Human Reproduction Class 12 Questions and Answers for CBSE Board Exam Practice
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 2 Human Reproduction - 2025-26
1. What is the correct step-by-step method for solving NCERT questions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 2, Human Reproduction?
To correctly solve NCERT questions for Human Reproduction, first, carefully read the question to identify its type (e.g., definition, process, diagram-based). Next, recall the key concepts directly from the NCERT textbook. Structure your answer by:
- Stating the main definition or principle first.
- Breaking down complex processes like fertilisation into numbered or bulleted steps.
- Drawing neat, well-labelled diagrams exactly as shown in the textbook.
- Using precise scientific terminology as expected in the CBSE 2025-26 board exams.
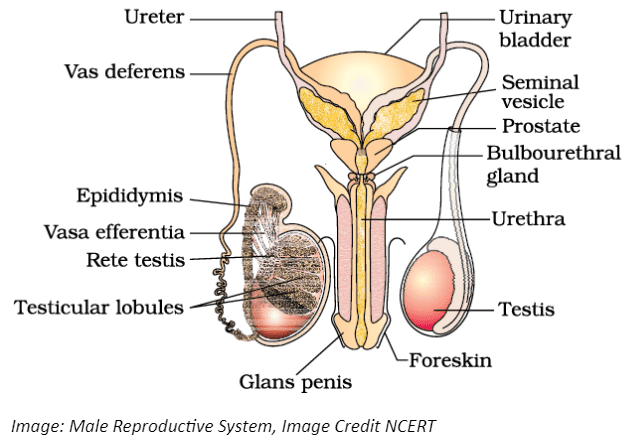
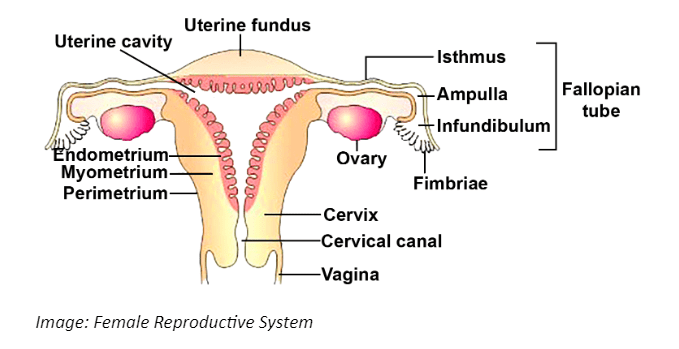
2. How should answers for diagram-based questions in Chapter 2, such as the male or female reproductive system, be structured for full marks?
For diagram-based questions, the correct method is to first draw a clean, proportional diagram with a pencil. Then, label all the essential parts accurately on one side, using straight lines. Ensure every label mentioned in the NCERT textbook (e.g., seminiferous tubules, Graafian follicle) is included. Finally, if the question asks for functions, briefly describe the role of key labelled parts below the diagram as per the CBSE pattern.
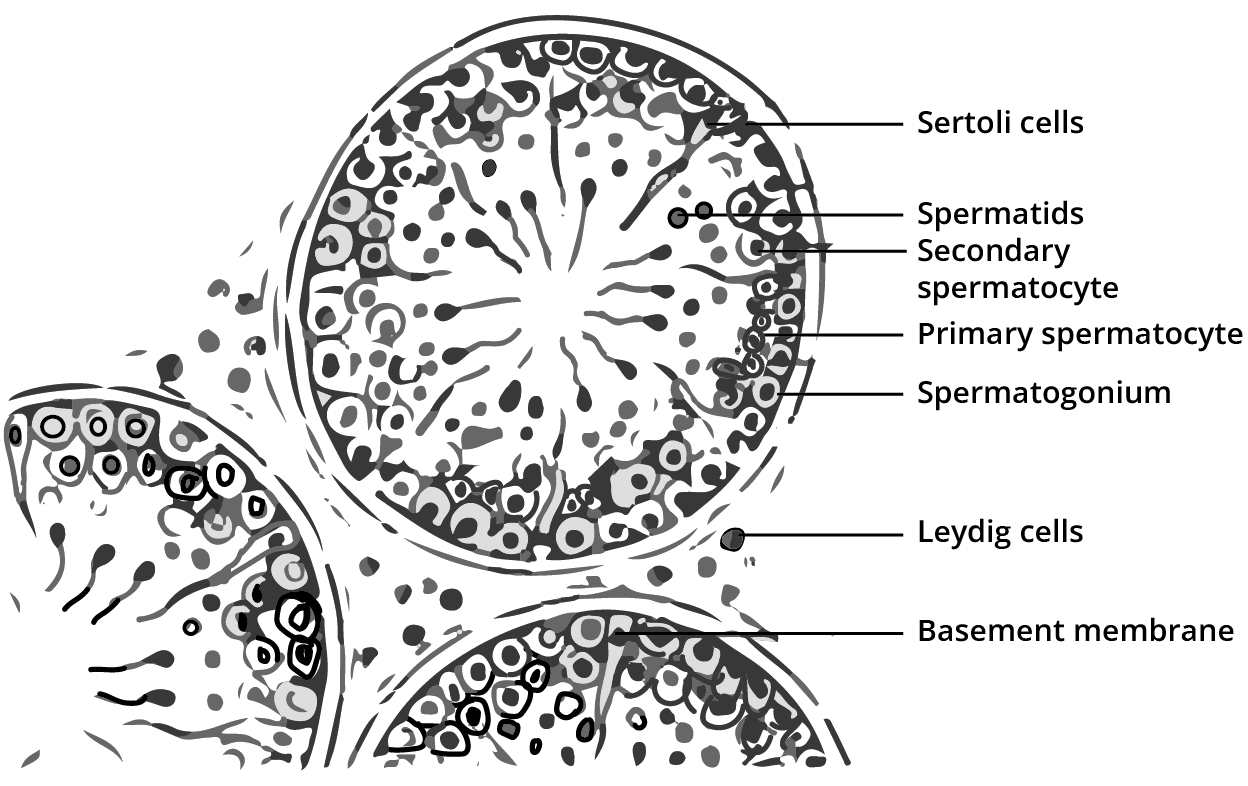
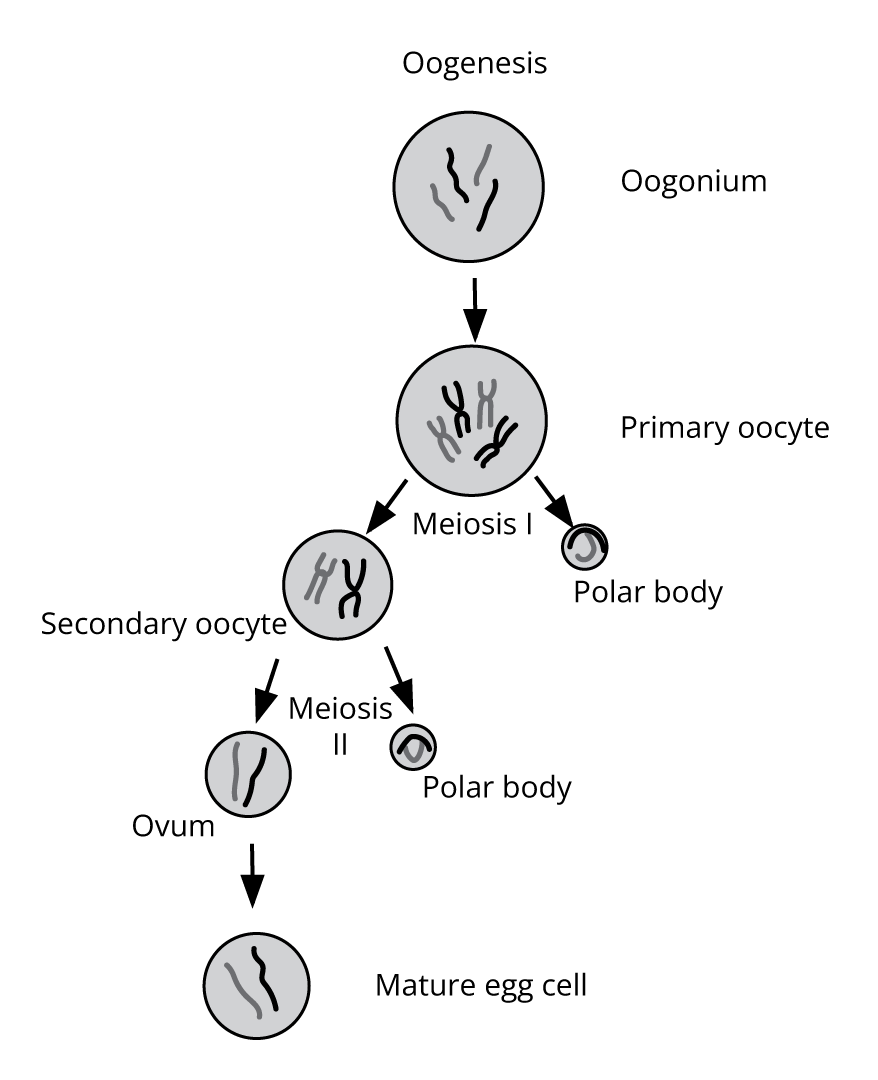
3. What is the best way to answer process-based questions, such as spermatogenesis or oogenesis, according to the NCERT Solutions format?
The correct method is to describe the process sequentially. Start with the initial cell (e.g., spermatogonium or oogonium) and describe each stage of division (mitosis, meiosis I, meiosis II) in order. Always mention the name and ploidy level (haploid/diploid) of the cells at each stage, such as primary spermatocyte, secondary oocyte, and spermatid. Conclude with the final products. Using a flowchart or numbered points can enhance clarity and match the expected answer format.
4. How do NCERT Solutions help in structuring a scientific answer for the question on why women are wrongly blamed for giving birth to daughters?
NCERT Solutions provide a precise, scientific framework for this application-based question. The correct method involves:
- Stating the chromosomal basis of sex determination in humans (XX for females, XY for males).
- Explaining that the female gamete (ovum) always carries the X chromosome.
- Clarifying that the male gamete (sperm) can carry either an X or a Y chromosome.
- Concluding logically that the sex of the child is determined by the sperm that fertilises the egg, making the genetic contribution of the father the determining factor.
5. Why is it crucial to follow the stepwise method shown in NCERT Solutions for scoring well in the CBSE board exam?
Following a stepwise method is crucial because the CBSE marking scheme often allocates marks for each specific point, keyword, or step in an answer. A structured, step-by-step answer ensures you don't miss any key points, especially in complex processes like the menstrual cycle or parturition. This approach demonstrates a clear understanding and makes your answer easy for the examiner to evaluate, thus maximising your score.
6. What are common errors to avoid when solving exercises for 'Human Reproduction', and how do NCERT Solutions help prevent them?
Common errors include mislabeling diagrams (e.g., parts of a sperm), confusing similar terms like spermiogenesis and spermiation, and writing incomplete explanations for hormonal regulation. NCERT Solutions help by providing the official, complete answers. By following them, you learn the precise terminology, the exact labels for diagrams, and the full sequence of events required for a complete answer as per the CBSE evaluation standards.
7. How should one approach HOTS (Higher Order Thinking Skills) questions in this chapter, such as the one about twins or puppies, using the NCERT Solutions methodology?
To answer HOTS questions, first identify the core NCERT concept being tested (e.g., ovulation, fertilisation). Begin your answer by stating this fundamental concept. Then, apply it to the given scenario. For a question on fraternal twins, you must explain that it results from the fertilisation of two separate ova by two separate sperms, unlike identical twins who develop from a single zygote. This shows you can apply foundational knowledge to solve a problem.
8. How do the NCERT Solutions for Chapter 2 clarify the functions of different hormones in the menstrual cycle for a high-scoring answer?
The solutions break down the complex hormonal interplay into a clear sequence. For a complete answer, you must mention the roles of four key hormones: FSH, LH, estrogen, and progesterone. The correct method is to explain their function phase-by-phase (follicular, ovulatory, luteal), stating which gland secretes each hormone and its specific effect on the ovary and uterus, following the precise cause-and-effect sequence detailed in the NCERT textbook.