
Which of the following Compounds does not exhibit tautomerism?
A) ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_2}$
B) ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_2}$
C) ${{\text{C}}_6}{{\text{H}}_5}{\text{CH = CH - OH}}$
D) ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{OH}}$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The essential condition for tautomerism is that there should be an electronegative atom present bonded by a double or triple bond and one alpha-hydrogen must be present on a saturated carbon.${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{OH}}$ is called ethyl alcohol. It contains a single bond between carbon atoms and is a saturated molecule but does not contain alpha hydrogen. Hence it does not show tautomerism.
Step-by-Step Explanation: Tautomerism is a phenomenon in which a chemical compound exists into $2$ or more interconvertible structures which differ in the position of hydrogen. The isomers formed are called tautomers as they have the same molecular formula but different structural formula. They change to give more stability to the compound. They exist in equilibrium with each other. The most common tautomerism exists between keto-enol pairs in which one structure is ketone and the other is –enol form.
The tautomers of nitro-methane, nitro-ethane and${{\text{C}}_6}{{\text{H}}_5}{\text{CH = CH - OH}}$ is given as-
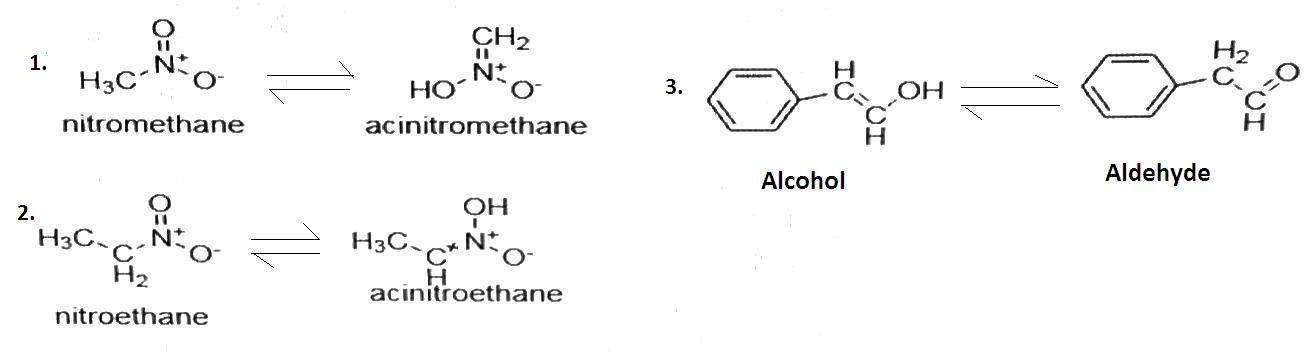
Here, ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{OH}}$ is a saturated molecule as it only has single bond so it cannot change its structure. Hence it does not exhibit tautomerism.
Hence the answer is ‘D’.
Note: Tautomerism occurs due to the more stability of keto form. Keto-enol tautomerism is the most common tautomerism. Both tautomers (keto and enol) are interconvertible into each other. It is possible only in the compounds that contain polar molecules and weakly acidic functional groups.
Step-by-Step Explanation: Tautomerism is a phenomenon in which a chemical compound exists into $2$ or more interconvertible structures which differ in the position of hydrogen. The isomers formed are called tautomers as they have the same molecular formula but different structural formula. They change to give more stability to the compound. They exist in equilibrium with each other. The most common tautomerism exists between keto-enol pairs in which one structure is ketone and the other is –enol form.
The tautomers of nitro-methane, nitro-ethane and${{\text{C}}_6}{{\text{H}}_5}{\text{CH = CH - OH}}$ is given as-

Here, ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{OH}}$ is a saturated molecule as it only has single bond so it cannot change its structure. Hence it does not exhibit tautomerism.
Hence the answer is ‘D’.
Note: Tautomerism occurs due to the more stability of keto form. Keto-enol tautomerism is the most common tautomerism. Both tautomers (keto and enol) are interconvertible into each other. It is possible only in the compounds that contain polar molecules and weakly acidic functional groups.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




