Chapter-wise Class 12 Business Studies Questions and Answers Free PDF Download
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Business Studies - 2025-26
1. What is included in the NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business Studies for the 2025-26 session?
These NCERT Solutions provide comprehensive, step-by-step answers for all the in-text and end-of-chapter questions from the Class 12 Business Studies NCERT textbook. They are fully aligned with the latest CBSE 2025-26 syllabus and cover every topic, ensuring you have the correct methodology for solving all problems.
2. How many chapters are covered in the latest NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business Studies?
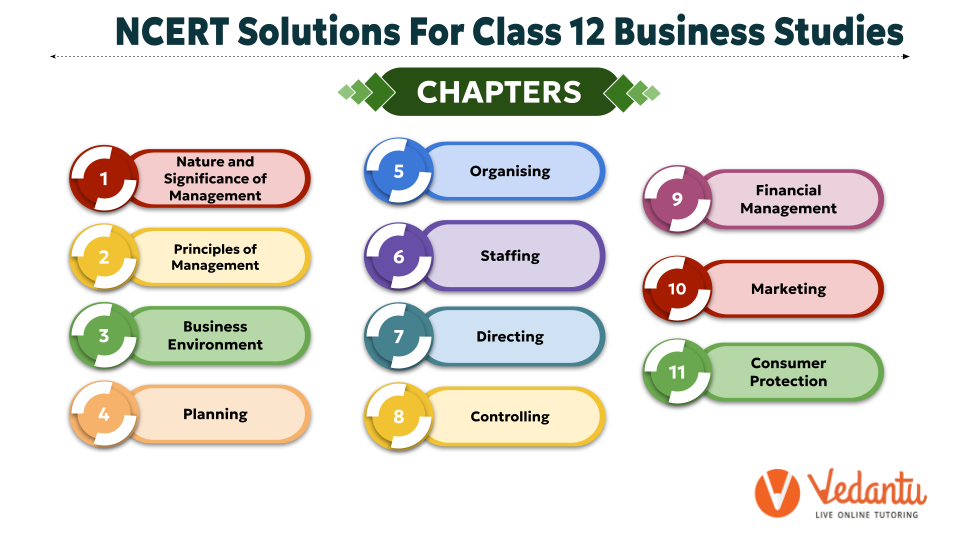
The NCERT Solutions for the 2025-26 academic year cover all 11 chapters prescribed by the CBSE. The solutions are organised chapter-wise to make studying systematic and easy. The two main parts are:
- Part A: Principles and Functions of Management (Chapters 1-8)
- Part B: Business Finance and Marketing (Chapters 9-11)
3. How should I use these NCERT Solutions to solve textbook questions effectively?
For maximum benefit, follow this approach: First, thoroughly read the relevant chapter from your NCERT textbook to understand the concepts. Next, attempt to answer the questions on your own. Finally, use the Vedantu NCERT Solutions to verify your answers, understand the correct step-wise format required by CBSE, and identify any conceptual gaps in your understanding.
4. Which chapters have been removed from the Class 12 Business Studies syllabus?
According to the rationalised syllabus by NCERT, two chapters have been removed and are no longer part of the curriculum for the board exams. These are Chapter 11: Financial Markets and Chapter 12: Entrepreneurship Development from the previous editions. Our solutions reflect this updated structure.
5. Do these NCERT Solutions just provide the final answer or explain the solving method?
These solutions focus on explaining the correct methodology. Each answer is presented in a detailed, step-by-step format, showing how to arrive at the conclusion. This is crucial for understanding the concepts and learning how to structure your answers correctly in the board exams, not just for memorising the final outcome.
6. How do the NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business Studies help with case study-based questions?
The solutions for case studies are particularly useful as they demonstrate how to:
- Identify the core business problem or principle hidden in the case.
- Quote relevant lines from the case study to support your answer.
- Structure the answer according to the CBSE pattern.
- Apply theoretical concepts to practical, real-world business scenarios, a skill essential for scoring high marks.
7. How do these solutions align with the CBSE's marking scheme for Business Studies?
The answers are framed by subject matter experts to align perfectly with the CBSE marking scheme. They are concise, include the necessary keywords that examiners look for, and are structured properly with headings and bullet points where needed. This helps you learn how to write answers that fetch full marks for questions of varying weights (1, 3, 4, or 6 marks).
8. Is it challenging to score well in Class 12 Business Studies, and how can these solutions help?
Class 12 Business Studies requires a clear understanding of concepts and the ability to apply them. It can be challenging if the fundamentals are not clear. These NCERT solutions make it easier by breaking down complex topics into simple, understandable answers. By consistently practising with these solutions, you can build a strong foundation and gain confidence, making it much easier to score high marks.
9. Can using NCERT Solutions help clarify the difference between similar concepts like 'delegation' and 'decentralisation'?
Yes, absolutely. The solutions are designed to provide clear and precise explanations. When answering questions related to confusing or similar-sounding concepts (like delegation vs. decentralisation, or different leadership styles), the answers highlight the subtle yet crucial differences in definition, scope, and application, thereby strengthening your conceptual clarity.
10. Are NCERT solutions sufficient for getting a top score in the Class 12 Business Studies board exam?
Mastering the NCERT textbook and its solutions is the most critical step and forms the foundation for your preparation, as a majority of the board exam questions are based directly on them. However, for a top score, it is advisable to supplement your preparation by solving CBSE sample papers and previous years' question papers to understand the exam pattern and time management.