Symmetry Questions and Answers - Free PDF Download
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Maths Chapter 9 Symmetry Exercise 9.2 - 2025-26
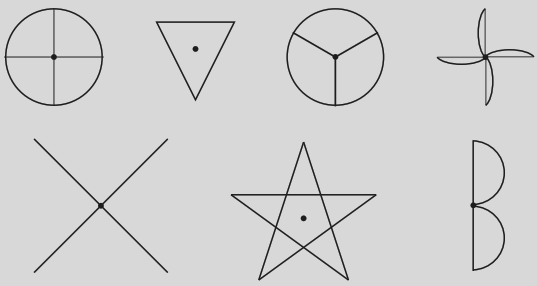
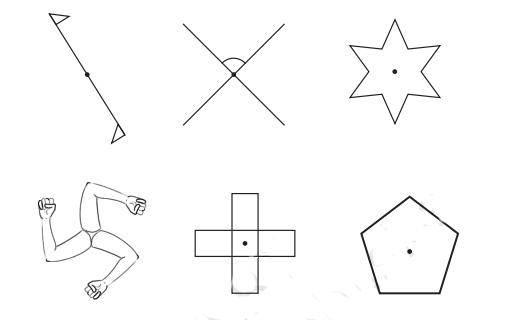
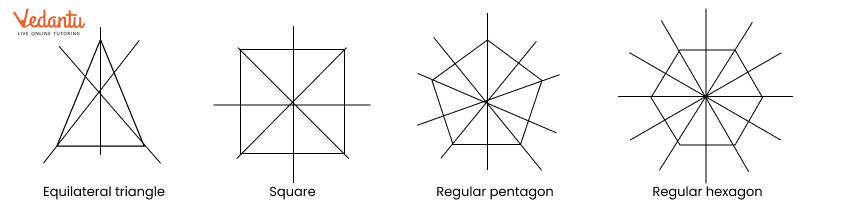
1. How are the lines of symmetry for different shapes correctly identified in the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 9?
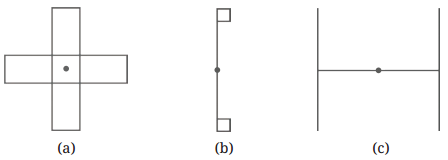
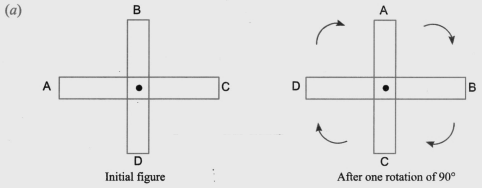
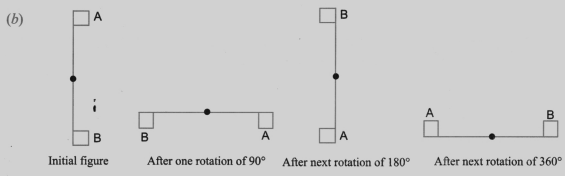
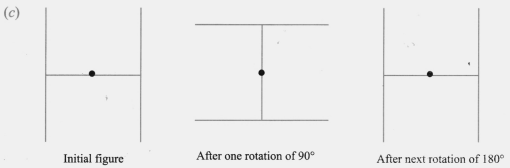
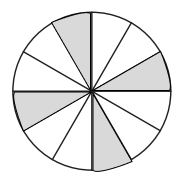
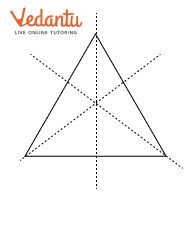
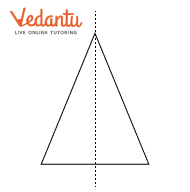
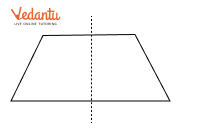
The solutions demonstrate a systematic approach. They guide you to first observe the shape and then imagine a line of reflection. The core method involves folding the shape along a potential line to see if one half perfectly overlaps the other. For each problem, the steps clearly show how to verify if a line is indeed a line of symmetry.
2. What is the correct method to solve problems asking to complete symmetrical figures in Exercise 9.2, as shown in the NCERT solutions?
The NCERT solutions teach a methodical way to complete shapes. The key is to treat the given line as a mirror line. For every point on the existing part of the figure, you learn to plot a corresponding point on the other side at the exact same distance from the line. Connecting these new points correctly completes the symmetrical figure as per NCERT guidelines.
3. Are the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 9 updated for the 2025-26 academic year?
Yes, the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 9 are fully aligned with the latest CBSE syllabus for the 2025-26 academic session. They are designed to help you master the concepts of symmetry exactly as prescribed in the NCERT textbook, ensuring you are preparing with the most current and relevant material.
4. Beyond just finding answers, how do the step-by-step NCERT Solutions for Chapter 9 help in understanding the core concept of symmetry?
The step-by-step solutions do more than provide final answers. They break down the process of identifying symmetry, forcing you to think about balance and reflection. By following each logical step, you move from simple observation to a deeper geometric understanding of why a shape is symmetrical, which is a foundational skill for higher-level geometry.
5. Why is it important to follow the precise steps given in the NCERT Solutions when drawing a line of symmetry, instead of just guessing?
Guessing a line of symmetry can often lead to errors, especially in complex figures. Following the precise steps from the NCERT Solutions is crucial because it reinforces the mathematical definition of symmetry. This methodical approach ensures accuracy, teaches you how to justify your answer, and helps avoid common mistakes like identifying a diagonal as a line of symmetry when it is not.
6. How can using the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 9 improve my exam scores?
Using these NCERT solutions can significantly boost exam performance in several ways:
They teach the correct format for presenting answers, which helps in securing full marks.
By practising with verified solutions, you build confidence and reduce errors.
You gain a thorough understanding of the types of questions that can be asked from the Symmetry chapter.
7. What common mistakes do students make when solving symmetry problems, and how do the NCERT Solutions help to prevent them?
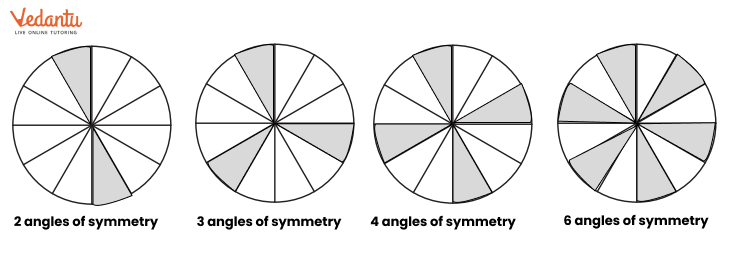
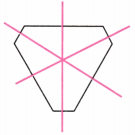
A common mistake is confusing a line that divides a shape into two equal areas with a true line of symmetry (e.g., a diagonal in a rectangle). Another error is miscounting the number of symmetry lines in regular polygons. The NCERT solutions prevent these by providing clear, step-by-step visual explanations for each problem, highlighting the exact criteria for a line of reflection and showing the complete set for each shape.
8. What types of geometrical shapes are covered in the NCERT Solutions for Chapter 9, Exercise 9.2?
The NCERT solutions for Exercise 9.2 cover a wide range of shapes to build a strong foundation. You will find solved problems for:
Different types of triangles (isosceles, equilateral).
Various quadrilaterals (squares, rectangles).
Other polygons and common geometrical figures.
Alphabets and other real-world shapes to test your understanding of lines of symmetry.