Class 7 Social Science Our Environment Chapter 3 Questions and Answers - Free PDF Download
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Social Science Our Environment Chapter 3 Our Changing Earth - 2025-26
1. Where can I find clear and correct NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science Chapter 3, 'Our Changing Earth'?
You can find reliable and easy-to-understand NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science Chapter 3 right here on Vedantu. All answers are prepared by subject experts and are fully aligned with the latest CBSE 2025-26 syllabus to help you score better in exams.
2. How should I structure my answer for the textbook question on endogenic and exogenic forces?
To answer this question correctly, you should first define each force.
- Start by explaining that endogenic forces are those that act in the interior of the Earth, like earthquakes and volcanoes.
- Then, explain that exogenic forces work on the surface of the Earth, such as the work of wind and water.
3. What key safety points from Chapter 3 should I include when answering the NCERT question on earthquake preparedness?
When solving the question on earthquake safety, make sure to list these key points from the chapter:
- Finding a safe spot, like under a kitchen counter or desk, and staying away from corners.
- Staying away from things that can fall, such as mirrors, picture frames, and windows.
- If outdoors, moving to an open area away from buildings, trees, and power lines.
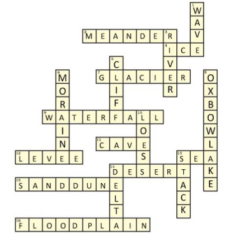
4. What is the correct method to explain the formation of a meander and an ox-bow lake for the Chapter 3 exercises?
For the best score, you should explain this in steps. First, describe how a river entering a plain twists and turns, forming large bends called meanders. Next, explain that due to continuous erosion and deposition, the ends of the meander loop get closer. Finally, state that over time, the river cuts through the narrow neck of land, leaving the old meander loop behind to form a cut-off lake, known as an ox-bow lake.
5. Why is it important to mention the movement of molten magma when explaining how lithospheric plates move in the NCERT solution?
It's crucial because the movement of molten magma inside the Earth is the direct cause of the plate movement. The NCERT solution explains that this magma moves in a circular manner, creating currents that push the lithospheric plates. Forgetting to mention the magma would leave your answer incomplete as it fails to explain the root cause of the Earth's surface changes.
6. How do the NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science Chapter 3 explain the work of wind in deserts?
The solutions explain that wind is a major agent of erosion and deposition in deserts. It erodes the lower section of rocks more than the upper part, creating mushroom rocks. When the wind blows, it transports sand and deposits it in low, hill-like structures called sand dunes when the wind speed decreases. This process clearly shows how wind shapes the desert landscape.
7. What is the main difference between how a river and a sea wave create landforms, according to the solutions for this chapter?
The main difference lies in the process and location. A river creates landforms like waterfalls and meanders through erosion and deposition along its path on land. In contrast, sea waves create coastal landforms like sea caves, sea arches, and stacks by constantly striking against rocks along the coast. The river's work is inland, while the sea waves' work is strictly coastal.
8. Why do the solutions often suggest using diagrams when answering questions about landforms from this chapter?
Using simple, labelled diagrams for landforms like a waterfall, an ox-bow lake, or a mushroom rock is highly recommended. A diagram makes your answer much clearer and helps the examiner understand that you have properly grasped the concept. It is a very effective way to score higher marks for questions on geographical formations as per the CBSE pattern.