Nightshade Plant Structure and Examples – Edible, Medicinal, and Toxic Types
Hello, plant explorers! Today at Vedantu, let’s take a magical journey into the world of the Nightshade Plant family. Did you know that some of your favorite veggies (even French fries!) come from nightshade relatives? But watch out—not all nightshade plants are safe to munch! Ready to spot the differences, learn their secrets, and become a nightshade plant pro? Let’s dig in!
Meet the Nightshade: Not Just a Spooky Name!
The nightshade plant might sound like something from a fairy tale, but it’s actually a huge family of real plants. Scientists call this family Solanaceae. Nightshade plants live all over the world, from home gardens to wild fields.
Where Nightshades Grow and Who’s in the Family?
Plants in the Solanaceae family grow in many climates—some like cool places, while others love the sun. The family has nearly 2,300 species. That’s a LOT of plant cousins! When you eat potatoes, tomatoes, brinjal (that’s eggplant), or even pick spicy chilies, you’re enjoying tasty members of the nightshade team.
Nightshade Family Quick List:
- Potato (Solanum tuberosum)
- Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum)
- Brinjal/Eggplant (Solanum melongena)
- Chili and Capsicum
- Deadly Nightshade (Atropa belladonna)
- Tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum)
- Datura (thorn apple)
Root to Fruit: Secret Parts of Nightshade Plants
Nightshade plants may look simple, but every part works hard! Even their flowers have cool features that help you spot them in any science test or garden.
Let’s Explore Plant Parts
- Roots: Usually fibrous or with tubers (think potatoes!).
- Stems: Can be green and soft (herbaceous) or woody in bushes.
- Leaves: Most often simple (one piece) and arranged one after another. They can have wavy or toothed edges.
- Flowers: Always radially symmetrical ("wheel-shaped"), often with five petals joined together, five sepals, and five stamens. Look for yellow, purple, or white flowers on many nightshades.
- Fruits: Usually berries (like tomatoes) or dry capsules (like in Datura).
Can You Picture a Nightshade Plant?
Imagine you have a tomato plant in front of you. It has soft stems, bright green leaves, yellow star-shaped flowers, and grows yummy red berries (the tomatoes!). If you peel back the flower, you’ll see five petals, five sepals, and the tiny parts that make pollen and seeds.
Nightshade Leaf Quick Diagram
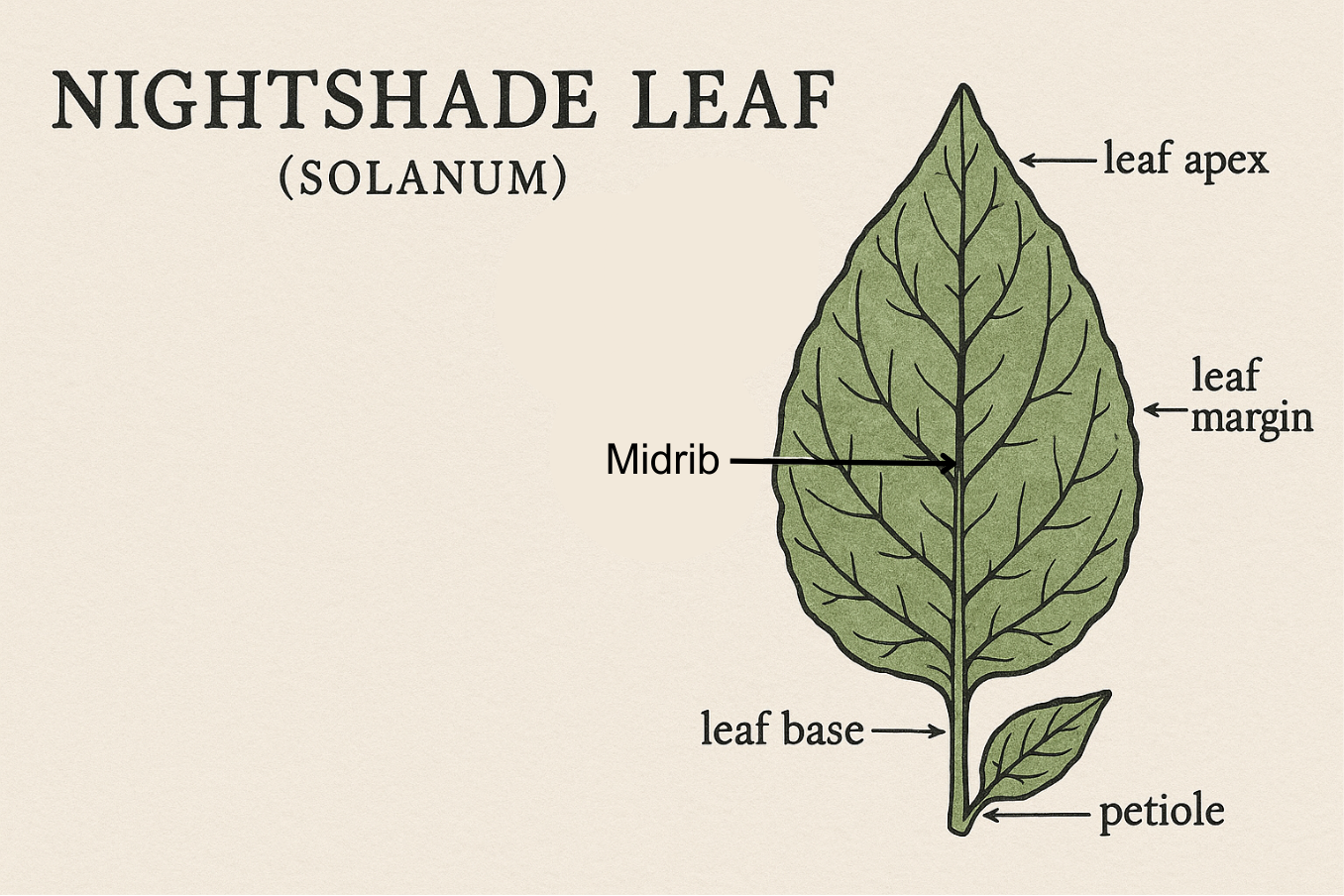
Parts: Petiole, Lamina, Margin, Veins
How Nightshades Live, Grow, & Trick the World
Photosynthesis and Beyond!
Nightshade plants, just like many others, use photosynthesis to make their own food from sunlight. Their leaves are green because of chlorophyll. They soak up sunlight and turn it—like magic—into food!
Smart Survival Tricks
- Some nightshade roots store extra food (like potato tubers) to help the plant survive winter.
- Bright red or yellow fruits attract animals and humans, who help spread their seeds.
- A few have special chemicals called "alkaloids"—good for medicine, but can be toxic!
Why Are Nightshade Plants So Famous?
Nightshade plants are superheroes in our kitchens and science labs. They can be tasty vegetables, important medicines, scary poison plants—or all three!
Super Uses (Food, Medicine, More!)
| Plant | Main Use | Extra Fact |
|---|---|---|
| Tomato | Food (fruit/veggie) | Rich in Vitamins |
| Potato | Food (tuber) | Grows underground |
| Brinjal/Eggplant | Food (fruit) | Called "Baingan" in India |
| Chili/Capsicum | Spice, medicine | Source of capsaicin |
| Deadly Nightshade | Medicine, poison | Very toxic—do not eat! |
| Tobacco | Industry, medicine | Nicotine plant |
Some nightshades save lives with their medicine, but others can be dangerous if eaten by mistake. Always check before tasting a wild plant!
Nightshade vs. Bean Family – Spot the Surprising Differences!
How Can You Tell Them Apart?
| Feature | Nightshade (Solanaceae) | Bean Family (Fabaceae) |
|---|---|---|
| Flower symmetry | Actinomorphic ("star" shape) | Zygomorphic ("butterfly" shape) |
| Fruit type | Berry/capsule | Legume (pod) |
| Famous members | Potato, Tomato, Brinjal | Peas, Beans, Gram |
So, if you see a plant with a “pod” (like a pea), it’s probably not a nightshade!
Speedy Quick Facts: Nightshade Table
| Feature | What It Means | Fun to Know |
|---|---|---|
| Family | Solanaceae | Called the nightshade family |
| Fruits | Usually berry or capsule | Tomato is a berry! |
| Edible parts | Fruits, tubers, leaves (rare) | Potato's "fruit" is underground! |
| Dangerous cousins? | Yes! Some are very poisonous | Like Deadly Nightshade |
| Famous for | Food, medicine, poison | Essential to global cuisine |
Who’s Who? Fun Example Time!
Question: Is a potato a root or a stem? Which family does it belong to?
Answer: Potato is actually a stem called a tuber (it has buds called "eyes"), not a root. It belongs to the nightshade family (Solanaceae)!
Time to Practice: Can You Answer These?
- Name two edible and one poisonous nightshade plant.
- What kind of fruit do most nightshades have?
- How do you tell a nightshade flower from a bean flower?
Don’t Get Tricked! Common Mix-Ups and Mistakes
Be careful—some members of the nightshade family look like harmless vegetables but are really toxic (like deadly nightshade or Datura!). Don’t eat wild nightshade berries unless you are 100% sure they are safe! The tomato and the potato are both nightshades, but one is fruit and the other is a tuber. And not every berry-shaped fruit is safe to eat!
Wrap-Up: Nightshade Ninjas—You Did It!
Now you know all about the amazing nightshade plant family—Solanaceae. From delicious food to important medicines and even poisons, these plants have a big story! Next time you see a tomato or potato, remember you’re looking at a superstar from the nightshade world. If you need more plant puzzles, word meanings, or help with botany, Vedantu is here for you.
Want to keep exploring the plant world? Try learning about plant classification and the plant kingdom—there’s always more to discover. Happy learning, plant detectives!


FAQs on Nightshade Plant (Solanaceae Family): Classification, Features & Importance
1. What is the Nightshade plant family?
Solanaceae, commonly known as the nightshade family, is a group of flowering plants that includes important edible, medicinal, and ornamental species.
- Members include potato, tomato, brinjal (eggplant), chili, and deadly nightshade (Atropa belladonna).
- Family shows features like actinomorphic flowers, superior ovary, and berry or capsule fruits.
- They are significant in NEET and CBSE for their economic and medicinal uses.
2. Is Nightshade poisonous?
Some nightshade plants are poisonous due to the presence of powerful alkaloids, while others are edible.
- Deadly nightshade (Atropa belladonna) and Datura are highly toxic species in this family.
- Edible members like tomato, potato, and brinjal are safe when properly prepared.
- Always identify the species, as toxicity varies within the Solanaceae family.
3. What are the economic uses of nightshade plants?
Nightshade plants (Solanaceae) have extensive economic importance:
- Food crops: Potato, tomato, brinjal, chili, and capsicum are major staples and vegetables.
- Medicinal plants: Atropa belladonna (source of atropine), Datura (alkaloids), and tobacco (nicotine).
- Industrial uses: Tobacco for products, and as insecticide.
- Ornamentals: Certain nightshade species are grown for ornamental value.
4. Name some edible members of the Nightshade (Solanaceae) family.
Several edible plants belong to the Solanaceae family:
- Potato (Solanum tuberosum)
- Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum)
- Brinjal/Eggplant (Solanum melongena)
- Chili and Capsicum (Capsicum spp.)
5. What is the structure of nightshade flowers?
Nightshade (Solanaceae) flowers are typically:
- Actinomorphic (radially symmetrical) and bisexual
- Have 5 fused sepals (calyx) and 5 fused petals (corolla)
- Possess 5 stamens attached to the petals (epipetalous)
- Ovary superior, bicarpellary, axile placentation
- Fruit is usually a berry or capsule
6. Classify the tomato plant based on its family and economic use.
Tomato is a member of the Solanaceae (nightshade) family and is classified as:
- Family: Solanaceae
- Genus: Solanum
- Species: Solanum lycopersicum
7. What are the medicinal uses of nightshade plants?
Nightshade plants have significant medicinal uses due to the alkaloids they produce:
- Atropa belladonna: Source of atropine (used in medicine to dilate pupils, treat bradycardia).
- Datura: Used in traditional medicine; source of scopolamine and hyoscyamine.
- Tobacco: Contains nicotine (used as nerve poison, insecticide).
8. How can you differentiate between Solanaceae and Fabaceae families?
Solanaceae and Fabaceae are distinguished by key morphological features:
- Solanaceae (Nightshade):
- Flower is actinomorphic
- Fruit is berry or capsule
- Leaves are simple, alternate
- Fabaceae (Bean):
- Flower is zygomorphic
- Fruit is legume
- Leaves are compound
9. What are the main characteristics of the Solanaceae family?
Solanaceae (nightshade family) displays several unique characteristics:
- Mostly herbs or shrubs, some small trees
- Leaves: Simple, alternate, exstipulate
- Flowers: Actinomorphic, bisexual, pentamerous
- Fruit: Berry or capsule
- Ovary: Superior, bicarpellary, axile placentation
10. Which Solanaceae plant is used as a source of atropine?
Atropa belladonna, commonly called deadly nightshade, is a major source of the alkaloid atropine.
- Atropine is used medicinally to dilate pupils and as an antidote for some poisons.
- All parts of this plant are highly toxic, so it must be used with care under proper guidance.
11. List two toxic members of the Nightshade family.
Two toxic members of the Solanaceae family are:
- Atropa belladonna (Deadly nightshade)
- Datura species
12. What is the NEET exam weightage for Solanaceae (Nightshade) family?
Questions related to the Solanaceae (Nightshade) family commonly carry 2–4 marks in NEET and 1–2 MCQs in CBSE/ICSE boards.
- Focus areas include family characteristics, economic importance, and diagrams of flowers and fruits.
- Preparation of plant morphology and uses is key for high scores.










