




Role of Government in Economy
Government Economics introduces you to the field of government and economics, a new area aimed at better understanding the role and behaviour of governments in the economy. Government intervention in the economy is inevitable as certain roles and responsibilities cannot be assumed by the private sector. Governments are meant to guide and direct the pace of economic activity in the country. It also needs to ensure stable growth, high employment, and price stability. Additionally, governments need to adjust tax rates and spending so that economic growth can either accelerate or slow down.
The government's invisible hand in the economy becomes apparent when governments intervene to correct identified deficiencies in market mechanisms. Governments keep private companies out by owning and operating certain companies, such as the military. The impact of government policies on business is positive on the note that it regulates businesses such as telephone companies, imposes taxes on citizens, and distributes profits to citizens. The role of government in the economy also includes the use of fiscal and monetary power to promote economic growth and development to adjust business cycles as needed also comes under the role of government.
Fiscal Functions of Government
Modern economists believe that government has three fiscal functions:
Allocation Function
Distribution Function
Stabilisation Function
Allocation Function: In a market economy, the allocation of production resources is generally made by the market mechanism to the price mechanism, which is not always optimal. Governments use their fiscal policies to optimise the desired allocation of productive resources or the allocation among different products. A pricing mechanism is a system in which the allocation of resources among various goods and services is based on relative market prices. Market mechanisms generally fail to achieve the desired results. Governments must intervene in the market through fiscal policy to achieve desired production, consumption, and distribution levels. Governments use tax policies, subsidy programs, regulations, restrictions, and licensing policies to achieve desired results. Through policies, the government allocates the resources necessary for the proper development of the economy.
Distributive Function: Due to monopoly inheritance laws, the market and price mechanisms cannot equitably distribute wealth and income. Because the welfare state is responsible for reducing economic inequality, the government seeks to reduce large economic inequalities through taxation. It uses progressive taxation, subsidies, transfer payments, public distribution systems, and many welfare programs for the poor to reduce economic and wealth inequality.
Stabilising Function: The nature of the market economy creates trading and price cycles. These cycles make the economy unstable and uncomfortable. Therefore, the government must reduce economic instability and stabilise the economy more and more. Governments use tax policies, fee policies, spending policies, fiscal deficits, public borrowing, etc. to control economic fluctuations in the economy.
Economic Policies
To ensure strong economic growth, there are two main economic policies through which the government may respond to economic activity.
Fiscal Policy
Monetary Policy

Fiscal Policy
Fiscal policy
Governments can also issue policies to adjust spending, change tax rates, or introduce tax incentives. When it comes to government budgets, governments decide whether to spend more than they plan to raise. This process of assessing public spending aims to promote economic prosperity or cool an overheated economy. Instead of focusing on how the government spends money, general fiscal policy is about how the government raises money. Offering tax incentives, additional tax credits, or tax relief relieves the financial burden on citizens and promotes economic growth. Repeal of favourable tax laws and tax increases slow down economic activity.
Monetary Policy
One of the most common ways governments influence a country's economic activity is by adjusting borrowing costs. Most often, this is done by lowering or raising the Federal Funds Rate, the target interest rate that affects short-term interest rates on debt such as consumer loans and credit cards. The Federal Reserve raises the federal funds rate to curb economic growth and lowers the federal funds rate to boost economic growth. Another form of monetary policy is the buying and selling of government securities by the Federal Reserve. When the Federal Reserve buys securities from a bank, it injects money into that bank to increase the money supply. Alternatively, you can sell your stocks to eliminate cash and reduce the money supply.
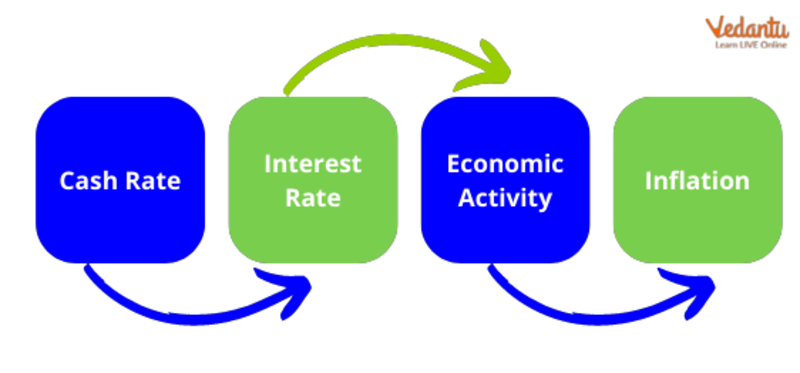
Monetary Policy
Impact of Government Policies on Business
The government sets many policies that guide businesses. The impact of government policies on business is highlighted below:
Governments can make tax policy changes that lead to changes in taxes, trade, subsidies, regulations, interest rates, licences, etc. Organisations must be flexible enough to accommodate changing rules and policies.
Government policies can affect the taxes communities pay, pensions, immigration status and laws, penalties for breaking the rules, the education system, trade and commerce in the economy.
Governments implement policies that change social behaviour in the business environment. Governments can make agreements to develop new technologies that bring about the necessary changes.
Declining private investment reduces the production of goods and services. This, in turn, could lead to job cuts. Government policies can affect interest rates, and higher interest rates increase borrowing costs.
Case Study
State the main objectives of Fiscal policy in India.
Ans: Fiscal policy in India is the driving force that helps determine how much money the government spends to support economic activity and how much income it collects from the system to keep the wheels of the economy spinning. In recent years, the importance of fiscal policy has increased to realise rapid economic growth in India and worldwide. The objectives are listed below:
Achieving rapid economic growth is one of the key fiscal policy objectives the Government of India set. Fiscal policy, along with monetary policy, plays an important role in managing a country's economy.
A country's government steers the economy through fiscal policy by controlling the flow of tax revenue and public spending. A government is in surplus if it receives more income than it spends and a deficit if it spends more than tax and non-tax income.
Summary
The government's invisible hand in the economy becomes apparent when governments intervene to correct identified deficiencies in market mechanisms. Governments keep private companies out by owning and operating certain companies, such as the military. Governments can influence the economy's performance through combined monetary and fiscal policies. Monetary policy refers to central banks' actions to influence the amount of money and credit in the economy. In contrast, fiscal policy refers to government decisions regarding taxes and spending. These two policy areas affect the economy through different mechanisms.
FAQs on The Role of Government in the Economy
1. What is the role of government in the economy?
The government plays a significant role in the economy by guiding and influencing economic activity through laws, policies, and public services. Its involvement helps ensure stable growth, correct market failures, and promote public welfare. Through regulation, taxation, spending, and monetary policy, government actions aim to balance economic efficiency with fairness. By maintaining a stable economic environment and protecting consumers and workers, the government supports both business growth and social well-being. Ultimately, active government participation is vital for a healthy and balanced economy.
2. Why does the government regulate markets?
Governments regulate markets to correct problems that can arise when businesses and individuals act purely out of self-interest. These issues, known as market failures, may include monopolies, unsafe products, or environmental harm. Regulations protect consumers, ensure fair competition, and maintain stable financial systems. By setting rules and standards, the government prevents abuses and risks that could damage the economy as a whole. This oversight is necessary to safeguard public interest, encourage ethical business practices, and promote long-term economic stability.
3. How does government spending affect the economy?
Government spending is a major tool for managing economic growth and stability. By investing in public goods such as infrastructure, education, and healthcare, the government directly stimulates economic activity. Increased spending can create jobs, boost demand for goods and services, and foster development. Conversely, reducing spending may slow economic growth. Through well-planned government expenditure, the state can address inequality, support essential services, and respond to recessions or emergencies, playing a vital role in sustaining national prosperity.
4. What are the main forms of government intervention in the economy?
Government intervention takes several forms to influence and manage the economy. The most common types include:
- Regulation: Setting rules for businesses to promote safety and fairness
- Taxation: Collecting revenue for public services and redistribution
- Subsidies and grants: Supporting industries or groups in need
- Public goods provision: Funding things like roads and schools
- Monetary and fiscal policy: Managing the money supply and government spending
Each type of intervention is used to achieve specific economic objectives, such as stability, growth, or equity.
5. How do taxes play a role in economic management?
Taxes are a primary tool used by the government to fund public services and influence economic behavior. They allow governments to gather revenue for education, healthcare, and infrastructure, which support overall economic development. Taxes can also be structured to reduce inequality by redistributing wealth or to discourage harmful activities through excise taxes. By adjusting tax rates and policies, the government can steer investment, control inflation, and sustain a vibrant economy while ensuring everyone shares in funding common goods.
6. What is the difference between a free market economy and a mixed economy?
A free market economy is one where private individuals and businesses freely make economic decisions with minimal government intervention. In contrast, a mixed economy combines features of both free markets and government involvement. In a mixed system, the government provides public goods, regulates certain industries, and sometimes owns key sectors while private businesses operate competitively elsewhere. Most modern economies are mixed, as this model balances economic freedom with protections for public welfare and market stability.
7. How does the government promote economic growth?
Governments promote economic growth by encouraging investment, innovation, and productivity through supportive policies and targeted spending. Some key strategies include:
- Infrastructure investment: Building roads, bridges, and utilities to support business growth
- Education and training: Developing a skilled workforce
- Research funding: Supporting scientific and technological advancement
- Incentives for business: Tax breaks or grants to encourage expansion
- Stable legal environment: Enforcing contracts and property rights
These measures create a strong foundation for long-term prosperity and higher living standards.
8. What is fiscal policy and how does it influence the economy?
Fiscal policy refers to government decisions on taxation and spending, aiming to influence economic activity. By adjusting tax levels and public expenditure, governments can stimulate growth or cool down an overheating economy. For example, increasing spending during a recession can boost demand and create jobs, while cutting back during a boom can help control inflation. Fiscal policy is vital for managing business cycles and supporting stable, sustained economic development.
9. Why is government involvement important during economic crises?
During economic crises, private markets often fail to restore stability on their own. Government intervention becomes essential to prevent deep recessions, rising unemployment, and widespread hardship. By using emergency spending, stabilizing financial systems, and supporting affected industries, the government can help restore confidence and economic activity. This involvement ensures basic needs are met and creates conditions for recovery. Effective government action often shortens the duration and lessens the severity of economic downturns.
10. How does the government address income inequality?
The government addresses income inequality through policies that redistribute wealth and support disadvantaged groups. Common tools include progressive taxation, where higher earners pay a larger share, and social welfare programs such as unemployment benefits, food assistance, or subsidized healthcare. By investing in public education and affordable housing, governments can help level the playing field. Addressing income inequality promotes social cohesion and ensures more people benefit from economic growth.
11. What are the risks of too much government intervention in the economy?
While government intervention can solve many economic issues, excessive involvement may create new problems. Overregulation can reduce competition, limit innovation, and raise business costs. Heavy taxation might discourage investment and work incentives. State-owned industries are sometimes less efficient than private ones. Finding the right balance is crucial, as too much control may lead to inefficiency, bureaucracy, and slower economic growth. A healthy economy usually requires both government oversight and space for private enterprise.
12. How does government regulation protect consumers and workers?
Government regulation aims to create safe, fair, and trustworthy markets for everyone involved. Consumer protection laws ensure products and services are safe, accurately described, and reasonably priced. Workplace regulations set standards for wages, health and safety, and working conditions. These rules prevent exploitation, reduce risks of accidents, and promote dignity at work. Regulatory oversight is crucial for building public trust and supporting a stable economy, making markets work better for all.























