Economics Notes for Chapter 2 Theory of Consumer Behaviour Class 12 - FREE PDF Download
FAQs on Theory of Consumer Behaviour Class 12 Economics Chapter 2 CBSE Notes - 2025-26
1. What is a quick summary of the key concepts in the Theory of Consumer Behaviour for Class 12?
The Theory of Consumer Behaviour explains how a consumer allocates their income to purchase different goods and services to maximise satisfaction. Key concepts for a quick revision include:
- Utility: The want-satisfying power of a commodity, analysed through Cardinal and Ordinal approaches.
- Consumer's Equilibrium: The point of maximum satisfaction, determined using utility analysis and indifference curves with budget constraints.
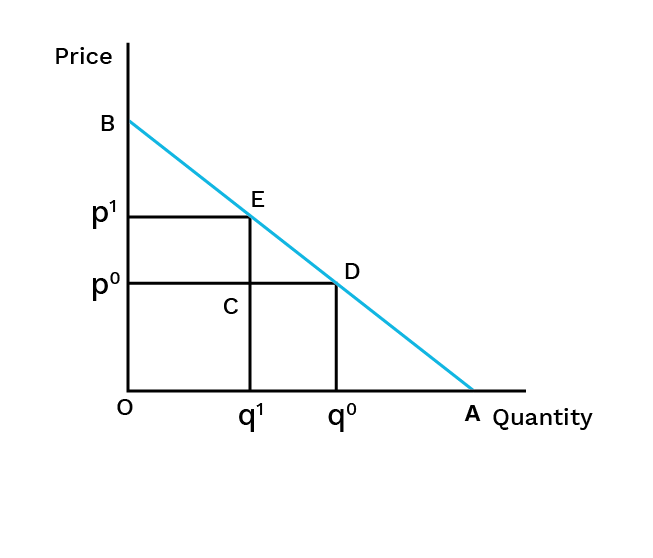
- Demand: The quantity of a commodity a consumer is willing and able to buy at a given price.
- Price Elasticity of Demand: The measure of how responsive quantity demanded is to a change in price.
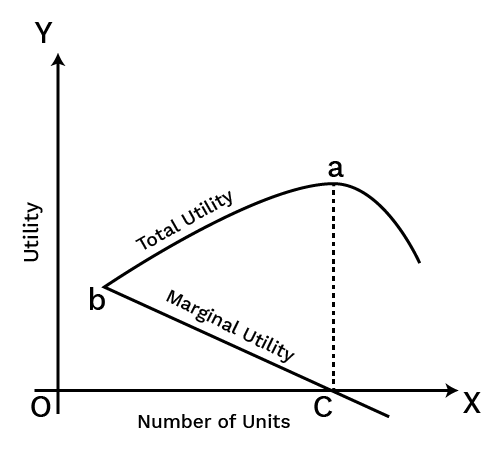
2. How are Total Utility (TU) and Marginal Utility (MU) explained in these revision notes?
Total Utility (TU) is the total satisfaction a consumer gets from consuming all units of a commodity. Marginal Utility (MU) is the additional satisfaction gained from consuming one more unit of that commodity. The relationship is key: TU increases as long as MU is positive. TU is at its maximum when MU is zero, and TU starts to fall when MU becomes negative.
3. What is the Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility?
The Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility is a fundamental principle stating that as a consumer consumes more and more units of a commodity, the marginal utility (additional satisfaction) derived from each successive unit goes on declining. This law forms the basis for understanding the downward slope of the demand curve.
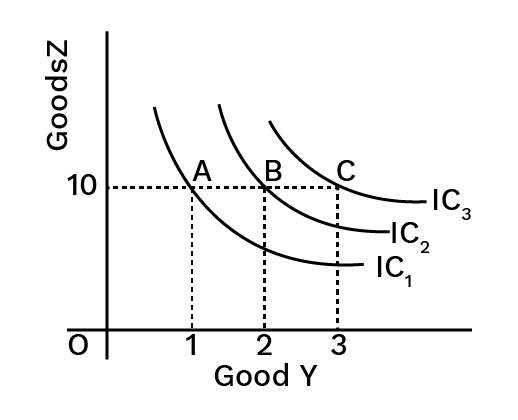
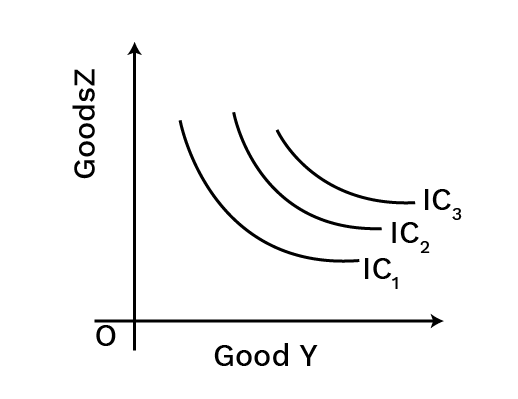
4. What is an indifference curve and what are its main properties for revision?
An indifference curve (IC) is a graph showing combinations of two goods that give a consumer equal satisfaction and utility. For revision, remember these key properties:
- They are downward sloping from left to right.
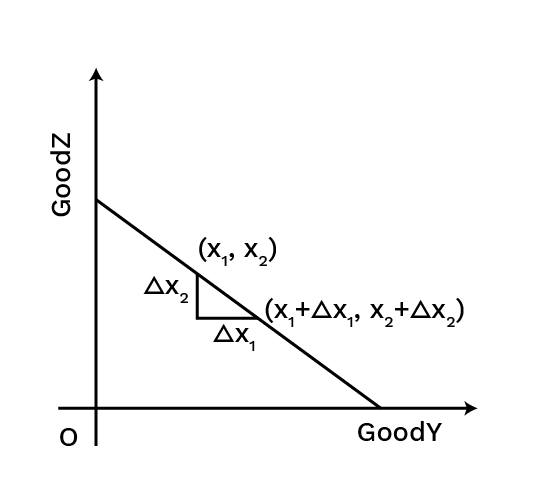
- They are convex to the origin due to the diminishing Marginal Rate of Substitution (MRS).
- Higher indifference curves represent higher levels of satisfaction.
- Indifference curves can never intersect each other.
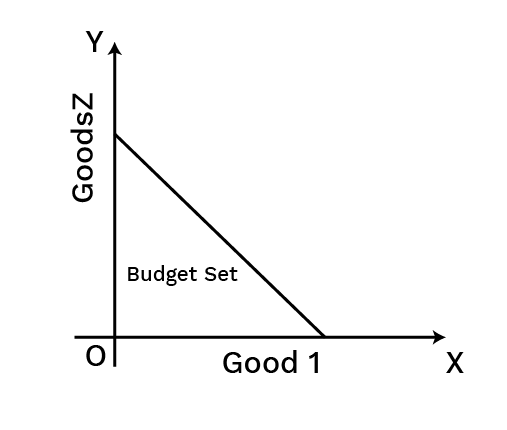
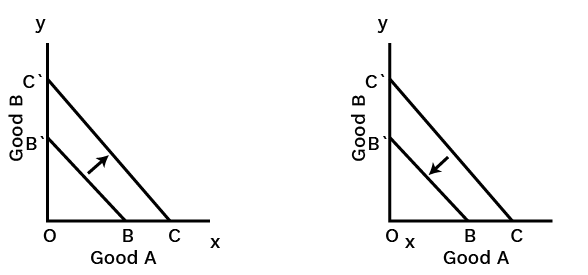
5. How do these notes explain a consumer's budget set and budget line?
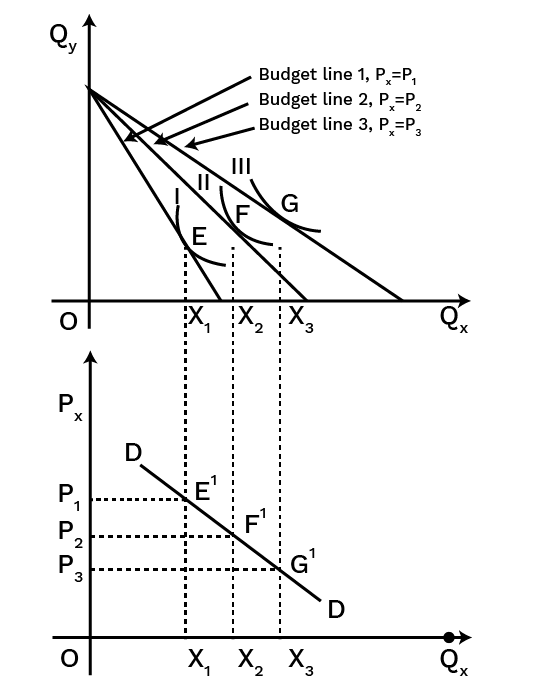
A budget set includes all possible combinations (bundles) of two goods that a consumer can afford with their given income at prevailing market prices. The budget line graphically represents the bundles that cost exactly equal to the consumer's entire income. It is a negatively sloped line, and its slope is determined by the ratio of the prices of the two goods (-Px/Py).
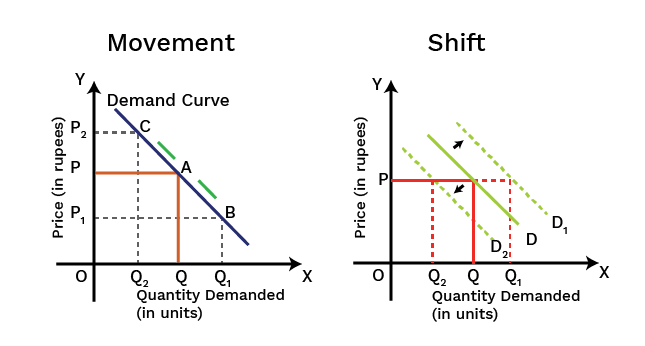
6. What is the difference between a 'movement along' and a 'shift' in the demand curve?
This is a crucial concept for revision. A movement along the demand curve occurs due to a change in the commodity's own price, leading to an 'expansion' or 'contraction' of demand. In contrast, a shift in the demand curve (either rightward or leftward) is caused by changes in factors other than the commodity's own price, such as the consumer's income, tastes, or the price of related goods.
7. How do the Cardinal and Ordinal utility approaches differ in explaining consumer behaviour?
The primary difference lies in how they measure utility. The Cardinal Utility approach assumes that utility can be measured and expressed in numerical units called 'utils'. It uses concepts like the Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility. The Ordinal Utility approach, considered more realistic, argues that utility cannot be measured numerically but can be ranked in order of preference. It uses tools like indifference curves to explain consumer choices.
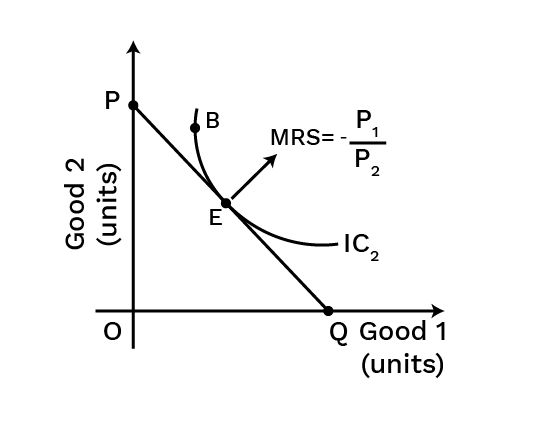
8. Why is a consumer's equilibrium achieved where the budget line is tangent to an indifference curve?
This point represents the highest possible satisfaction a consumer can achieve given their budget. At the point of tangency, the slope of the indifference curve (MRS) is equal to the slope of the budget line (price ratio). This means the rate at which the consumer is willing to substitute one good for another is exactly equal to the rate at which the market allows them to, thereby maximising their utility within their financial constraints.
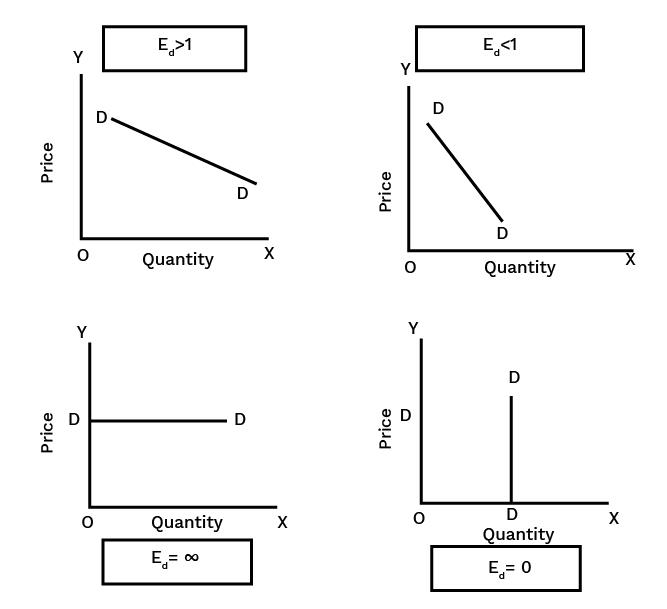
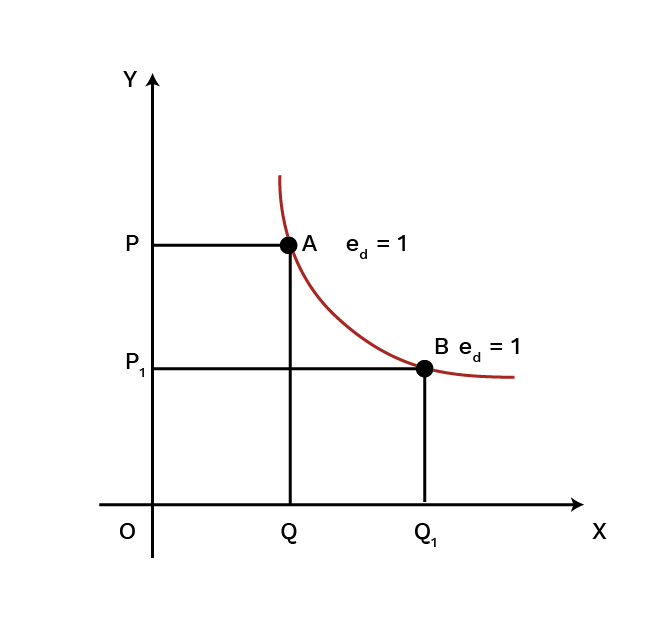
9. How does understanding the price elasticity of demand help in revising this chapter?
Understanding price elasticity of demand (Ed) is crucial as it summarises consumer responsiveness. It explains by how much the quantity demanded will change in response to a price change. For revision, knowing the different degrees (perfectly elastic/inelastic, unitary, elastic, inelastic) helps connect the theory to real-world goods, such as why the demand for necessities is inelastic while demand for luxuries is elastic.
10. What is the connection between the Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility and the Law of Demand?
The Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility provides the reason behind the Law of Demand. As a consumer buys more of a good, its marginal utility decreases. Therefore, the consumer will only be willing to buy an additional unit if the price falls. This inverse relationship between the price a consumer is willing to pay and the quantity they consume is the essence of the Law of Demand.