
Show how you will synthesise:
(i) 1-Phenylethanol from a suitable alkene.
(ii) Cyclohexylmethanol using an alkyl halide by a \[S{N^2}\]reaction.
(iii) Pentan-1-ol using a suitable alkyl halide.
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: These reactions are either electrophilic addition or nucleophilic substitution reaction. In an electrophilic addition reaction, a $\pi $ bond is broken and two new $\sigma $ bonds are formed. In nucleophilic substitution reaction, a leaving group is replaced by an electron rich compound.
Complete step by step solution:
Synthesis of the following reaction:
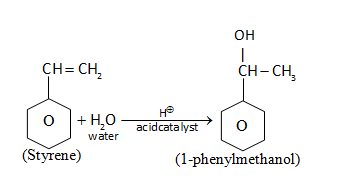
(i) 1-phenylethanol from suitable alkene.
Alkene is treated with \[{H_2}O\]in the presence of acid (acid catalyzed hydrolysis) to give 1-phenylmethanol
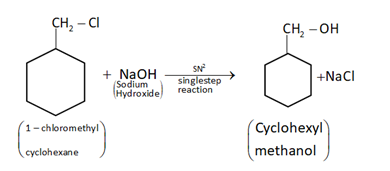
(ii) Cyclohexylmethanol using an alkyl halide by a \[S{N^2}\] reaction.
When chloromethylcyclohexane is treated with sodium hydroxide, then it will give cyclohexylmethanol by \[S{N^2}\]mechanism.
(iii) Pentan-1-ol using a suitable alkyl halide.
When chloropentane is treated with aq.$NaOH$, then it will give pentan-1-ol.
\[\mathop {C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_2}}\limits_{\left( {1 - Chloropen\tan e} \right)} - Cl + \mathop {aq.NaOH}\limits_{\left( \begin{subarray}{l}
Sodium \\
Hydroxide
\end{subarray} \right)} \xrightarrow{{}}\mathop {C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_2} - OH + NaCl}\limits_{\left( {Pen\tan - 1 - ol} \right)} \]
Note: Alpha methylbenzyl alcohol appears as a colourless liquid which is insoluble in water and less dense than water. Cyclohexylmethanol is an organic compound and these reactions are bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reactions. 1 - Pentanol is a colourless liquid with a distinctive aroma. It is the straight- chain form of amyl alcohol and the hydroxyl group is the active site of many reactions. Electrophilic addition reactions are an important class of reaction that allow the inter conversion of $C = C$and $C \equiv C$ into a range of important functional groups including alkyl halides and alcohols. Addition reaction is the reverse of elimination reactions and in nucleophilic substitution reactions, the stronger nucleophile replaces a weaker nucleophile.
Complete step by step solution:
Synthesis of the following reaction:
(i) 1-phenylethanol from suitable alkene.
Alkene is treated with \[{H_2}O\]in the presence of acid (acid catalyzed hydrolysis) to give 1-phenylmethanol

(ii) Cyclohexylmethanol using an alkyl halide by a \[S{N^2}\] reaction.
When chloromethylcyclohexane is treated with sodium hydroxide, then it will give cyclohexylmethanol by \[S{N^2}\]mechanism.

(iii) Pentan-1-ol using a suitable alkyl halide.
When chloropentane is treated with aq.$NaOH$, then it will give pentan-1-ol.
\[\mathop {C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_2}}\limits_{\left( {1 - Chloropen\tan e} \right)} - Cl + \mathop {aq.NaOH}\limits_{\left( \begin{subarray}{l}
Sodium \\
Hydroxide
\end{subarray} \right)} \xrightarrow{{}}\mathop {C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_2} - OH + NaCl}\limits_{\left( {Pen\tan - 1 - ol} \right)} \]
Note: Alpha methylbenzyl alcohol appears as a colourless liquid which is insoluble in water and less dense than water. Cyclohexylmethanol is an organic compound and these reactions are bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reactions. 1 - Pentanol is a colourless liquid with a distinctive aroma. It is the straight- chain form of amyl alcohol and the hydroxyl group is the active site of many reactions. Electrophilic addition reactions are an important class of reaction that allow the inter conversion of $C = C$and $C \equiv C$ into a range of important functional groups including alkyl halides and alcohols. Addition reaction is the reverse of elimination reactions and in nucleophilic substitution reactions, the stronger nucleophile replaces a weaker nucleophile.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




