Compare Steps, Equations, and Roles in Energy Flow
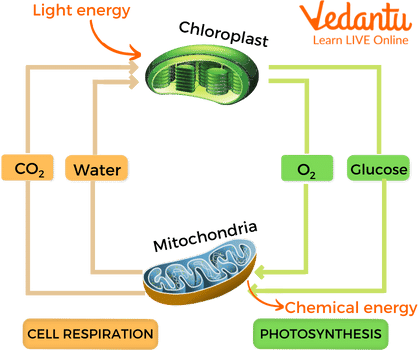
Photosynthesis and respiration are two essential biological processes that help sustain life on our planet. Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants, algae, and certain bacteria convert sunlight into chemical energy stored in glucose, releasing oxygen as a by-product. Cellular respiration takes place in the cells of almost all living organisms, breaking down glucose in the presence of oxygen to produce energy (ATP), carbon dioxide, and water.
Despite being closely connected, these processes are almost opposite in their overall reactions. One produces oxygen (photosynthesis), while the other consumes it (respiration). Both are vital for the balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Equation
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration equation for photosynthesis:
6CO2 + 6H2O sunlight → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration equation for respiration:
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy (ATP)
These two equations show in which way are photosynthesis and cellular respiration different—the reactants of one are the products of the other.
Key Differences between Photosynthesis and Respiration in Table Form
Additional Insights
Interdependence: Plants produce the oxygen needed for respiration, and all organisms (including plants at night) produce carbon dioxide needed for photosynthesis.
Role in Atmosphere: Photosynthesis helps reduce carbon dioxide levels and increase oxygen levels, while respiration balances this by releasing carbon dioxide and consuming oxygen.
Energy Flow: Photosynthesis is the primary source of energy input to the biosphere, capturing light energy and storing it in glucose. Respiration releases this stored energy for growth, reproduction, and other cellular activities.
Quiz (With Answers)
Try this short quiz to check your understanding:
Which organelle in plant cells is responsible for photosynthesis?
A) Mitochondria
B) Chloroplast
C) Ribosome
D) Nucleus
Answer: B) Chloroplast
Which gas is taken in during aerobic cellular respiration?
A) Carbon dioxide
B) Oxygen
C) Nitrogen
D) Hydrogen
Answer: B) Oxygen
Name the main energy-carrying molecule produced by cellular respiration.
A) ATP
B) Glucose
C) ADP
D) NADH
Answer: A) ATP
Which of the following is a by-product of photosynthesis?
A) Carbon dioxide
B) Oxygen
C) ATP
D) Water
Answer: B) Oxygen
Related Topics


FAQs on Photosynthesis vs Cellular Respiration: Main Differences
1. What are the key differences between photosynthesis and respiration?
The key differences lie in their purpose, location, reactants, and products. Photosynthesis uses light energy, water, and carbon dioxide to create glucose (food) and occurs in the chloroplasts of plants and some other organisms. Respiration, on the other hand, breaks down glucose using oxygen to release energy (ATP) for cellular functions and takes place in the mitochondria of all living cells.
2. Why is photosynthesis considered an anabolic process while respiration is a catabolic process?
Photosynthesis is anabolic (a building-up process) because it synthesises complex organic molecules (glucose) from simpler inorganic ones (CO₂ and H₂O), storing energy in the process. Respiration is catabolic (a breaking-down process) because it breaks down complex glucose molecules to release stored chemical energy in the form of ATP.
3. If plants produce their own food through photosynthesis, why do they also need to respire?
Plants need to respire for the same reason animals do: to power their life functions. Photosynthesis creates glucose, which is a stable energy storage molecule. However, for a plant to grow, repair tissues, or transport nutrients, it must convert the energy stored in glucose into a usable form. Respiration is the process that unlocks the energy from glucose and converts it into ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the direct energy currency of the cell.
4. What are the raw materials and end products for photosynthesis versus respiration?
The two processes have opposite requirements and outputs:
Photosynthesis Raw Materials: Carbon Dioxide (CO₂), Water (H₂O), and Light Energy.
Photosynthesis End Products: Glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) and Oxygen (O₂).
Respiration Raw Materials: Glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) and Oxygen (O₂).
Respiration End Products: Carbon Dioxide (CO₂), Water (H₂O), and Energy (ATP).
5. Are photosynthesis and respiration simply reverse reactions of each other?
No, this is a common misconception. While their overall chemical equations appear to be opposites, the biochemical pathways are entirely different. They take place in different cellular organelles (chloroplasts vs. mitochondria), are controlled by a distinct set of enzymes, and involve unique intermediate steps and energy carriers. They are complementary processes, not simple reversals of one another.
6. How does the location within the cell differ for photosynthesis and respiration, and why is this significant?
Photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplasts, which are equipped with chlorophyll to capture sunlight. Cellular respiration primarily occurs in the mitochondria, known as the cell's 'powerhouse'. This structural separation is crucial as it allows the energy-storing (photosynthesis) and energy-releasing (respiration) processes to happen simultaneously and efficiently within the same cell without interfering with each other.
7. Which organisms can perform photosynthesis and which perform respiration?
Photosynthesis is performed by autotrophs, which are organisms that can produce their own food. This includes all green plants, algae, and some bacteria like cyanobacteria. In contrast, cellular respiration is a fundamental process for life and is performed by nearly all living organisms—including plants, animals, fungi, and most microbes—to release energy from food.
8. How do the net gas exchanges in a plant differ between day and night?
The net gas exchange changes based on the dominant process:
During the day: Photosynthesis is highly active. The plant takes in more CO₂ than it releases and gives off more O₂ than it consumes. The net effect is the uptake of CO₂ and release of O₂.
During the night: With no light, photosynthesis stops, but respiration continues. The plant takes in O₂ and releases CO₂ to generate energy for its metabolic needs.
9. What is the primary role of sunlight in photosynthesis compared to the role of glucose in respiration?
Their roles are fundamentally about energy conversion. In photosynthesis, sunlight acts as the initial external energy source, which is captured and converted into stored chemical energy. In respiration, glucose serves as the internal chemical fuel; its bonds are broken to release that stored energy in a form the cell can use (ATP).










