
Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 Pair Of Linear Equations In Two Variables Question Answers Explained
If you're looking for Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 Pair Of Linear Equations In Two Variables Exercise 3.1 solutions, you're in the right place! Our exercise 3.1 class 10 maths NCERT solutions provide detailed explanations to help you understand each step. From basic problems to more complex ones, we break down the solutions to make learning easy and effective.
 Table of Content
Table of ContentThese Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 question answers are designed to help you grasp key concepts and prepare thoroughly for your exams. Whether you're solving for linear equations or understanding the properties of different types of equations, this guide will help you navigate through the problems smoothly.
NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 Pair Of Linear Equations In Two Variables Exercise 3.1 - 2025-26
How Can Step By Step NCERT Solutions Help With Class 8 Science Crop Production And Management Exam Preparation
Exercise No. 3.1
1. Form the pair of linear equations in the following problems, and find their solutions graphically.
(i) $10$ students of Class $X$ took part in a Mathematics quiz. If the number of girls is $4$ more than the number of boys, find the number of boys and girls who took part in the quiz.
Ans: Given that $10$ students of Class $X$ took part in a Mathematics quiz.
We have to find the number of boys and girls who took part in the quiz.
Let the number of girls be $\text{x}$.
And, number of boys be $\text{y}$.
Then we get
$x+y=10$ ……..(1)
Now, according to the question, number of girls is $4$ more than the number of boys.
Then we get
$x-y=4$ ……(2)
Now, the algebraic representation of equation (1) and (2) is
$x+y=10$
$\Rightarrow x=10-y$
The solution table for the above equation is
$x$ | $5$ | $4$ | $6$ |
$y$ | $5$ | $6$ | $4$ |
Now, for eq. (2)
$x-y=4$
$\Rightarrow x=4+y$
The solution table for the above equation is
$x$ | $5$ | $4$ | $3$ |
$y$ | $1$ | $0$ | $-1$ |
Now, the graphical representation is
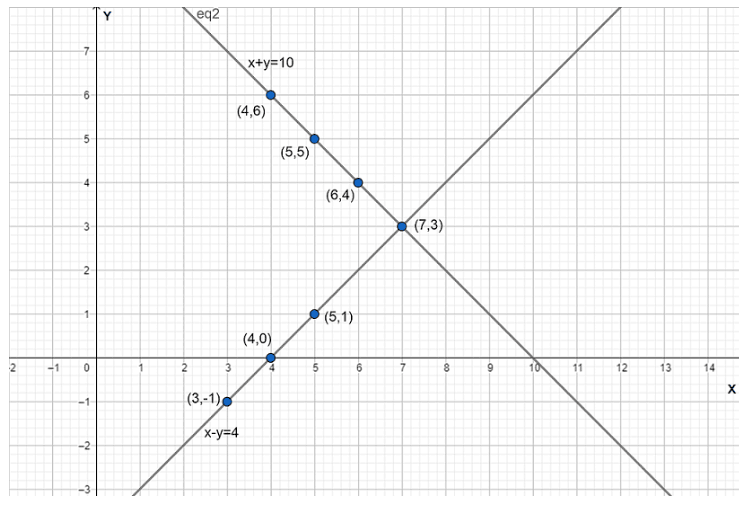
By observing the above graph we can say that the lines intersect each other at point $\left( 7,3 \right)$.
Therefore, $3$ boys and $7$ girls took part in the quiz.
(ii) $5$ pencils and $7$ pens together cost $Rs.\text{ 50}$, whereas $7$ pencils and $5$ pens together cost $Rs.\text{ 46}$. Find the cost of one pencil and that of one pen.
Ans: Given that $5$ pencils and $7$ pens together cost $Rs.\text{ 50}$, whereas $7$ pencils and $5$ pens together cost $Rs.\text{ 46}$.
We have to find the cost of one pencil and that of one pen.
Let the price of $1$ pencil be $Rs.\text{ x}$.
And, price of $1$ pen be $Rs.\text{ y}$.
Now, according to the question, total cost of $5$ pencils and $7$ pens together is $Rs.\text{ 50}$.
Then we get
$5x+7y=50$ ……(1)
Also, total cost of $7$ pencils and $5$ pens together is $Rs.\text{ 46}$.
Then we get
$7x+5y=46$ ……(2)
Now, the algebraic representation of equation (1) and (2) is
$5x+7y=50$
$\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{50-7y}{5}$
The solution table for the above equation is
$x$ | $3$ | $10$ | $-4$ |
$y$ | $5$ | $0$ | $10$ |
Now, for eq. (2)
$7x+5y=46$
$\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{46-5y}{7}$
The solution table for the above equation is
$x$ | $8$ | $3$ | $-2$ |
$y$ | $-2$ | $5$ | $12$ |
Now, the graphical representation is
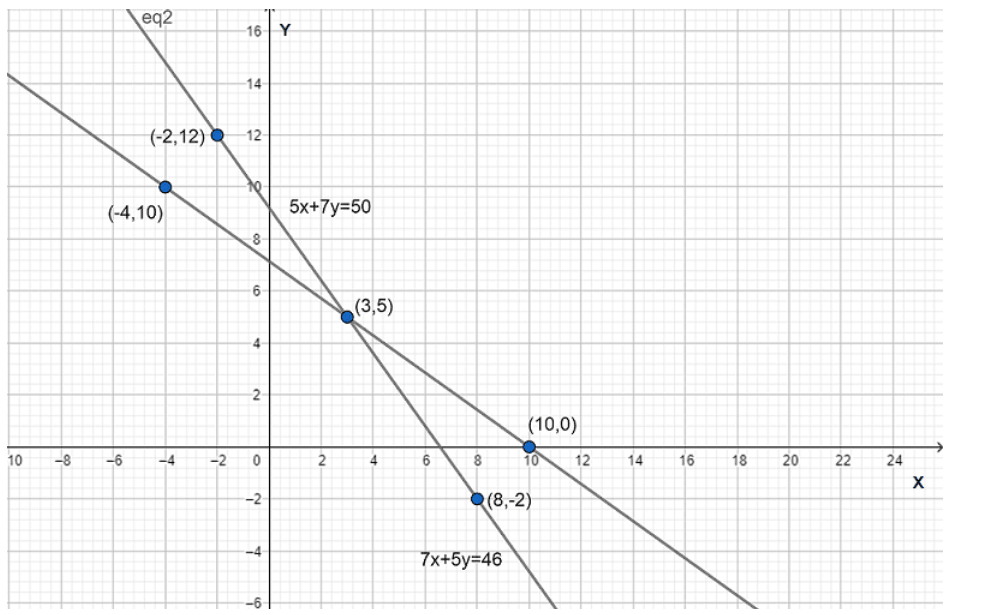
By observing the above graph we can say that the lines intersect each other at point $\left( 3,5 \right)$.
Therefore, the cost of one pencil is $Rs.\text{ 3}$ and cost of one pen is $Rs.\text{ 5}$.
2. On comparing the ratios $\dfrac{{{a}_{1}}}{{{a}_{2}}}$,$\dfrac{{{b}_{1}}}{{{b}_{2}}}$, and $\dfrac{{{c}_{1}}}{{{c}_{2}}}$, find out whether the lines representing the following pairs of linear equations at a point, are parallel or coincident:
(i) $5x-4y+8=0$
$7x+6y-9=0$
Ans: Given pair of linear equations $5x-4y+8=0$ and $7x+6y-9=0$.
When we compare the given equations with the standard equations
${{a}_{1}}x+{{b}_{1}}y+{{c}_{1}}=0$
${{a}_{2}}x+{{b}_{2}}y+{{c}_{2}}=0$
We get
${{a}_{1}}=5$, ${{b}_{1}}=-4$, ${{c}_{1}}=8$
${{a}_{2}}=7$, ${{b}_{2}}=6$, ${{c}_{2}}=-9$
Now, we get
$\dfrac{{{a}_{1}}}{{{a}_{2}}}=\dfrac{5}{7}$, $\dfrac{{{b}_{1}}}{{{b}_{2}}}=\dfrac{-4}{6}=\dfrac{-2}{3}$, $\dfrac{{{c}_{1}}}{{{c}_{2}}}=\dfrac{8}{-9}$
We get
$\dfrac{{{a}_{1}}}{{{a}_{2}}}\ne \dfrac{{{b}_{1}}}{{{b}_{2}}}\ne \dfrac{{{c}_{1}}}{{{c}_{2}}}$
Therefore, the given pair of lines is intersecting each other and has a unique solution.
(ii) $9x+3y+12=0$
$18x+6y+24=0$
Ans: Given pair of linear equations $9x+3y+12=0$ and $18x+6y+24=0$.
When we compare the given equations with the standard equations
${{a}_{1}}x+{{b}_{1}}y+{{c}_{1}}=0$
${{a}_{2}}x+{{b}_{2}}y+{{c}_{2}}=0$
We get
${{a}_{1}}=9$, ${{b}_{1}}=3$, ${{c}_{1}}=12$
${{a}_{2}}=18$, ${{b}_{2}}=6$, ${{c}_{2}}=24$
Now, we get
$\dfrac{{{a}_{1}}}{{{a}_{2}}}=\dfrac{9}{18}=\dfrac{1}{2}$,
$\dfrac{{{b}_{1}}}{{{b}_{2}}}=\dfrac{3}{6}=\dfrac{1}{2}$,
$\dfrac{{{c}_{1}}}{{{c}_{2}}}=\dfrac{12}{24}=\dfrac{1}{2}$
We get
$\dfrac{{{a}_{1}}}{{{a}_{2}}}=\dfrac{{{b}_{1}}}{{{b}_{2}}}=\dfrac{{{c}_{1}}}{{{c}_{2}}}$
Therefore, the given pair of lines overlaps each other and has infinite solutions.
(iii) $6x-3y+10=0$
$2x-y+9=0$
Ans: Given pair of linear equations $6x-3y+10=0$ and $2x-y+9=0$.
When we compare the given equations with the standard equations
${{a}_{1}}x+{{b}_{1}}y+{{c}_{1}}=0$
${{a}_{2}}x+{{b}_{2}}y+{{c}_{2}}=0$
We get
${{a}_{1}}=6$, ${{b}_{1}}=-3$, ${{c}_{1}}=10$
${{a}_{2}}=2$, ${{b}_{2}}=-1$, ${{c}_{2}}=9$
Now, we get
$\dfrac{{{a}_{1}}}{{{a}_{2}}}=\dfrac{6}{2}=\dfrac{3}{1}$,
$\dfrac{{{b}_{1}}}{{{b}_{2}}}=\dfrac{-3}{-1}=\dfrac{3}{1}$,
$\dfrac{{{c}_{1}}}{{{c}_{2}}}=\dfrac{10}{9}$
We get,
$\dfrac{{{a}_{1}}}{{{a}_{2}}}=\dfrac{{{b}_{1}}}{{{b}_{2}}}\ne \dfrac{{{c}_{1}}}{{{c}_{2}}}$
Therefore, the given pair of lines is parallel to each other. Therefore, the lines formed by given equations not intersect each other and thus, there will not be any solution for these equations.
3. On comparing the ratios $\dfrac{{{a}_{1}}}{{{a}_{2}}}$,$\dfrac{{{b}_{1}}}{{{b}_{2}}}$, and $\dfrac{{{c}_{1}}}{{{c}_{2}}}$, find out whether the following pair of linear equations are consistent, or inconsistent.
(i) $3x+2y=5$; $2x-3y=7$
Ans: Given pair of linear equations $3x+2y=5$ and $2x-3y=7$.
When we compare the given equations with the standard equations
${{a}_{1}}x+{{b}_{1}}y+{{c}_{1}}=0$
${{a}_{2}}x+{{b}_{2}}y+{{c}_{2}}=0$
We get
$\dfrac{{{a}_{1}}}{{{a}_{2}}}=\dfrac{3}{2}$, $\dfrac{{{b}_{1}}}{{{b}_{2}}}=-\dfrac{2}{3}$, $\dfrac{{{c}_{1}}}{{{c}_{2}}}=\dfrac{5}{7}$
We get
$\dfrac{{{a}_{1}}}{{{a}_{2}}}\ne \dfrac{{{b}_{1}}}{{{b}_{2}}}\ne \dfrac{{{c}_{1}}}{{{c}_{2}}}$
Therefore, the given pair of lines is intersecting each other at a point and has one unique solution.
We know that if a system has at least one solution, it is known as consistent.
Therefore, the given pair of linear equations is consistent.
(ii) $2x-3y=8$; $4x-6y=9$
Ans: Given pair of linear equations $2x-3y=8$ and $4x-6y=9$.
When we compare the given equations with the standard equations
${{a}_{1}}x+{{b}_{1}}y+{{c}_{1}}=0$
${{a}_{2}}x+{{b}_{2}}y+{{c}_{2}}=0$
We get
$\dfrac{{{a}_{1}}}{{{a}_{2}}}=\dfrac{2}{4}=\dfrac{1}{2}$, $\dfrac{{{b}_{1}}}{{{b}_{2}}}=\dfrac{-3}{-6}=\dfrac{1}{2}$,$\dfrac{{{c}_{1}}}{{{c}_{2}}}=\dfrac{8}{9}$
We get
$\dfrac{{{a}_{1}}}{{{a}_{2}}}=\dfrac{{{b}_{1}}}{{{b}_{2}}}\ne \dfrac{{{c}_{1}}}{{{c}_{2}}}$
Therefore, the given pair of lines is parallel to each other and there will not be any solution for these equations.
We know that if a system has at no solution, it is known as inconsistent.
Therefore, the given pair of linear equations is inconsistent.
(iii) $\dfrac{3}{2}x+\dfrac{5}{3}y=7$; $9x-10y=14$
Ans: Given pair of linear equations $\dfrac{3}{2}x+\dfrac{5}{3}y=7$ and $9x-10y=14$.
When we compare the given equations with the standard equations
${{a}_{1}}x+{{b}_{1}}y+{{c}_{1}}=0$
${{a}_{2}}x+{{b}_{2}}y+{{c}_{2}}=0$
We get
$\dfrac{{{a}_{1}}}{{{a}_{2}}}=\dfrac{\dfrac{3}{2}}{9}=\dfrac{1}{6}$,
$\dfrac{{{b}_{1}}}{{{b}_{2}}}=\dfrac{\dfrac{5}{3}}{-10}=\dfrac{-1}{6}$,
$\dfrac{{{c}_{1}}}{{{c}_{2}}}=\dfrac{7}{14}=\dfrac{1}{2}$
We get
$\dfrac{{{a}_{1}}}{{{a}_{2}}}\ne \dfrac{{{b}_{1}}}{{{b}_{2}}}\ne \dfrac{{{c}_{1}}}{{{c}_{2}}}$
Therefore, the given pair of lines is intersecting each other at a point and has one unique solution.
We know that if a system has at least one solution, it is known as consistent.
Therefore, the given pair of linear equations is consistent.
(iv) $5x-3y=11$; $-10x+6y=-22$
Ans: Given pair of linear equations $5x-3y=11$ and $-10x+6y=-22$.
When we compare the given equations with the standard equations
${{a}_{1}}x+{{b}_{1}}y+{{c}_{1}}=0$
${{a}_{2}}x+{{b}_{2}}y+{{c}_{2}}=0$
We get
$\dfrac{{{a}_{1}}}{{{a}_{2}}}=\dfrac{5}{-10}=-\dfrac{1}{2}$,
$\dfrac{{{b}_{1}}}{{{b}_{2}}}=\dfrac{-3}{6}=-\dfrac{1}{2}$,
$\dfrac{{{c}_{1}}}{{{c}_{2}}}=\dfrac{11}{-22}=-\dfrac{1}{2}$
We get
$\dfrac{{{a}_{1}}}{{{a}_{2}}}=\dfrac{{{b}_{1}}}{{{b}_{2}}}=\dfrac{{{c}_{1}}}{{{c}_{2}}}$
Therefore, the given pair of lines overlaps each other and has infinite solutions.
We know that if a system has at least one solution, it is known as consistent.
Therefore, the given pair of linear equations is consistent.
(v) $\dfrac{4}{3}x+2y=8$; $2x+3y=12$
Ans: Given pair of linear equations $\dfrac{4}{3}x+2y=8$ and $2x+3y=12$.
When we compare the given equations with the standard equations
${{a}_{1}}x+{{b}_{1}}y+{{c}_{1}}=0$
${{a}_{2}}x+{{b}_{2}}y+{{c}_{2}}=0$
We get
$\dfrac{{{a}_{1}}}{{{a}_{2}}}=\dfrac{\dfrac{4}{3}}{2}=\dfrac{2}{3}$,
$\dfrac{{{b}_{1}}}{{{b}_{2}}}=\dfrac{2}{3}$,
$\dfrac{{{c}_{1}}}{{{c}_{2}}}=\dfrac{8}{12}=\dfrac{2}{3}$
We get
$\dfrac{{{a}_{1}}}{{{a}_{2}}}=\dfrac{{{b}_{1}}}{{{b}_{2}}}=\dfrac{{{c}_{1}}}{{{c}_{2}}}$
Therefore, the given pair of lines overlaps each other and has infinite solutions.
We know that if a system has at least one solution, it is known as consistent.
Therefore, the given pair of linear equations is consistent.
4. Which of the following pairs of linear equations are consistent/ inconsistent? If consistent, obtain the solution graphically:
(i) $x+y=5$, $2x+2y=10$
Ans: Given pair of linear equations $x+y=5$ and $2x+2y=10$.
We get
$\dfrac{{{a}_{1}}}{{{a}_{2}}}=\dfrac{1}{2}$, $\dfrac{{{b}_{1}}}{{{b}_{2}}}=\dfrac{1}{2}$, $\dfrac{{{c}_{1}}}{{{c}_{2}}}=\dfrac{5}{10}=\dfrac{1}{2}$
Since, we get
$\dfrac{{{a}_{1}}}{{{a}_{2}}}=\dfrac{{{b}_{1}}}{{{b}_{2}}}=\dfrac{{{c}_{1}}}{{{c}_{2}}}$
Therefore, the given pair of lines overlaps each other and has infinite solutions.
We know that if a system has at least one solution, it is known as consistent.
Therefore, the given pair of linear equations is consistent.
Now, the algebraic representation of equation is
$x+y=5$
$\Rightarrow x=5-y$
The solution table for the above equation is
$x$ | $4$ | $3$ | $2$ |
$y$ | $1$ | $2$ | $3$ |
$2x+2y=10$
$\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{10-2y}{2}$
The solution table for the above equation is
$x$ | $4$ | $3$ | $2$ |
$y$ | $1$ | $2$ | $3$ |
The graphic representation is as follows:
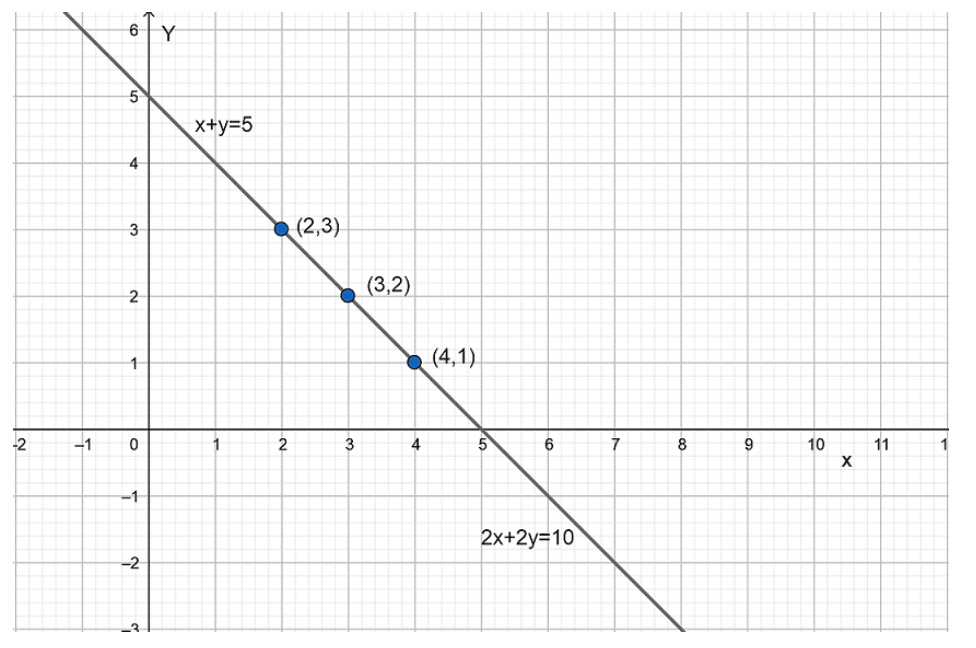
From the above graph, we can observe that the lines are overlapping each other.
Therefore, given pair of equations has infinite number of solutions.
(ii) $x-y=8$, $3x-3y=16$
Ans: Given pair of linear equations $x-y=8$ and $3x-3y=16$.
We get
$\dfrac{{{a}_{1}}}{{{a}_{2}}}=\dfrac{1}{3}$, $\dfrac{{{b}_{1}}}{{{b}_{2}}}=\dfrac{1}{3}$, $\dfrac{{{c}_{1}}}{{{c}_{2}}}=\dfrac{8}{16}=\dfrac{1}{2}$
Since, we get
$\dfrac{{{a}_{1}}}{{{a}_{2}}}=\dfrac{{{b}_{1}}}{{{b}_{2}}}\ne \dfrac{{{c}_{1}}}{{{c}_{2}}}$
Therefore, the given pair of lines is parallel to each other and there will not be any solution for these equations.
We know that if a system has no solution, it is known as inconsistent.
Therefore, the given pair of linear equations is inconsistent.
(iii) $2x+y-6=0$, $4x-2y-4=0$
Ans: Given pair of linear equations $2x+y-6=0$ and $4x-2y-4=0$.
We get
$\dfrac{{{a}_{1}}}{{{a}_{2}}}=\dfrac{2}{4}=\dfrac{1}{2}$, $\dfrac{{{b}_{1}}}{{{b}_{2}}}=\dfrac{-1}{2}$, $\dfrac{{{c}_{1}}}{{{c}_{2}}}=\dfrac{-6}{-4}=\dfrac{3}{2}$
Since, we get
$\dfrac{{{a}_{1}}}{{{a}_{2}}}\ne \dfrac{{{b}_{1}}}{{{b}_{2}}}\ne \dfrac{{{c}_{1}}}{{{c}_{2}}}$
Therefore, the given pair of lines is intersecting each other at a point and has one unique solution.
We know that if a system has at least one solution, it is known as consistent.
Therefore, the given pair of linear equations is consistent.
Now, the algebraic representation of equation is
$2x+y-6=0$
$\Rightarrow y=6-2x$
The solution table for the above equation is
$x$ | $0$ | $1$ | $2$ |
$y$ | $6$ | $4$ | $2$ |
$4x-2y-4=0$
$\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{4x-4}{2}$
The solution table for the above equation is
$x$ | $1$ | $2$ | $3$ |
$y$ | $0$ | $2$ | $4$ |
The graphic representation is as follows:
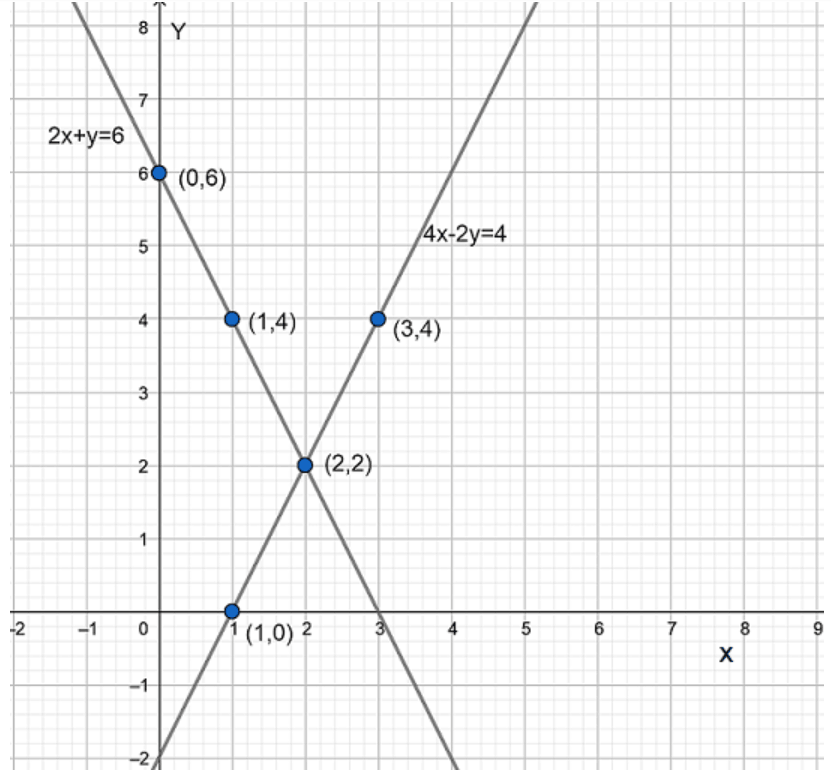
From the above graph, we can observe that the lines are intersecting each other at a point $\left( 2,2 \right)$.
Therefore, $\left( 2,2 \right)$ is the unique solution for given pair of equations.
(iv) $2x-2y-2=0$, $4x-4y-5=0$
Ans: Given pair of linear equations $2x-2y-2=0$ and $4x-4y-5=0$.
We get
$\dfrac{{{a}_{1}}}{{{a}_{2}}}=\dfrac{2}{4}=\dfrac{1}{2}$, $\dfrac{{{b}_{1}}}{{{b}_{2}}}=\dfrac{-2}{-4}=\dfrac{1}{2}$, $\dfrac{{{c}_{1}}}{{{c}_{2}}}=\dfrac{2}{5}$
Since, we get
$\dfrac{{{a}_{1}}}{{{a}_{2}}}=\dfrac{{{b}_{1}}}{{{b}_{2}}}\ne \dfrac{{{c}_{1}}}{{{c}_{2}}}$
Therefore, the given pair of lines is parallel to each other and there will not be any solution for these equations.
We know that if a system has at no solution, it is known as inconsistent.
Therefore, the given pair of linear equations is inconsistent.
5. Half the perimeter of a rectangular garden, whose length is $4\text{ m}$ more than its width, is $\text{36 m}$. Find the dimensions of the garden.
Ans: We have to find the dimensions of a rectangular garden.
Let the width of the garden be $x$ and the length of the garden be $y$.
Now, according to the question length of a garden is $4\text{ m}$ more than its width.
Then, we get
$y-x=4$……….(1)
Also given that the half the perimeter is $\text{36 m}$.
Then, we get
$y+x=36$ ……….(2)
Now, the algebraic representation of equation is
$y-x=4$
$\Rightarrow y=x+4$
The solution table for the above equation is
$x$ | $0$ | $8$ | $12$ |
$y$ | $4$ | $12$ | $16$ |
$y+x=36$
$\Rightarrow y=36-x$
The solution table for the above equation is
$x$ | $0$ | $36$ | $16$ |
$y$ | $36$ | $0$ | $20$ |
The graphic representation is as follows:
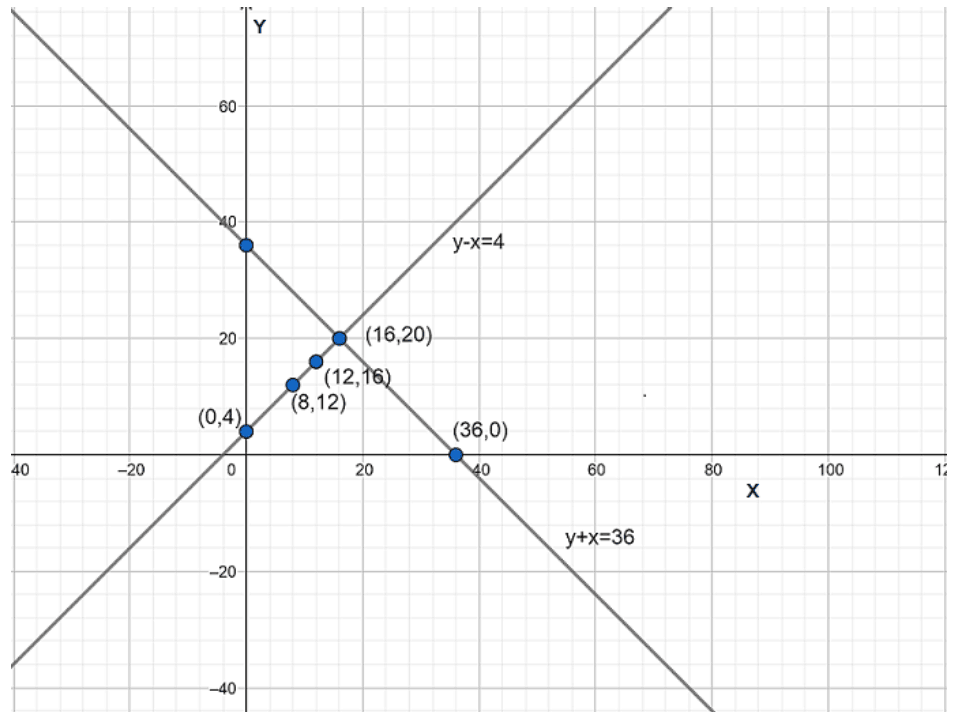
From the above graph, we can observe that the lines are intersecting each other at a point $\left( 16,20 \right)$.
Therefore, the length of the garden is $20\text{ m}$ and the width of the garden is $16\text{ m}$.
6. Given the linear equation $2x+3y-8=0$, write another linear equations in two variables such that the geometrical representation of the pair so formed is:
(i) Intersecting lines
Ans: Given linear equation is $2x+3y-8=0$.
We have to find the other linear equation which intersects the given line.
Now, we know that the necessary condition for the lines to intersect each other is $\dfrac{{{a}_{1}}}{{{a}_{2}}}\ne \dfrac{{{b}_{1}}}{{{b}_{2}}}\ne \dfrac{{{c}_{1}}}{{{c}_{2}}}$
Now, assume that the second equation of line can be $2x+4y-6=0$.
Then, we get
$\dfrac{{{a}_{1}}}{{{a}_{2}}}=\dfrac{2}{2}=1$ and $\dfrac{{{b}_{1}}}{{{b}_{2}}}=\dfrac{3}{4}$
Therefore, $\dfrac{{{a}_{1}}}{{{a}_{2}}}\ne \dfrac{{{b}_{1}}}{{{b}_{2}}}$.
(ii) Parallel lines
Ans: Given linear equation is $2x+3y-8=0$.
We have to find the other linear equation which is parallel to the given line.
Now, we know that the necessary condition for the lines to parallel to each other is $\dfrac{{{a}_{1}}}{{{a}_{2}}}=\dfrac{{{b}_{1}}}{{{b}_{2}}}\ne \dfrac{{{c}_{1}}}{{{c}_{2}}}$
Now, assume that the second equation of line can be $4x+6y-8=0$.
Then, we get
$\dfrac{{{a}_{1}}}{{{a}_{2}}}=\dfrac{2}{4}=\dfrac{1}{2}$, $\dfrac{{{b}_{1}}}{{{b}_{2}}}=\dfrac{3}{6}=\dfrac{1}{2}$, $\dfrac{{{c}_{1}}}{{{c}_{2}}}=\dfrac{-8}{-8}=1$
Therefore, $\dfrac{{{a}_{1}}}{{{a}_{2}}}=\dfrac{{{b}_{1}}}{{{b}_{2}}}\ne \dfrac{{{c}_{1}}}{{{c}_{2}}}$.
(iii) Coincident lines
Ans: Given linear equation is $2x+3y-8=0$.
We have to find the other linear equation which is parallel to the given line.
Now, we know that the necessary condition for the lines to parallel to each other is $\dfrac{{{a}_{1}}}{{{a}_{2}}}=\dfrac{{{b}_{1}}}{{{b}_{2}}}=\dfrac{{{c}_{1}}}{{{c}_{2}}}$
Now, assume that the second equation of line can be $6x+9y-24=0$.
Then, we get
$\dfrac{{{a}_{1}}}{{{a}_{2}}}=\dfrac{2}{6}=\dfrac{1}{3}$, $\dfrac{{{b}_{1}}}{{{b}_{2}}}=\dfrac{3}{9}=\dfrac{1}{3}$, $\dfrac{{{c}_{1}}}{{{c}_{2}}}=\dfrac{-8}{24}=\dfrac{1}{3}$
Therefore, $\dfrac{{{a}_{1}}}{{{a}_{2}}}=\dfrac{{{b}_{1}}}{{{b}_{2}}}=\dfrac{{{c}_{1}}}{{{c}_{2}}}$.
7. Draw the graphs of the equations $x-y+1=0$ and $3x+2y-12=0$. Determine the coordinates of the vertices of the triangle formed by these lines and the x-axis, and shade the triangular region.
Ans: We have to draw the graphs of the equations $x-y+1=0$ and $3x+2y-12=0$.
Now, the algebraic representation of equation is
$x-y+1=0$
$\Rightarrow x=y-1$
The solution table for the above equation is
$x$ | $0$ | $1$ | $2$ |
$y$ | $1$ | $2$ | $3$ |
$3x+2y-12=0$
$\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{12-2y}{3}$
The solution table for the above equation is
$x$ | $4$ | $2$ | $0$ |
$y$ | $0$ | $3$ | $6$ |
The graphic representation is as follows:
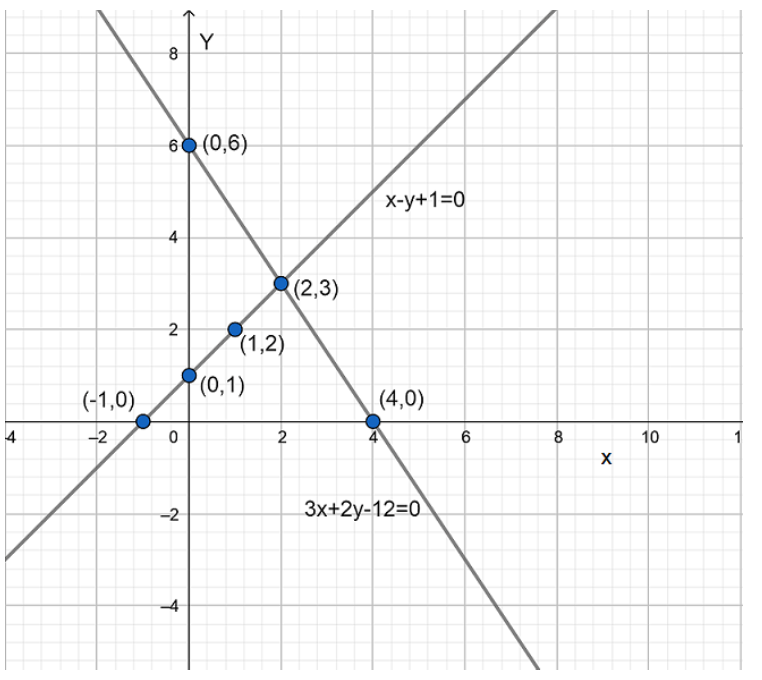
From the above graph, we can observe that the lines are intersecting each other at a point $\left( 2,3 \right)$ and x-axis at $\left( -1,0 \right)$ and $\left( 4,0 \right)$.
Therefore, we get the vertices of the triangle as $\left( 2,3 \right)$,$\left( -1,0 \right)$ and $\left( 4,0 \right)$.
An Overview of the Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1
We will look at the Graphical Method of Solving a Pair of Linear Equations in this exercise. We already know that a pair of linear equations will be graphically represented by two straight lines that can be parallel, intersect, or coincide.
Now, we will consider certain cases here.
When two lines intersect each other at only one point, then we conclude that there is one and only one solution. It means that a unique solution exists for this pair of linear equations in two variables. This type of pair of linear equations is called a consistent pair of linear equations.
If the two lines are coincident, we can say that the pair of linear equations will have infinitely many solutions. This type of pair of linear equations can be called an inconsistent pair of linear equations.
If the two lines are parallel to each other, which means they do not meet at all, then we can say that the two linear equations will not have any common solution. This type of pair of linear equations will be called the dependent pair of linear equations.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 All Other Exercises
Chapter 3 - Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables All Exercises in PDF Format | |
3 Questions & Solutions (2 Short Answers, 1 Long Answer) | |
2 Questions & Solutions (2 Long Answers) | |
Conclusion
In Exercise 3.1 of Class 10 Maths Chapter 3, you learn how to solve pairs of linear equations using graphical methods. Class 10 Ex 3.1 is crucial for understanding how two variables interact in real-life scenarios. Focus on accurately plotting the graphs and identifying the point of intersection, as this represents the solution to the equations. Pay attention to the method of drawing lines and checking if they intersect, are parallel, or coincide. Understanding these concepts is essential for mastering linear equations. Practice regularly to strengthen your skills.
Other Related Links
Chapter-Specific NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
Given below are the chapter-wise NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths. Go through these chapter-wise solutions to be thoroughly familiar with the concepts.
S.No. | NCERT Solutions Class 10 Chapter-wise Maths PDF |
1 | |
2 | |
3 | Chapter 3 - Pair Of Linear Equations In Two Variables Solutions |
4 | |
5 | |
6 | |
7 | |
8 | |
9 | |
10 | |
11 | |
12 | |
13 | |
14 |
NCERT Study Resources for Class 10 Maths
For complete preparation of Maths for CBSE Class 10 board exams, check out the following links for different study materials available at Vedantu.
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 Pair Of Linear Equations In Two Variables Exercise 3.1 - 2025-26
1. Are Exercise 3.1 Class 10 Maths solutions helpful for homework?
Yes, Exercise 3.1 Class 10 Maths solutions from Vedantu provide clear answers that students can use for homework and written practice.
2. Do the Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 solutions cover all textbook questions?
Yes, the Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 solutions on Vedantu include answers to all questions listed in the NCERT textbook.
3. Are the Exercise 3.1 Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions written step-by-step?
Yes, the Exercise 3.1 Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions on Vedantu provide step-by-step explanations to help students understand problem solving.
4. Do Class 10th Maths Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 solutions follow the NCERT book order?
Yes, Class 10th Maths Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 solutions on Vedantu follow the same question sequence as the NCERT textbook.
5. Are Class 10 Math Exercise 3.1 solutions useful for school exams?
Yes, the Class 10 Math Exercise 3.1 solutions on Vedantu are written in an exam-ready format suitable for school assessments.
6. Can private candidates use Class 10 Maths Exercise 3.1 solutions?
Yes, private candidates following the NCERT syllabus can use Class 10 Maths Exercise 3.1 solutions available on Vedantu.
7. Are the Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 answers written in simple language?
Yes, the Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 answers on Vedantu are written in clear, student-friendly language.
8. Do Exercise 3.1 Class 10 Maths solutions help improve solving skills?
Yes, Exercise 3.1 Class 10 Maths solutions on Vedantu help students understand correct solving methods and improve accuracy.
9. Are Class 10 Maths Exercise 3.1 solutions aligned with the latest syllabus?
Yes, Class 10 Maths Exercise 3.1 solutions on Vedantu are aligned with the current NCERT and CBSE syllabus.




















 Watch Video
Watch Video

















