Class 10 Social Science Geography Chapter 5 Summary Notes PDF Download

FAQs on CBSE Notes Class 10 social science geography Chapter 5 - Minerals and Energy Resources - 2025-26
1. What are the key concepts to summarise from Chapter 5, Minerals and Energy Resources?
When revising this chapter, focus on a few core areas. Start with the definition of a mineral and its classification into metallic and non-metallic types. Then, review the major mineral belts in India. For energy, summarise the key differences between conventional sources (like coal and petroleum) and non-conventional sources (like solar and wind). Finally, understand the importance of the conservation of all these resources.
2. How are minerals broadly classified for a quick revision?
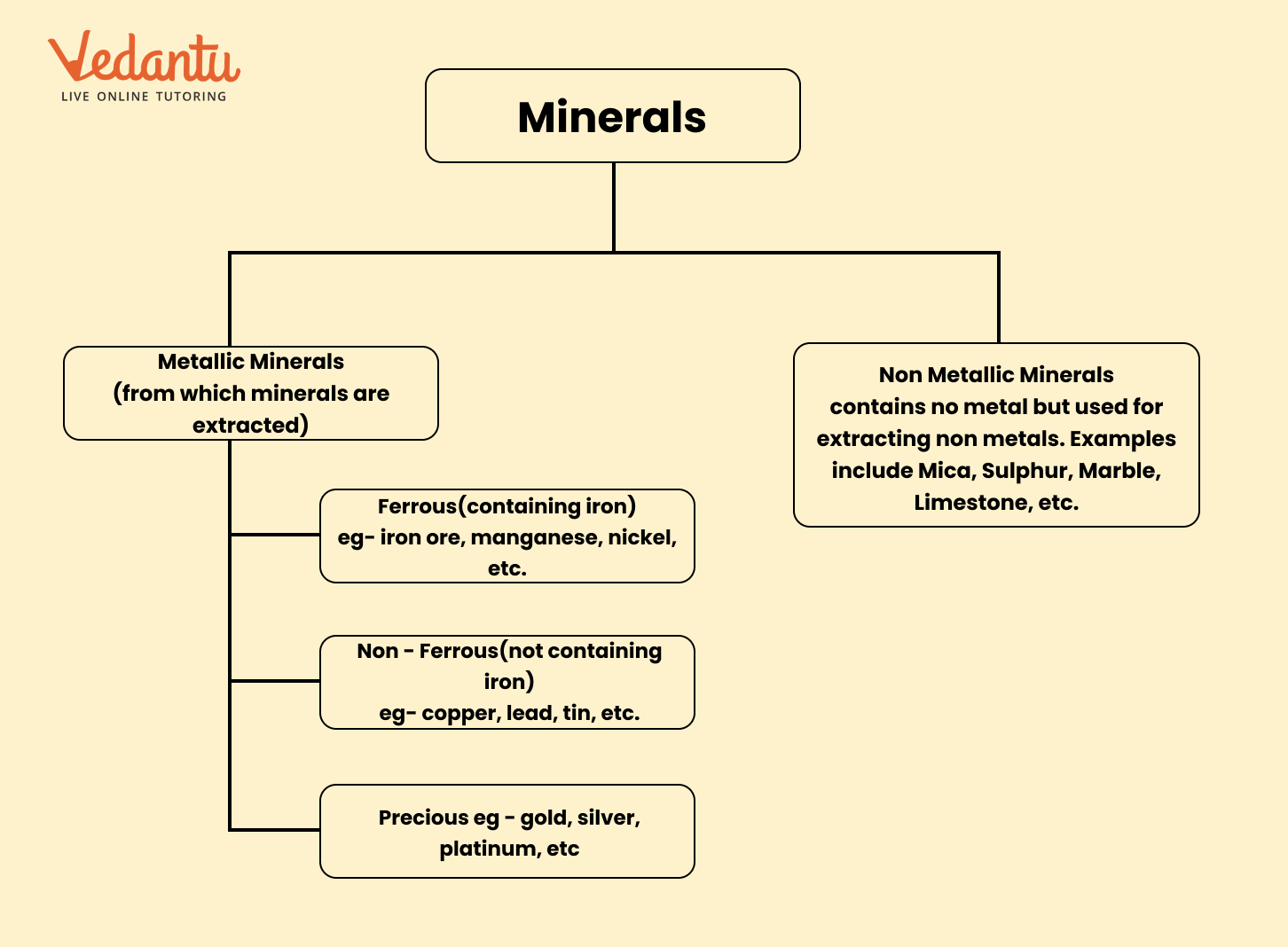
For a quick recap, minerals are classified into three main categories based on their composition:
- Metallic Minerals: These contain metal. They are further divided into:
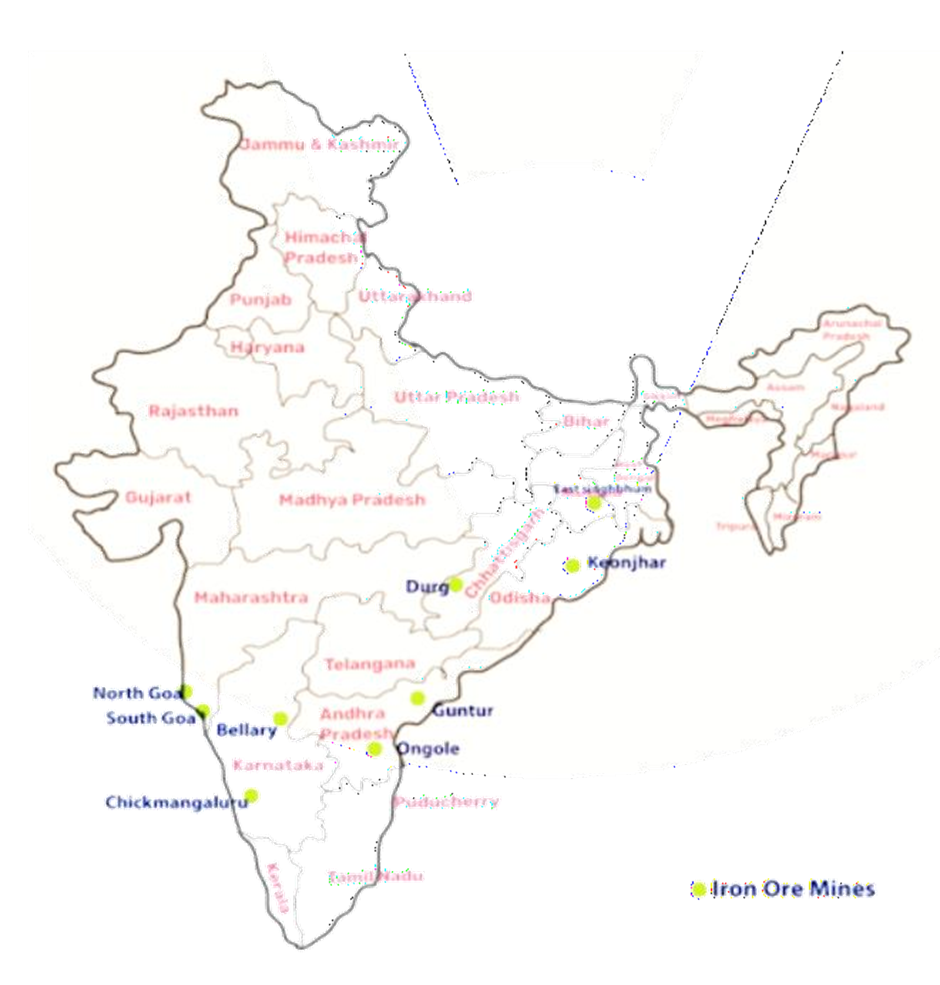
- Ferrous: Minerals containing iron, such as iron ore and manganese.
- Non-ferrous: Minerals containing metals other than iron, such as copper and bauxite.
- Non-Metallic Minerals: These do not contain metals, such as mica and limestone.
- Energy Minerals: These are fossil fuels used to generate power, like coal, petroleum, and natural gas.
3. What is the main difference between ferrous and non-ferrous minerals? Provide key examples.
The primary difference lies in the presence of iron. Ferrous minerals contain iron as a key component and are crucial for the iron and steel industry. Key examples include iron ore, manganese, and chromite. In contrast, non-ferrous minerals do not have iron content and are valued for other properties. Examples include copper (for conductivity) and bauxite (the ore of aluminium).
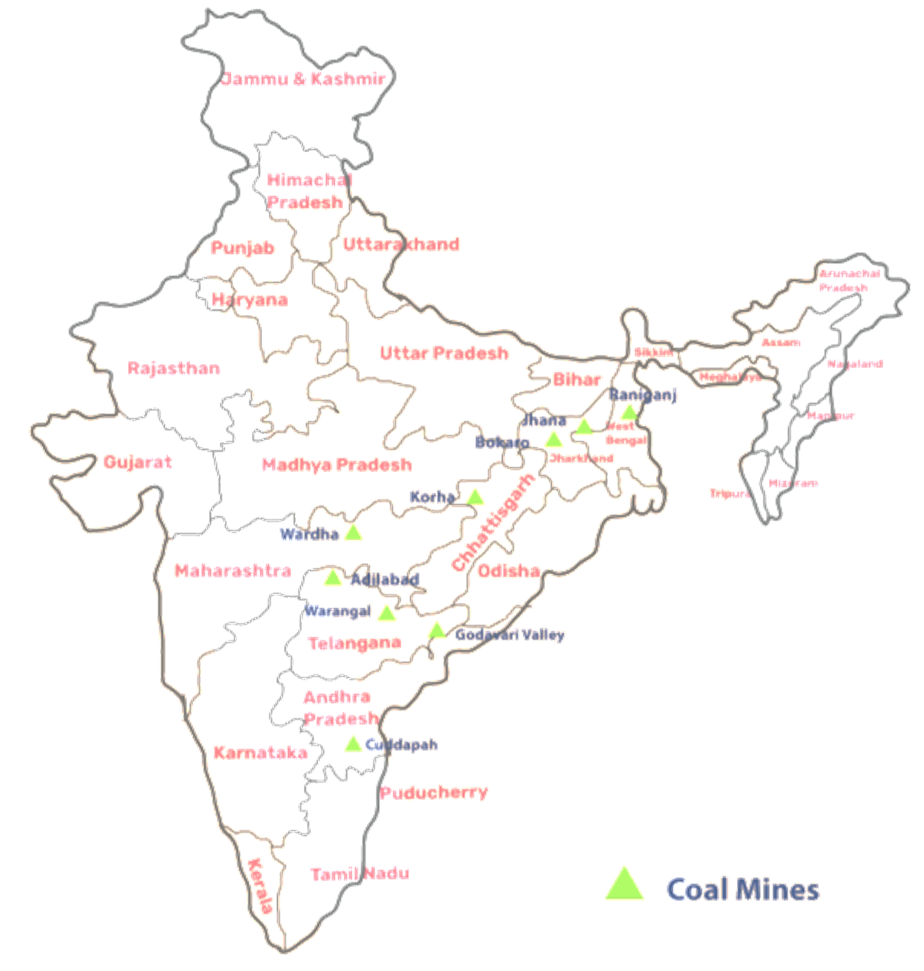
4. Why is coal considered a crucial conventional energy resource in India?
Coal is a crucial conventional energy resource in India primarily because it is found in abundance and has been the backbone of the country's industrial development. It is the main source for generating thermal power, which supplies a significant portion of India's electricity. It is also a vital raw material for industries like iron and steel and is used as a domestic fuel in many parts of the country.
5. How can one effectively distinguish between conventional and non-conventional energy sources?
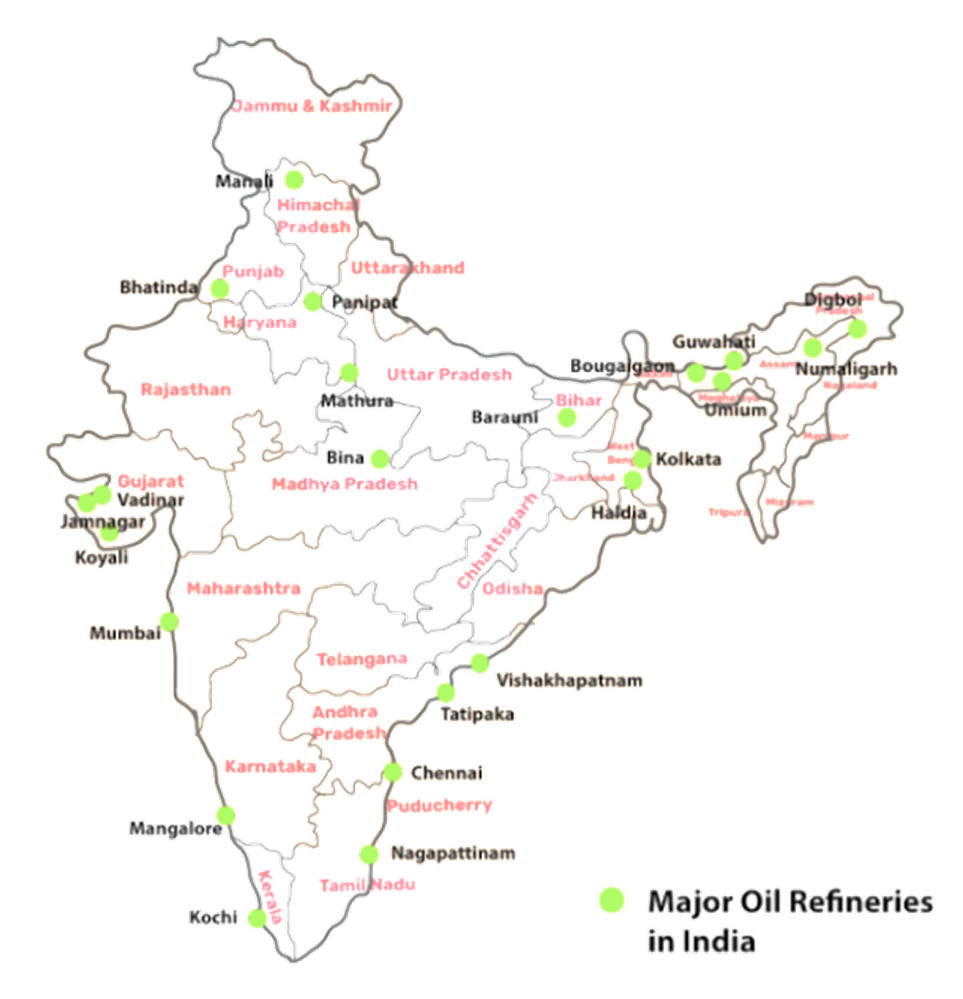
To effectively distinguish between them, focus on three points: renewability, environmental impact, and usage history. Conventional sources, like coal and petroleum, are non-renewable (finite), generally cause more pollution, and have been in large-scale commercial use for a long time. Non-conventional sources, like solar, wind, and geothermal energy, are renewable (inexhaustible), largely eco-friendly, and their large-scale use is more recent.
6. What makes non-conventional energy sources like solar and wind a key focus for the future?
Non-conventional energy sources are a key focus for the future because they offer a solution to the problems created by fossil fuels. They are sustainable and renewable, meaning they won't run out. Critically, they are eco-friendly, producing little to no greenhouse gas emissions, which helps combat climate change. Their increasing affordability and India's geographical advantages (ample sunlight and long coastline) make them essential for achieving energy security.
7. Beyond their definitions, what is the practical importance of non-ferrous minerals like copper and bauxite?
Their practical importance lies in their unique properties. Copper is highly valued in the electrical and electronics industries because it is an excellent conductor of electricity and is very ductile (can be drawn into wires). Bauxite is the source of aluminium, a metal prized for being both strong and lightweight. This makes aluminium essential for manufacturing aircraft, automobiles, and even everyday items like beverage cans.
8. Why is the conservation of minerals and energy resources a critical concept in this chapter?
Conservation is a critical concept because the minerals and conventional energy sources discussed are finite and non-renewable. They have taken millions of years to form and are being consumed at a rapid rate. Without conservation, these resources will be depleted, hindering industrial and economic development for future generations. Conservation ensures sustainable development by using resources judiciously and exploring alternatives.