
The geometry of $\left[ Ni{{\left( CO \right)}_{4}} \right]$ and $\left[ NiC{{l}_{2}}{{\left( PP{{h}_{3}} \right)}_{3}} \right]$ are:
(A) Both square planar
(B) Tetrahedral and square planar respectively
(C) Both tetrahedral
(D) square planar and tetrahedral respectively
Answer
240.6k+ views
Hint: Coordination compounds have 2 valencies, primary and secondary. The geometry of a coordination compound is decided by its secondary valency which is also called coordination number. With its help, we can find geometries of the above compounds.
Complete step by step solution:
-The given compounds are coordination compounds. Such compounds are different from other compounds. They retain their identity in the solution.
-Central metal atom in a coordination compound shows 2 types of valencies named primary and secondary valencies. Primary valency is related to the oxidation state of the compound while the secondary valency is related to the coordination number of the compound.
- The number of secondary valencies is fixed for all the metal atoms. A particular metal can have a certain coordination number only. Also, it is non-ionic or non-ionisable. It can be satisfied both by negative and neutral molecules.
-Secondary valencies are responsible for a fixed shape of the coordination compounds. The shape can be decided based on coordination number as
-The first compound has only one type of 4 ligands which is CO. The coordination number is 4 and the oxidation number is 0. According to the table, the shape can either be tetrahedral or square planar. So the shape will be decided by the type of hybridization. If the hybridization is $s{{p}^{3}}$, then the geometry will be tetrahedral. If the hybridization is $ds{{p}^{2}}$, the shape will be square planar.
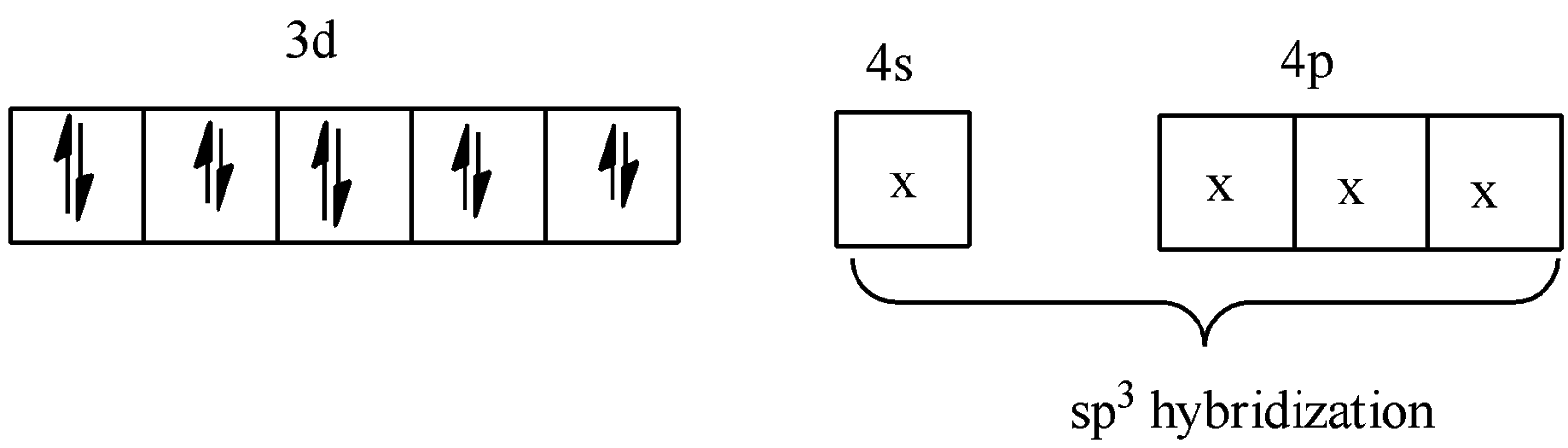
-Thus we see that the valence bond theory comes into play here also. CO is a strong ligand. The 4 pairs of electrons from the CO molecule get accommodated into the s and p hybrid orbitals as the electrons of 4s jump to the 3d orbitals of Ni. So the compound is diamagnetic and $s{{p}^{3}}$hybridized.
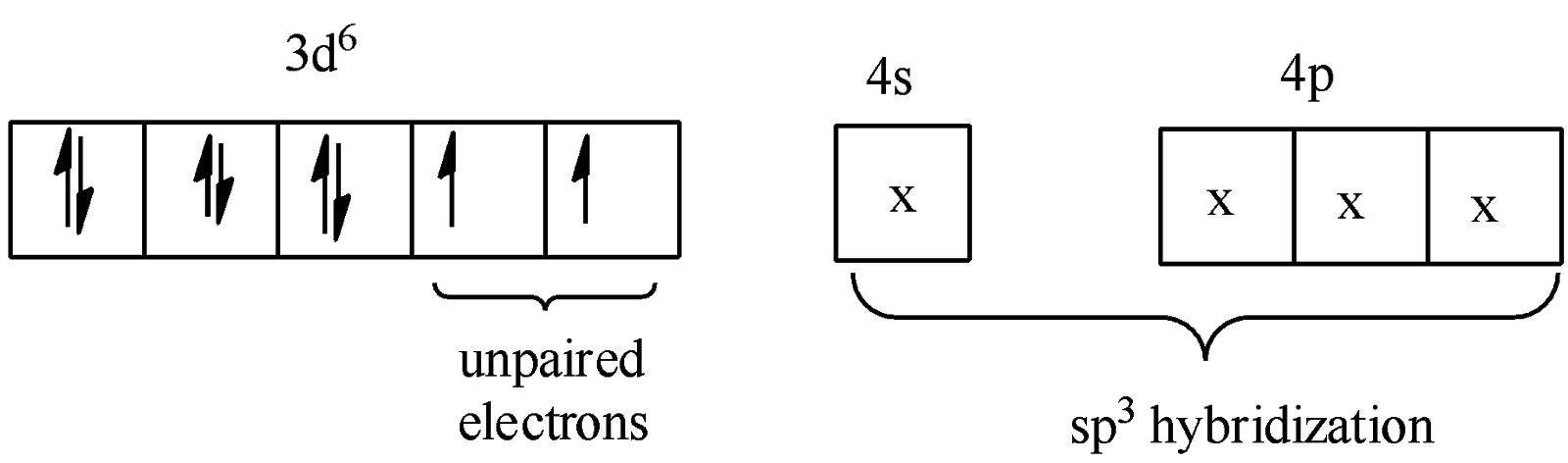
-The oxidation number of Ni in the 2nd compound is +2 and its coordination number is 4. The electronic configuration of $N{{i}^{2+}}=1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{6}}3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{6}}3{{d}^{8}}$. Due to this, hybridization is $s{{p}^{3}}$only and so the shape is tetrahedral.
Thus the correct option is C.
Note: One thing to keep in mind here is though the shape of both the compounds is the same yet they are different. The first compound is diamagnetic, has oxidation number 0 and coordination number 4. The second compound is paramagnetic, has oxidation number 2 and coordination number 4.
Complete step by step solution:
-The given compounds are coordination compounds. Such compounds are different from other compounds. They retain their identity in the solution.
-Central metal atom in a coordination compound shows 2 types of valencies named primary and secondary valencies. Primary valency is related to the oxidation state of the compound while the secondary valency is related to the coordination number of the compound.
- The number of secondary valencies is fixed for all the metal atoms. A particular metal can have a certain coordination number only. Also, it is non-ionic or non-ionisable. It can be satisfied both by negative and neutral molecules.
-Secondary valencies are responsible for a fixed shape of the coordination compounds. The shape can be decided based on coordination number as
| COORDINATION NUMBER | SHAPE |
| 2 | Linear |
| 3 | Triangular |
| 4 | Tetrahedral or square planar |
| 6 | octahedral |
-The first compound has only one type of 4 ligands which is CO. The coordination number is 4 and the oxidation number is 0. According to the table, the shape can either be tetrahedral or square planar. So the shape will be decided by the type of hybridization. If the hybridization is $s{{p}^{3}}$, then the geometry will be tetrahedral. If the hybridization is $ds{{p}^{2}}$, the shape will be square planar.
-Thus we see that the valence bond theory comes into play here also. CO is a strong ligand. The 4 pairs of electrons from the CO molecule get accommodated into the s and p hybrid orbitals as the electrons of 4s jump to the 3d orbitals of Ni. So the compound is diamagnetic and $s{{p}^{3}}$hybridized.

-The oxidation number of Ni in the 2nd compound is +2 and its coordination number is 4. The electronic configuration of $N{{i}^{2+}}=1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{6}}3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{6}}3{{d}^{8}}$. Due to this, hybridization is $s{{p}^{3}}$only and so the shape is tetrahedral.

Thus the correct option is C.
Note: One thing to keep in mind here is though the shape of both the compounds is the same yet they are different. The first compound is diamagnetic, has oxidation number 0 and coordination number 4. The second compound is paramagnetic, has oxidation number 2 and coordination number 4.
Recently Updated Pages
Know The Difference Between Fluid And Liquid

Difference Between Crystalline and Amorphous Solid: Table & Examples

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

Hess Law of Constant Heat Summation: Definition, Formula & Applications

Disproportionation Reaction: Definition, Example & JEE Guide

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 - Hydrocarbons - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 - Thermodynamics - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 - Equilibrium - 2025-26

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength




