Science Notes for Chapter 7 How Do Organisms Reproduce Class 10 - FREE PDF Download
CBSE Notes Class 10 Science Chapter 7 - How Do Organisms Reproduce - 2025-26
FAQs on CBSE Notes Class 10 Science Chapter 7 - How Do Organisms Reproduce - 2025-26
1. What are the core concepts to summarise for a quick revision of CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 7, How Do Organisms Reproduce?
For a quick revision of this chapter, focus on these main concepts:
- The importance of DNA copying and variation.
- The key differences between asexual and sexual reproduction.
- The various modes of asexual reproduction (fission, budding, fragmentation, etc.).
- The complete process of sexual reproduction in flowering plants, from pollination to germination.
- The structure and function of the male and female reproductive systems in humans.
- The events of fertilisation, embryo development, and the menstrual cycle.
- The basics of reproductive health, including contraception and sexually transmitted diseases (STDs).
2. How can I quickly recall the different types of asexual reproduction with examples?
Here is a quick summary of the main types of asexual reproduction:
- Fission: A parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells. This is seen in unicellular organisms like Amoeba (binary fission) and Plasmodium (multiple fission).
- Fragmentation: An organism breaks into smaller pieces, and each piece grows into a new individual. An example is Spirogyra.
- Regeneration: If an organism is cut into pieces, each piece can grow into a complete organism. This is seen in Planaria and Hydra.
- Budding: A bud develops as an outgrowth on the parent body, which then detaches to become a new individual. An example is Hydra.
- Vegetative Propagation: New plants are grown from vegetative parts like roots, stems, or leaves. For example, roses are grown from stem cuttings and Bryophyllum from leaf buds.
- Spore Formation: An organism produces spores that can develop into new individuals under favourable conditions. This is common in fungi like Rhizopus.
3. What is the fundamental difference between regeneration and fragmentation?
The key difference lies in the complexity and cellular process. Fragmentation is a simple process where a multicellular organism with a relatively simple body organisation breaks into pieces, and each piece grows into a new organism, like in Spirogyra. Regeneration, as seen in complex organisms like Planaria, is the ability of a fully differentiated organism to regrow a lost body part or form a whole new organism from a cut segment. It involves the proliferation of specialised cells to recreate different tissues and organs, making it a more complex process of redevelopment rather than just growth.
4. What are the main advantages of using vegetative propagation for growing certain plants?
Vegetative propagation is advantageous for two primary reasons. First, plants grown this way can bear flowers and fruits much earlier than those produced from seeds. Second, since it is a form of asexual reproduction, all new plants are genetically identical to the parent plant. This allows horticulturists to preserve and replicate desirable traits like flower colour, fruit taste, or disease resistance with certainty.
5. What is the correct sequence of events during sexual reproduction in flowering plants?
The sequence for sexual reproduction in flowering plants can be summarised as follows:
- Pollination: Transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma.
- Pollen Germination: A pollen tube grows from the pollen grain down through the style to the ovule.
- Fertilisation: The male gamete from the pollen tube fuses with the female gamete (egg) inside the ovule to form a zygote.
- Seed and Fruit Formation: The zygote develops into an embryo, the ovule develops into a seed, and the surrounding ovary ripens into a fruit.
- Germination: The seed, under favourable conditions, develops into a new seedling.
6. Why is cross-pollination generally considered more beneficial for a plant species than self-pollination?
Cross-pollination is considered more beneficial because it involves the transfer of pollen between two different plants of the same species. This process mixes genetic material from two different parents, leading to greater genetic variation in the offspring. This variation is crucial for the long-term survival of the species, as it increases the chances that some individuals will be able to adapt to changing environmental conditions, resist new diseases, or thrive in new habitats. Self-pollination, while reliable, produces genetically uniform offspring, making the population more vulnerable.
7. What are the key functions of the main parts of the male reproductive system for a quick revision?
For a quick revision, remember these key functions:
- Testes: Produce male gametes (sperm) and the hormone testosterone. They are located in the scrotum.
- Scrotum: A pouch-like structure that holds the testes at a temperature slightly lower than the body, which is optimal for sperm production.
- Vas Deferens: A tube that transports sperm from the testes to the urethra.
- Prostate Gland & Seminal Vesicles: These glands add their secretions to the sperm to form semen. This fluid provides nourishment and helps in the transport of sperm.
- Urethra: A common passage for both urine and semen to exit the body.
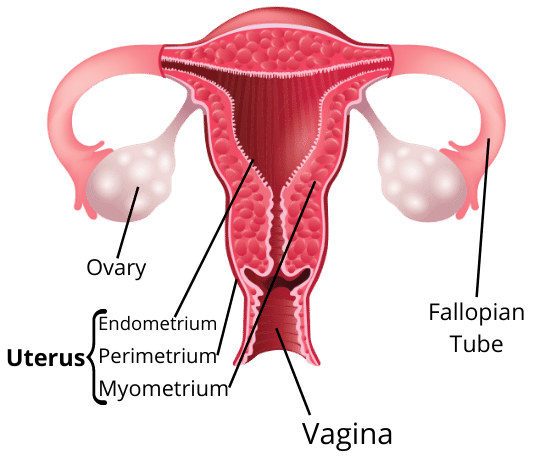
8. What are the key functions of the main parts of the female reproductive system for a quick revision?
For a quick revision, remember these key functions:
- Ovaries: Produce female gametes (eggs or ova) and the hormones oestrogen and progesterone. A female is born with thousands of immature eggs.
- Fallopian Tube (Oviduct): The site where fertilisation of the egg by a sperm usually occurs. It transports the egg from the ovary to the uterus.
- Uterus: A muscular, elastic bag where the fertilised egg implants and develops into a foetus during pregnancy.
- Cervix: The lower part of the uterus that opens into the vagina.
- Vagina: Receives sperm during intercourse and serves as the birth canal.
9. What happens during the menstrual cycle if the egg is not fertilised?
Each month, the uterus prepares for a potential pregnancy by developing a thick, spongy lining rich in blood vessels (the endometrium) to nourish an embryo. If fertilisation does not occur, this lining is no longer needed. Consequently, the lining breaks down and is shed, along with the unfertilised egg and blood, through the vagina. This monthly discharge of blood and mucosal tissue is known as menstruation.
10. Why is the creation of variations through sexual reproduction so important for a species?
The creation of variations through sexual reproduction is crucial because it is the raw material for evolution and adaptation. An environment is never constant; it can change due to factors like climate shifts, new predators, or diseases. If all individuals in a species were identical (as in asexual reproduction), a single change could wipe out the entire population. Genetic variation ensures that some individuals in a population will have traits that make them better suited to survive and reproduce in the new conditions, ensuring the continuation of the species over time.
11. For revision, what are the key methods of contraception mentioned in this chapter?
The key contraceptive methods to revise are:
- Physical Barriers: These prevent sperm from reaching the egg. Examples include condoms and diaphragms.
- Hormonal Methods: These alter the body's hormonal balance to prevent ovulation or implantation. Examples include oral contraceptive pills.
- Intra-Uterine Contraceptive Devices (IUCDs): Devices like the Copper-T are placed in the uterus to prevent implantation.
- Surgical Methods: These are permanent methods that block gamete transport. Vasectomy in males (blocking the vas deferens) and Tubectomy in females (blocking the fallopian tubes) are the examples.




















 Watch Video
Watch Video