Business Studies Notes for Chapter 8 Controlling Class 12 - FREE PDF Download


FAQs on Controlling Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26
1. What are the main concepts highlighted in Controlling Class 12 Revision Notes for Business Studies?
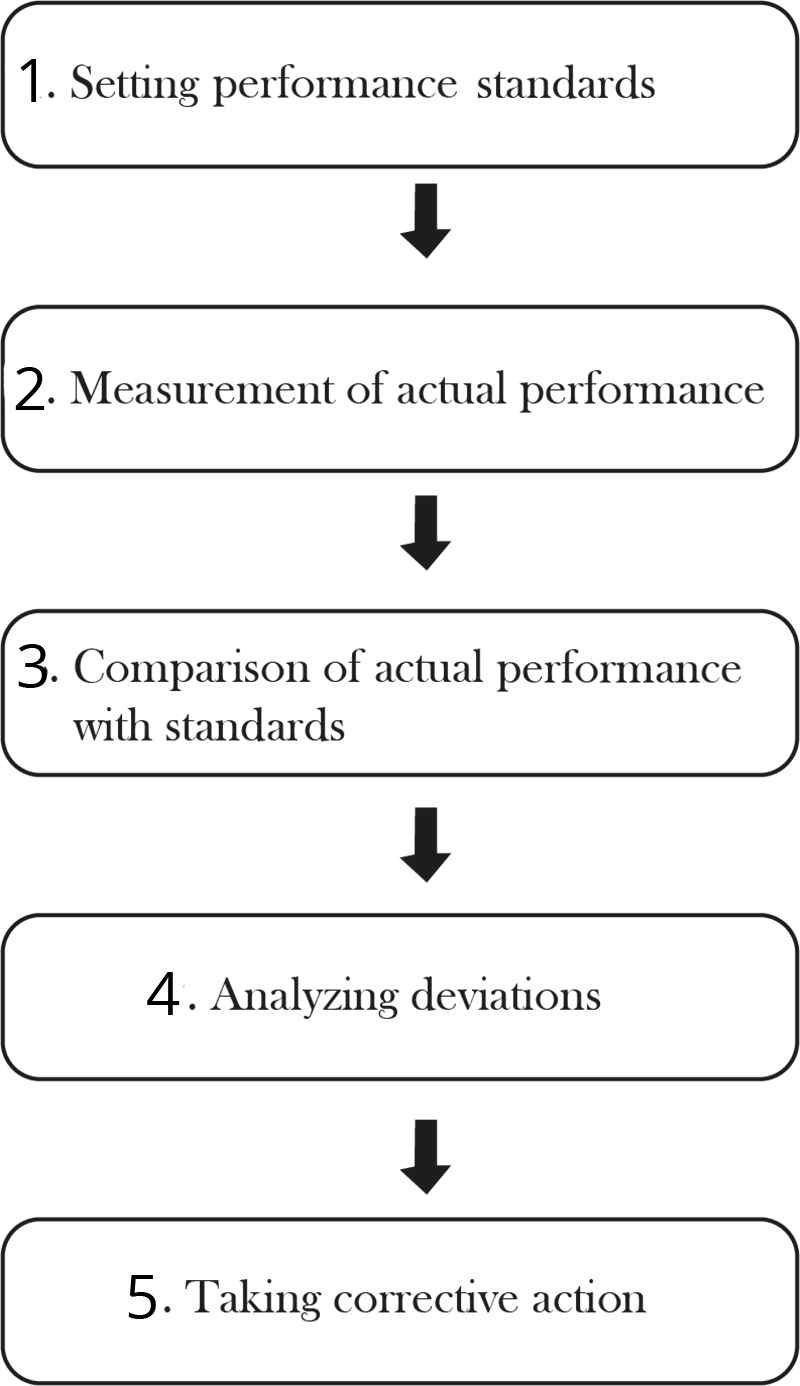
The main concepts emphasised include the meaning of controlling, its importance in management, the controlling process (setting standards, measuring performance, correcting deviations), and the relationship between planning and controlling. The notes also discuss the features and limitations of controlling as per the CBSE 2025–26 syllabus.
2. How does the process of controlling ensure successful management in organisations?
Controlling ensures that actual performance is compared with set standards. When deviations are found, corrective actions are taken to align results with the goals. This continuous cycle helps achieve organisational objectives and maintains efficiency.
3. Why is controlling considered a continuous and forward-looking managerial function?
Controlling is continuous because it involves regular monitoring and assessment of performance at every stage. It is forward-looking because the insights gained help managers adjust future plans and strategies, ensuring ongoing improvement and goal achievement.
4. What are the limitations of the controlling function as discussed in Class 12 notes?
The main limitations include:
- Difficulty in setting quantitative standards for all areas
- Limited control over external factors like government policies and competition
- Resistance from employees to monitoring
- Expense of implementing control systems
5. What is the relationship between planning and controlling in business organisations?
Planning and controlling are interdependent functions. Planning sets the direction and standards, while controlling measures actual results against these plans. Effective controlling can highlight flaws in planning and lead to better future plans, making the two functions inseparable for successful management.
6. How can students use revision notes for Chapter 8 Controlling effectively before exams?
Students should focus on summarised key points, create concept maps for processes like steps in controlling, revisit important definitions, and use the notes for quick revision sessions. Frequent review aids in memory retention and builds exam confidence.
7. What are the critical features of the controlling function that help in achieving organisational goals?
The controlling function is goal-oriented, pervasive at all levels, continuous, action-oriented, and dependent on planning. By regularly tracking performance, it keeps everyone aligned with organisational objectives.
8. Why might employees resist the controlling process, and how can this challenge be managed?
Employees may resist controlling due to perceptions of strict monitoring or lack of trust. This can impact motivation and morale. To manage this, managers should communicate the purpose of controlling clearly, involve employees in goal-setting, and provide constructive feedback rather than criticism.
9. How does effective controlling contribute to efficient resource management?
By monitoring the use of resources against planned standards and taking corrective actions promptly, controlling helps minimise waste, optimise costs, and ensure that resources are allocated where they are most needed for organisational efficiency.
10. What changes should Class 12 students be aware of in the 2025–26 CBSE syllabus for the Controlling chapter?
As per the CBSE 2025–26 syllabus, the topic "Techniques of Controlling" has been deleted from Chapter 8. Students should revise only the prescribed topics and focus on the updated content for their exams.