Master Fractions Class 6 NCERT Solutions With Vedantu's Expert Guidance
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Maths Chapter 7 Fractions - 2025-26
1. What topics are covered in the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 7 Fractions?
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 7 Fractions include explanations and solved examples for topics such as:
- Identification of proper and improper fractions
- Conversion between mixed and improper fractions
- Equivalent fractions and simplest form
- Comparison and ordering of fractions
- Addition and subtraction of fractions
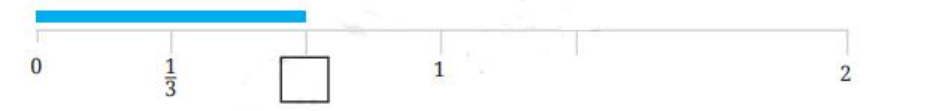
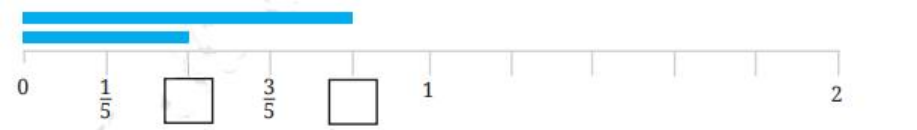
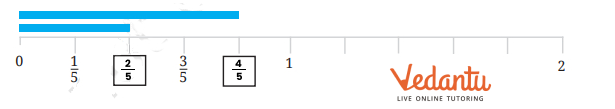
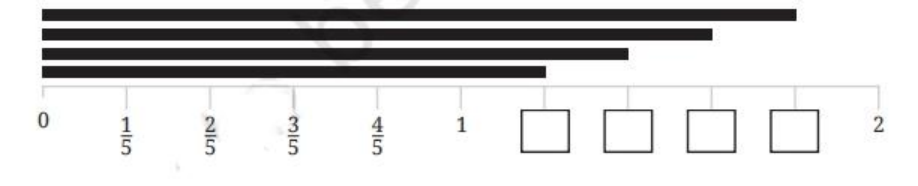
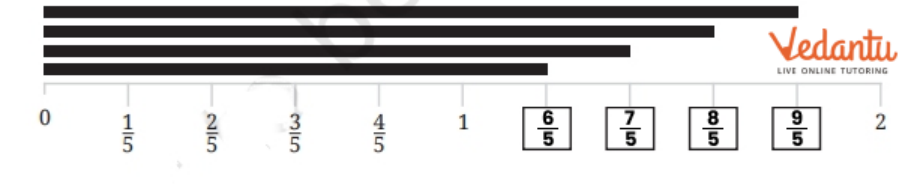
- Fractions on a number line
- Real-life applications of fractions
2. How are equivalent fractions explained in NCERT Class 6 Maths Chapter 7 Solutions?
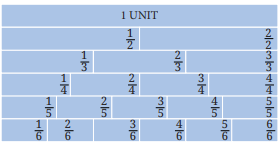
Equivalent fractions are explained using visual methods like fraction walls, number lines, and comparing areas. The solutions show how multiplying or dividing both numerator and denominator by the same number yields equivalent fractions. Example: 2/4 and 1/2 are equivalent because 2÷2 = 1 and 4÷2 = 2.
3. What is the method to convert an improper fraction to a mixed number in the Chapter 7 Fractions solutions?
To convert an improper fraction to a mixed number:
- Divide the numerator by the denominator
- The quotient is the whole number part
- The remainder is the numerator of the fractional part (over the same denominator)
4. How do the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 7 help in understanding addition and subtraction of fractions?
The solutions break down the process for adding and subtracting fractions by:
- Finding a common denominator
- Rewriting the fractions with common numerators or denominators
- Adding or subtracting numerators as per the operation
- Simplifying the result if necessary
5. Why is understanding proper and improper fractions important, as explained in NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Fractions?
Understanding proper and improper fractions is crucial because:
- It forms the foundation for complex fraction operations
- It helps differentiate between values less than and greater than one
- These concepts are essential for topics like mixed numbers, decimals, and ratios introduced in higher classes
6. What is a common misconception students have about fractions, according to the NCERT Class 6 Fractions Solutions?
One common misconception is that fractions with larger denominators are always smaller. The solutions clarify this by providing counterexamples (e.g., 1/2 is greater than 1/3, even though 3 is larger than 2) and using visual aids like number lines and area models to build correct intuition.
7. How are mixed fractions and improper fractions related in Class 6 Maths Chapter 7?
Mixed fractions and improper fractions represent the same value in different forms. NCERT Solutions show:
- Converting a mixed fraction to improper: Multiply whole number by denominator, add numerator, keep same denominator
- Converting improper to mixed: Divide numerator by denominator
8. In what ways does the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 7 align with the CBSE syllabus for 2025–26?
These solutions strictly follow the latest CBSE Class 6 Maths syllabus (2025–26), ensuring all exercises, terminology, and methods are updated and relevant for current exams. All stepwise explanations reflect prescribed formats and marks distribution.
9. What strategies are suggested in the NCERT Solutions for comparing two fractions?
NCERT Solutions recommend:
- Converting to common denominators to compare numerators directly
- Cross-multiplication for quick comparison
- Visual representation on number lines
10. How can understanding fractions through real-life examples aid student learning as shown in Chapter 7?
Applying fractions to real-life contexts (e.g., dividing food, measuring lengths) helps students visualize and internalize mathematical concepts. The NCERT Solutions include practical word problems and illustrations, making abstract ideas accessible and relatable.
11. What should a student do if their answer is not in the simplest form, according to the NCERT Solutions?
The Solutions instruct students to always simplify answers to lowest terms by dividing numerator and denominator by their GCD. This step is crucial for full marks in exams and understanding equivalent fractions.
12. What if two fractions have different denominators in an addition question?
Find the least common denominator (LCD) of both fractions. Rewrite each fraction with the LCD, adjust numerators accordingly, then add. Simplify the final answer if possible.
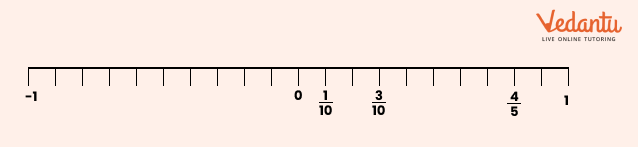
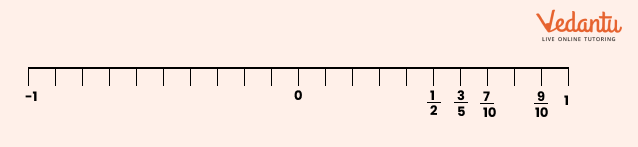
13. How are fractions represented on a number line, as described in Class 6 Maths Chapter 7?
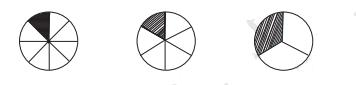
Fractions are shown by dividing the segment between 0 and 1 into equal parts as per denominator. Each part's endpoint represents a fraction (e.g., 3/4 is three marks right from 0 when the segment is in 4 parts). This builds understanding of relative size and value.
14. What advanced concept related to fractions does the NCERT Solutions introduce for Class 6 (as a FUQ)?
Beyond basics, the solutions introduce pattern recognition in equivalent fractions, connections with ratio concepts, and ‘what if’ cases like adding unlike denominators with large numbers. These build a foundation for later topics in percentages and algebra.
15. How do NCERT Solutions for Chapter 7 Fractions foster problem-solving skills for exams?
Students practice step-by-step methods, review solved examples for complex cases, and attempt ‘apply and analyze’ questions. The focus on reasoning, simplification, and real-world problems prepares students for all exam formats and question types.