NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Social Science Our Environment Chapter 2 Inside Our Earth - 2025-26
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Social Science Our Environment Chapter 2 Inside Our Earth - 2025-26
1. How should one describe the main layers of the Earth's interior for a Class 7 NCERT question?
To provide a correct answer as per the NCERT solutions for Class 7 Social Science Chapter 2, you should describe the Earth's interior in three main layers:
Crust: The thinnest, outermost layer. It is about 35 km thick on continental masses (composed of sial - silica and alumina) and only 5 km on ocean floors (composed of sima - silica and magnesium).
Mantle: Located just beneath the crust, extending up to a depth of 2900 km.
Core: The innermost layer with a radius of about 3500 km. It is made of nife (nickel and iron) and experiences extremely high temperature and pressure.
2. What is the correct way to classify the three major types of rocks as per NCERT Class 7 Geography Chapter 2?
According to the NCERT textbook, the three major types of rocks are classified based on their formation:
Igneous Rocks: Formed when molten magma cools and becomes solid. Examples include granite and basalt.
Sedimentary Rocks: Formed when small particles of rocks (sediments) are transported, deposited, and compressed over time. Examples include sandstone and limestone.
Metamorphic Rocks: Formed when igneous and sedimentary rocks are subjected to great heat and pressure, changing their form and character. Examples include slate (from clay) and marble (from limestone).
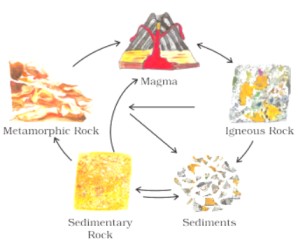
3. How can the rock cycle be explained step-by-step using the NCERT solution format?
The rock cycle is a continuous process where rocks transform from one type to another. A step-by-step explanation is as follows:
Molten magma from inside the Earth cools and solidifies to form igneous rocks.
These igneous rocks are broken down into small particles called sediments by processes like weathering and erosion.
These sediments are transported and deposited in layers. Over time, they are compressed and hardened to form sedimentary rocks.
When igneous and sedimentary rocks are subjected to intense heat and pressure, they change into metamorphic rocks.
Under extreme heat, metamorphic rocks can melt down again to form molten magma, and the cycle continues.
4. Why is the innermost layer of the Earth, the core, mostly made of nickel and iron (nife)?
The core is the innermost layer and experiences the highest pressure and temperature. It is primarily composed of heavy metals like nickel (ni) and iron (fe) because during the Earth's formation, heavier materials sank towards the centre due to gravity, while lighter materials rose to the surface to form the crust and mantle. This is why the core has such high density.
5. How does the formation of intrusive igneous rocks differ from extrusive igneous rocks, as explained in the NCERT solutions?
The key difference lies in where the molten magma cools:
Extrusive Igneous Rocks: Formed when molten lava comes onto the Earth's surface, cools down rapidly, and becomes solid. This rapid cooling results in very fine-grained structures. Basalt is a common example.
Intrusive Igneous Rocks: Formed when molten magma cools down slowly deep inside the Earth's crust. The slow cooling allows for the formation of large crystals. Granite is a typical example.
6. What is the scientific reason that only sedimentary rocks contain fossils?
Fossils are the preserved remains of ancient plants and animals. They are found almost exclusively in sedimentary rocks because these rocks are formed by the gradual accumulation and compression of sediments. This gentle process allows the remains of organisms to be buried and preserved. The immense heat and pressure that create igneous and metamorphic rocks would destroy any organic matter, preventing fossils from forming in them.
7. How do Vedantu's NCERT Solutions for Chapter 2 help in understanding the Earth's structure?
Vedantu's NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Geography Chapter 2 provide clear, step-by-step answers to all textbook questions. They break down complex concepts like the rock cycle and the layers of the Earth into easy-to-understand points. By following these solutions, students can learn the correct methodology to answer questions, understand key definitions, and grasp the core concepts required for their exams as per the 2025-26 CBSE syllabus.
8. What is the practical difference between a rock and a mineral, and why is this important for solving questions in Chapter 2?
The practical difference is based on composition and structure:
A mineral is a naturally occurring substance with a definite chemical composition and a specific crystal structure. For example, quartz.
A rock is an aggregate of one or more minerals and does not have a fixed chemical composition. For example, granite is a rock made up of minerals like quartz, feldspar, and mica.
Understanding this is crucial because questions in Chapter 2 often require identifying rocks based on their mineral content or explaining how minerals are the 'building blocks' of rocks.
9. Why can't we travel to the centre of the Earth, as discussed in the chapter?
As per Chapter 2, 'Inside Our Earth', travelling to the centre of the Earth is impossible. The core is located at a depth of over 6,000 km. To reach it, one would have to dig through the crust and mantle. The primary barriers are the extreme temperature and pressure, which increase dramatically with depth. The temperature at the centre is estimated to be as high as the surface of the sun, and the pressure is immense enough to crush any vehicle or human.