene regulation aids in developing strategies to combat bacterial infections.
- Agriculture: The operon's principles help improve traits in crops and microbiology-based agriculture.
Connecting with core topics like biomolecules and RNA can provide deeper insights for biotechnology students.
Lac Operon Examples and Related Questions
The lac operon is often cited in textbooks as an example of an inducible operon—a system that is usually off but can be switched on by an environmental trigger. Some common lac operon questions in exams include:
- Label and explain a lac operon diagram.
- How does the presence of lactose switch on the operon?
- What happens if the operator region mutates?
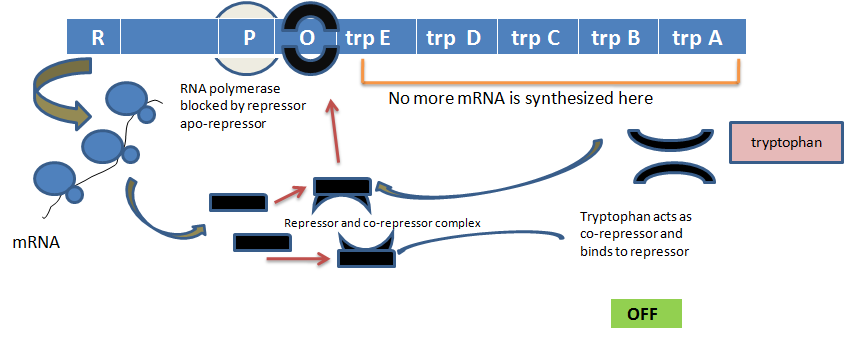
- Compare the lac operon to a repressible operon, such as the trp operon.
For exam practice, check lac operon mcqs and related practice sheets, as well as comprehensive summaries in class 12 biology guides.
Key Differences: Inducible vs Repressible Operons
| Features | Inducible Operon (e.g., Lac Operon) | Repressible Operon (e.g., trp Operon) |
|---|---|---|
| Default State | Off | On |
| Switched On By | Presence of substrate (lactose) | Absence of end-product (tryptophan) |
| Main Example | Lac Operon | trp Operon |
The table highlights why the lac operon is key for teaching inducible gene regulation and metabolic control in prokaryotes.
Practice Questions on Lac Operon
To assess your understanding, here are some typical lac operon questions you may encounter in exams:
- Define lac operon and explain its components.
- Draw and label the lac operon diagram.
- Describe the effect of lactose and glucose on lac operon regulation.
- Explain the significance of the operator region.
- Compare the mechanisms of lac operon and trp operon.
Practising these questions will help reinforce concepts. For fundamentals, see Vedantu’s cell theory and bacteria articles.
Related Topics for Deeper Understanding
Understanding the lac operon also helps when studying other genetic control systems. Explore more on:
For more detailed reading, students can refer to various biology resources and diagrams offered by Vedantu.
The lac operon is an essential model in genetics, showing how bacteria efficiently adapt to changes in their environment. Its study links core ideas from molecular biology, microbiology, and biotechnology. Mastering this topic boosts your fundamental understanding—beneficial for exams and real-life applications like medicine, environmental science, and genetic engineering.


FAQs on Lac Operon: Structure and Function in Gene Regulation
1. What is the lac operon and why is it important in gene regulation?
The lac operon is a classic example of a gene regulation system in prokaryotes, specifically in Escherichia coli, that controls the metabolism of lactose. It allows the bacteria to use lactose as an energy source only when glucose is not available. Key points:
- Lac operon includes structural genes, promoter, operator and a regulator gene
- It is an inducible system activated when lactose is present
- Regulates enzyme production needed for lactose breakdown
- Demonstrates negative and positive regulation in gene expression
2. How does the lac operon function?
The lac operon functions as an inducible gene system that controls the expression of enzymes for lactose metabolism:
- When lactose is absent, the repressor protein binds to the operator, blocking transcription
- When lactose is present, it binds to the repressor, causing it to detach from the operator
- This allows RNA polymerase to transcribe the lac genes, leading to enzyme synthesis
3. What are the main components of the lac operon?
The lac operon consists of several key components involved in gene regulation in E. coli:
- Structural genes (lacZ, lacY, lacA) for enzyme synthesis
- Promoter – site for RNA polymerase binding
- Operator – regulatory sequence where repressor attaches
- Regulator gene (lacI) – produces the repressor protein
4. Explain the role of the repressor in the lac operon.
The repressor protein controls gene expression in the lac operon by preventing transcription:
- Produced by the lacI gene
- Binds to the operator region in the absence of lactose
- Blocks RNA polymerase from transcribing the lac genes
- When lactose (allolactose) is present, it inactivates the repressor, allowing transcription
5. Describe the structural genes of the lac operon and their functions.
Structural genes in the lac operon code for enzymes that metabolize lactose in E. coli:
- lacZ: Encodes β-galactosidase to break lactose into glucose and galactose
- lacY: Encodes permease for lactose transport into the cell
- lacA: Encodes transacetylase (function less clear in lactose metabolism)
6. What happens to the lac operon in the absence of lactose?
In the absence of lactose, the lac operon is turned off and structural genes are not transcribed:
- The repressor protein binds to the operator region
- Blocks RNA polymerase from initiating transcription
- No enzyme for lactose metabolism is produced
7. How does glucose availability affect the lac operon?
The presence of glucose inhibits the activation of the lac operon through catabolite repression:
- High glucose = low cAMP levels, so CAP-cAMP complex does not form
- Without the complex, RNA polymerase binding is weak, and the operon remains off
- Only when glucose is low and lactose is present does the operon turn on efficiently
8. What is the significance of the lac operon in molecular biology?
The lac operon serves as a model for understanding gene regulation in prokaryotes:
- Demonstrates how cells respond to environmental changes
- Introduces key concepts like operon model, inducible systems, and regulation by repressors
- Forms the basis for many biotechnological and genetic engineering applications
9. Can you define an inducible operon using the lac operon example?
An inducible operon is a gene system that is usually inactive but becomes active in the presence of a specific substrate, as seen in the lac operon:
- Inactive when lactose is absent
- Activated (induced) by presence of lactose
- Allows controlled enzyme production based on cell needs
10. What are the differences between inducible and repressible operons?
Inducible and repressible operons are two types of gene regulatory systems in prokaryotes:
- Inducible operons (e.g., lac operon) are turned on by the presence of a substrate (like lactose)
- Repressible operons (e.g., trp operon) are usually on but can be turned off when a specific product is abundant
- The regulation mechanisms reflect cell adaptation to environmental conditions
11. What is the function of the operator region in the lac operon?
The operator region in the lac operon acts as a regulatory sequence:
- Serves as binding site for the repressor protein
- Controls access of RNA polymerase to the structural genes
- Acts like a genetic switch to turn the operon on or off
12. Who proposed the operon model and what is its significance?
The operon model was proposed by Francois Jacob and Jacques Monod in 1961:
- Explains coordinated regulation of gene clusters in prokaryotes
- Helps understand mechanisms of gene expression and control
- Was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1965










