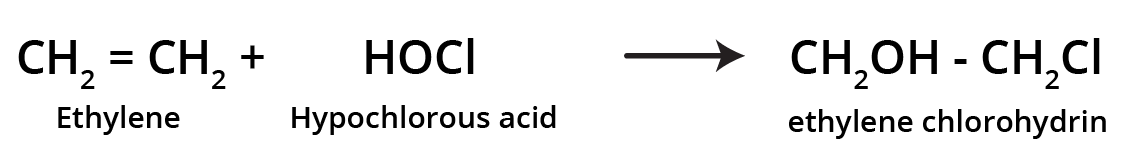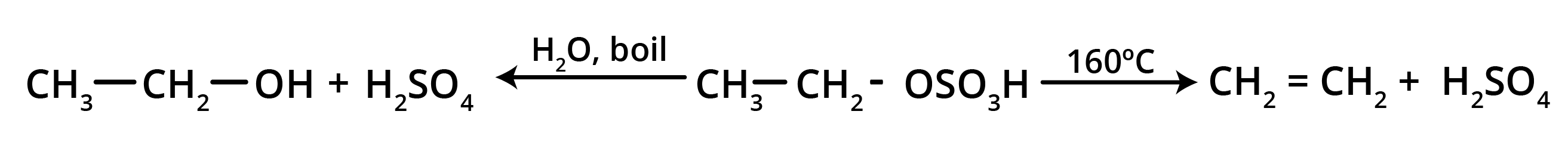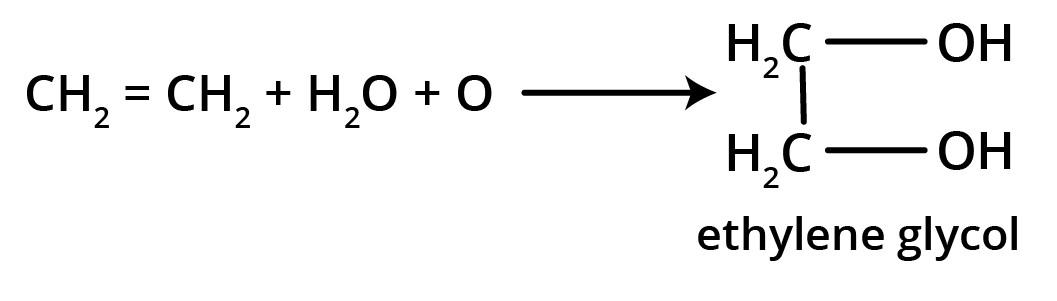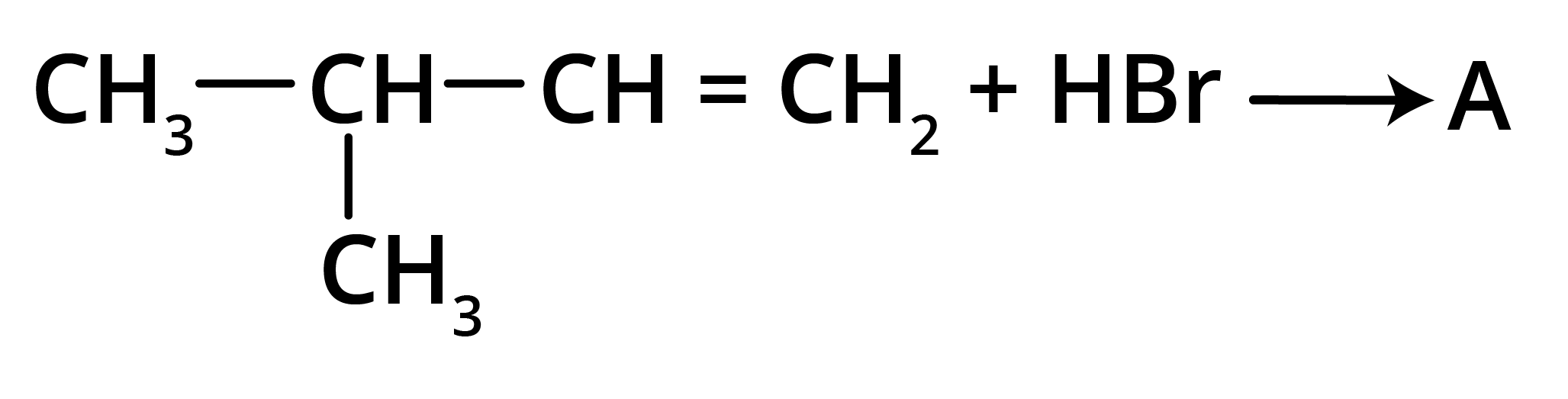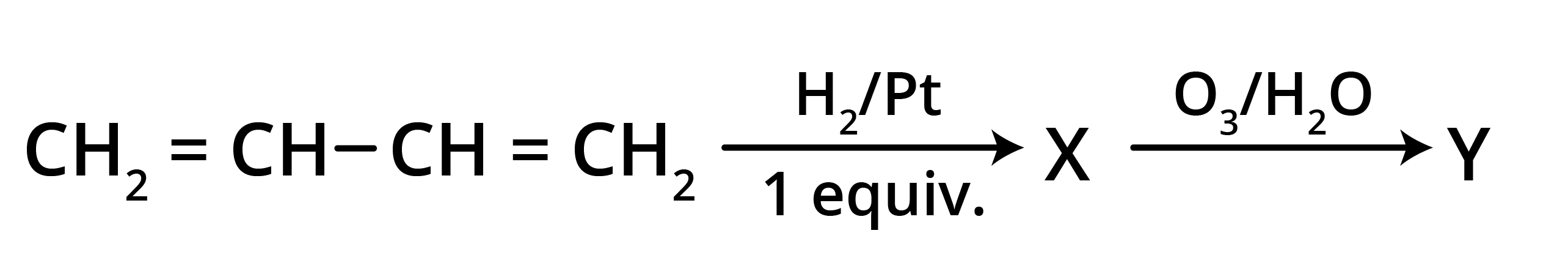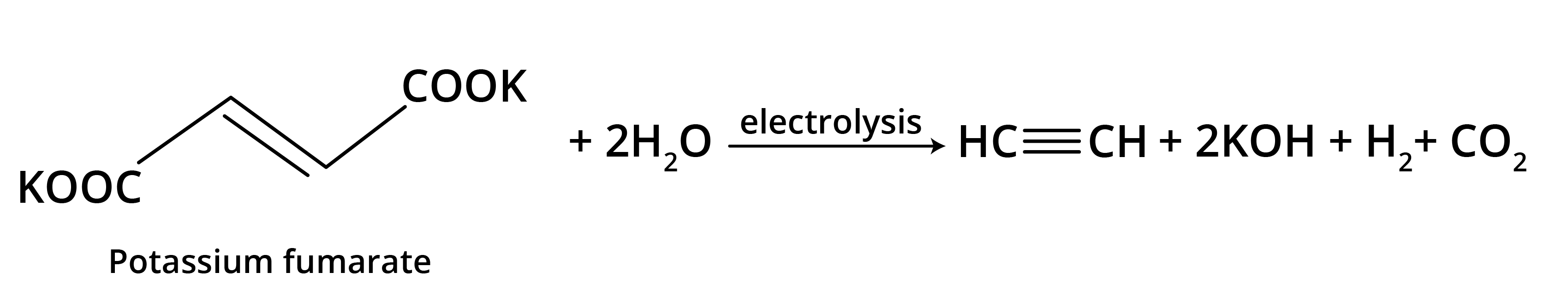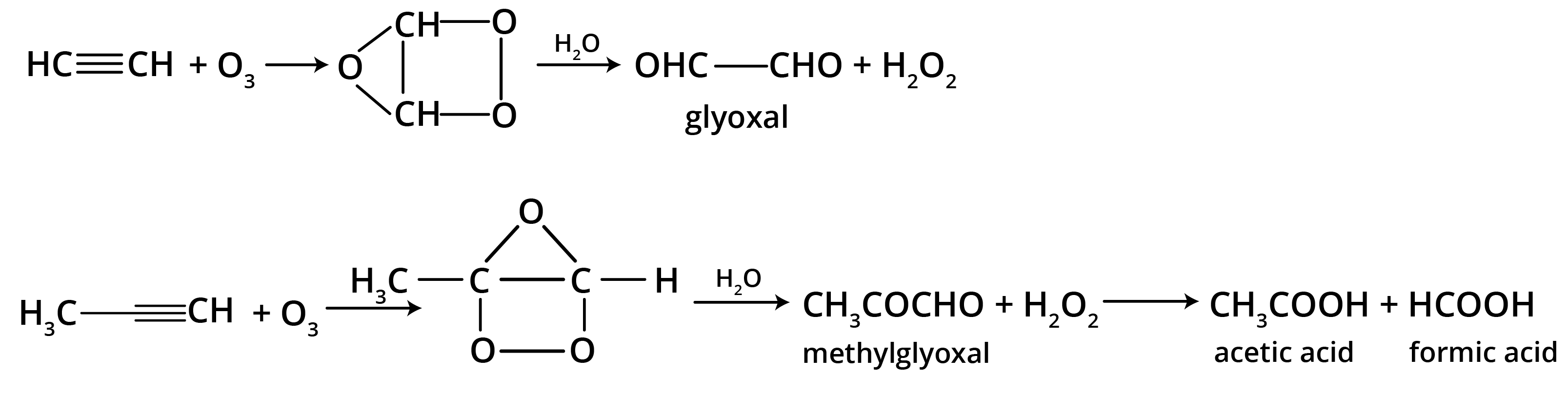Chemistry Notes for Chapter 9 Hydrocarbons Class 11 - FREE PDF Download
FAQs on CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 - Hydrocarbons - 2025-26
1. What are the main types of hydrocarbons to focus on for a quick revision of Class 11 Chapter 9?
For a quick revision, focus on the four main categories of hydrocarbons:
- Alkanes: Saturated hydrocarbons with only single carbon-carbon bonds (C-C).
- Alkenes: Unsaturated hydrocarbons containing at least one carbon-carbon double bond (C=C).
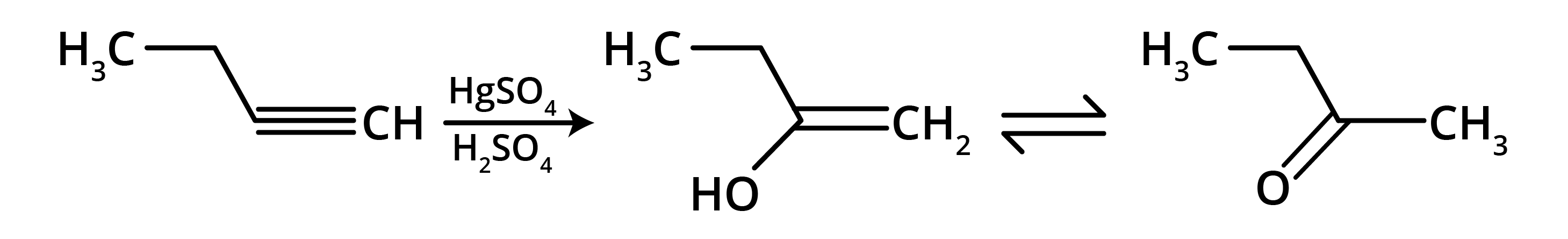
- Alkynes: Unsaturated hydrocarbons containing at least one carbon-carbon triple bond (C≡C).
- Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Cyclic compounds containing a stable benzene ring.
2. What is the core concept to remember about isomerism in hydrocarbons?
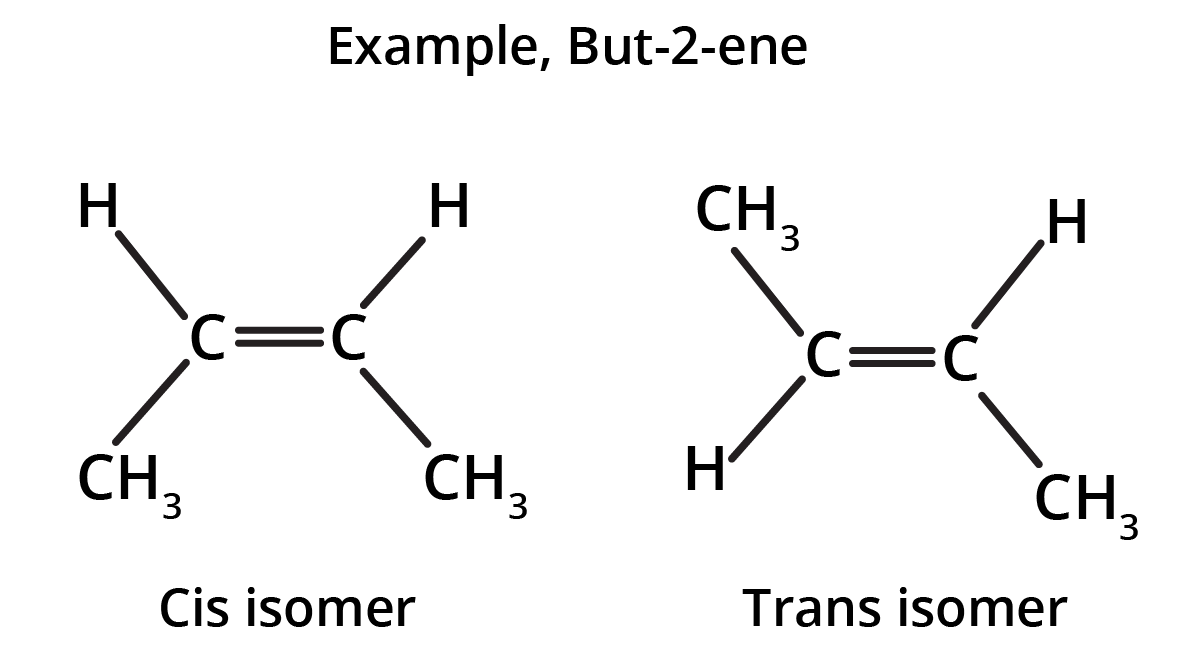
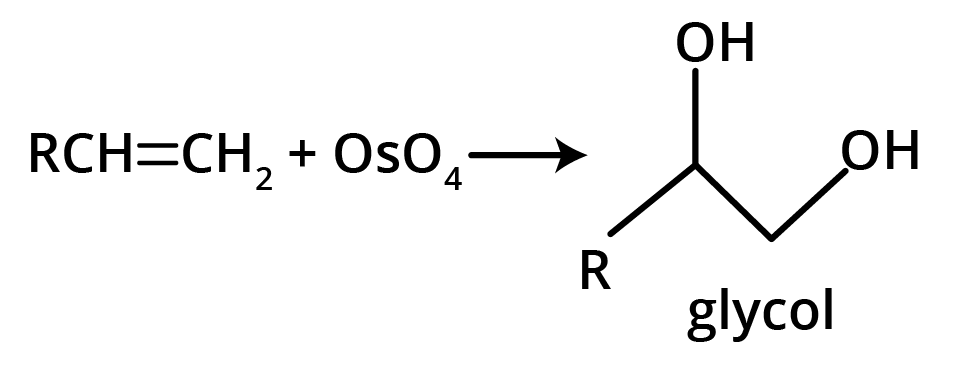
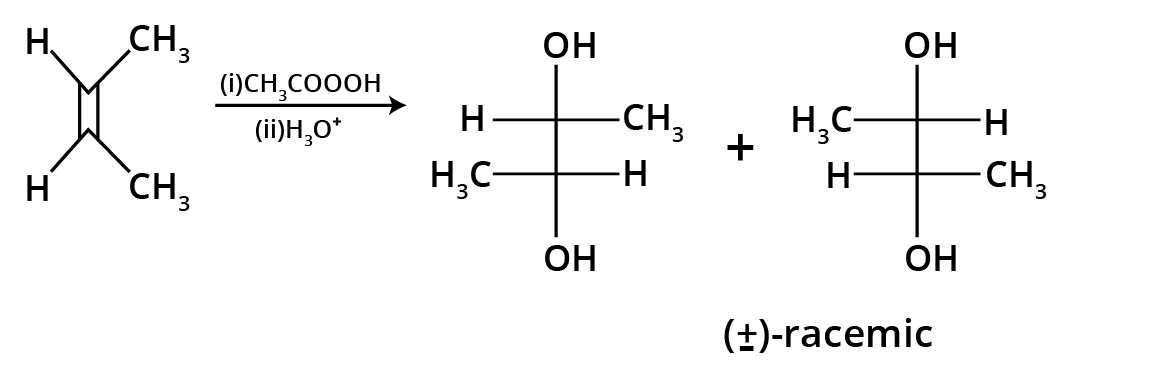
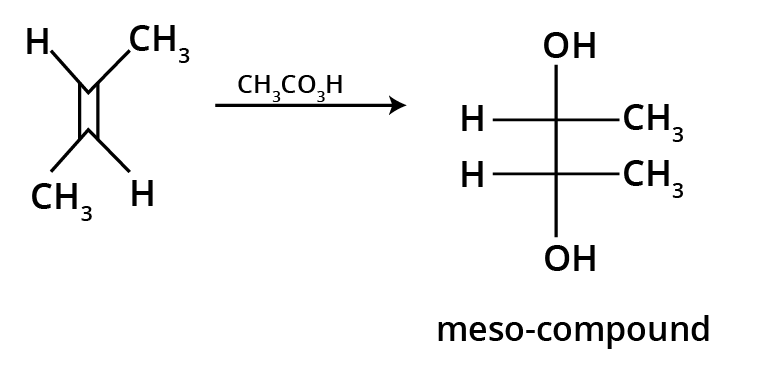
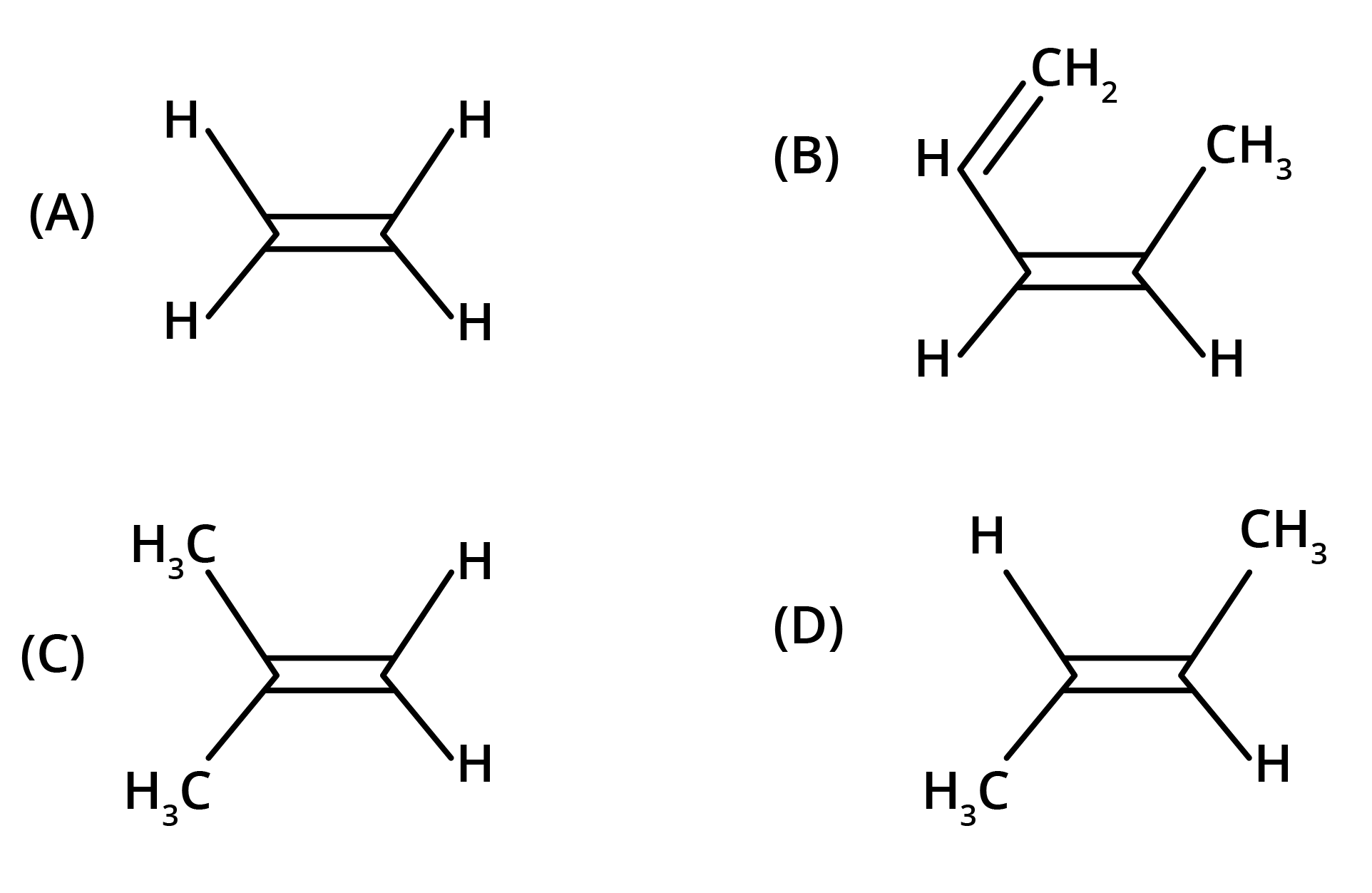
The key concept is that isomers have the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements. For revision, focus on two main types: Structural Isomerism (different connectivity, like chain and position isomers) and Geometrical Isomerism (different spatial arrangement around a double bond, known as cis-trans isomerism).
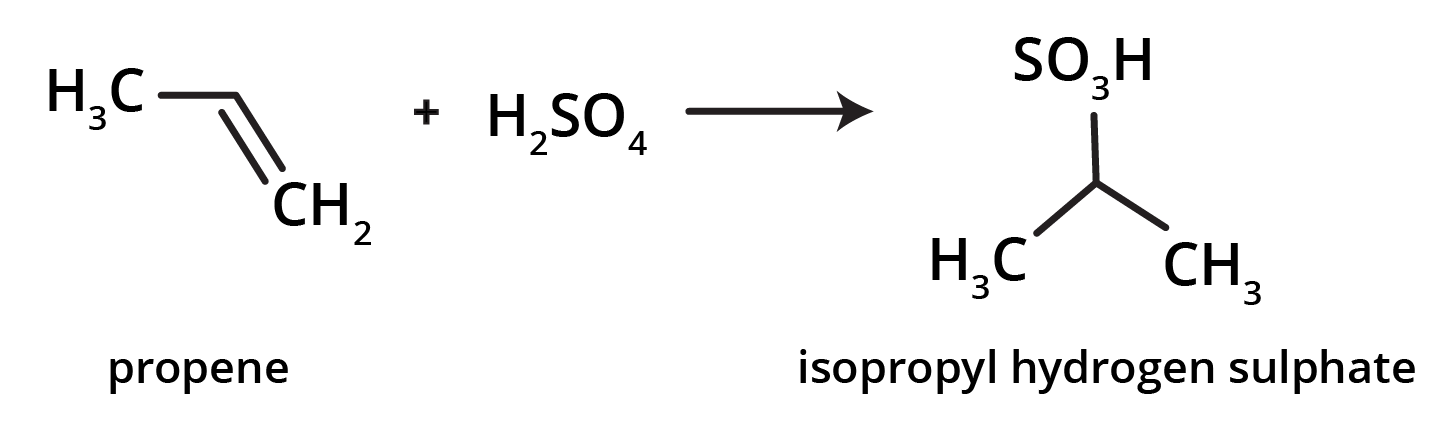
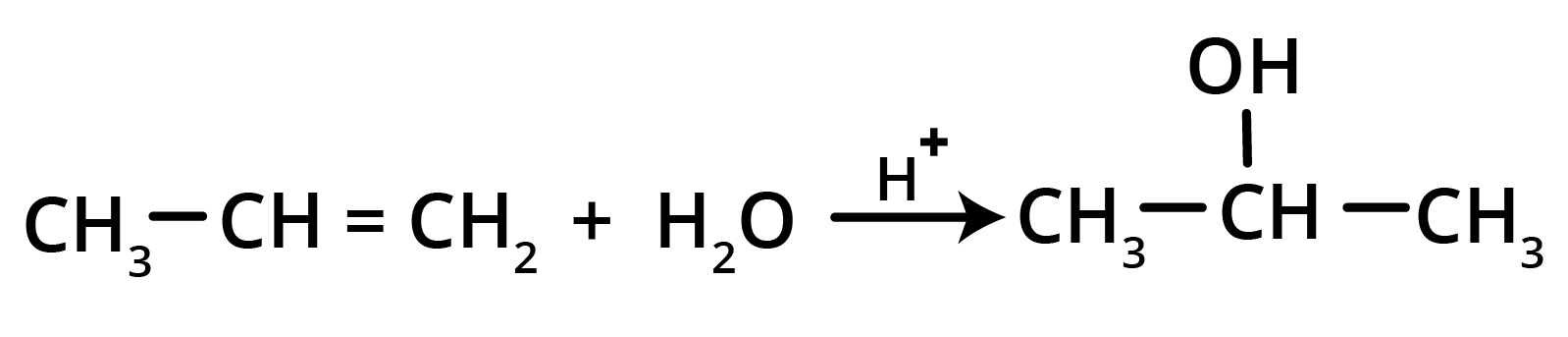
3. How can I quickly summarise the key preparation methods for alkenes?
For a quick summary, remember these four primary methods for preparing alkenes:
- Dehydration of Alcohols: Removing a water molecule from an alcohol using an acid catalyst.
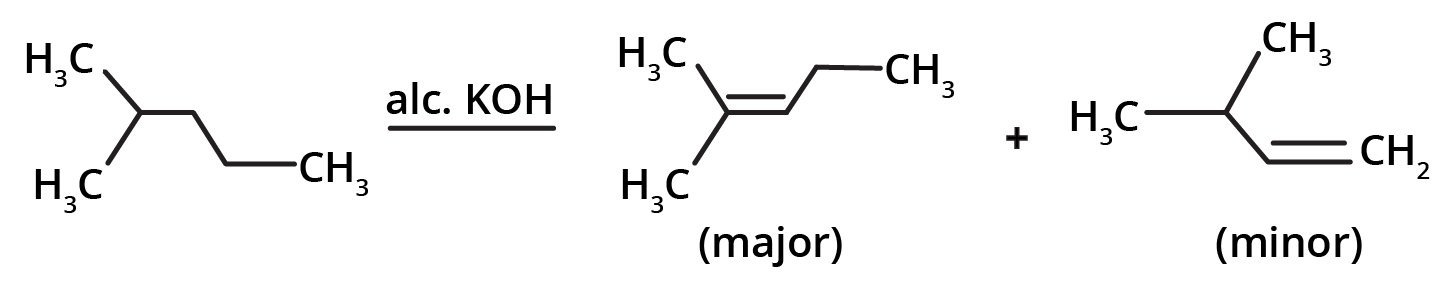
- Dehydrohalogenation of Alkyl Halides: Removing a hydrogen halide (HX) using an alcoholic base, often following Saytzeff's rule.
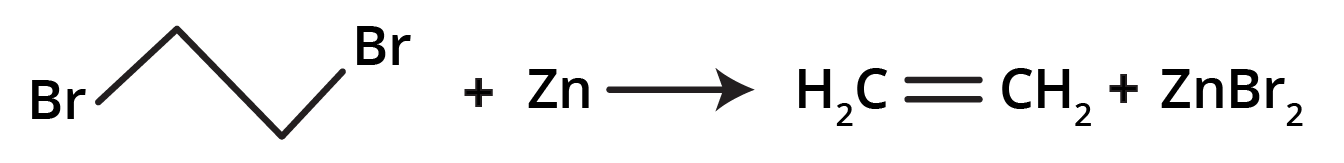
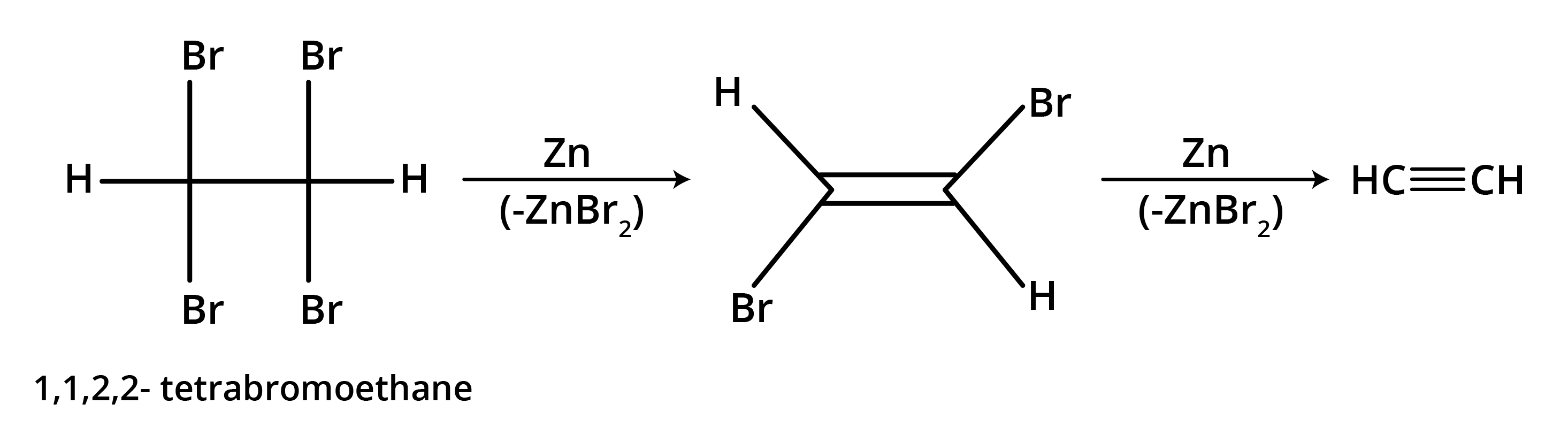
- Dehalogenation of Vicinal Dihalides: Removing two halogen atoms from adjacent carbons using zinc dust.
- Kolbe's Electrolytic Method: Electrolysis of sodium or potassium salts of dicarboxylic acids.
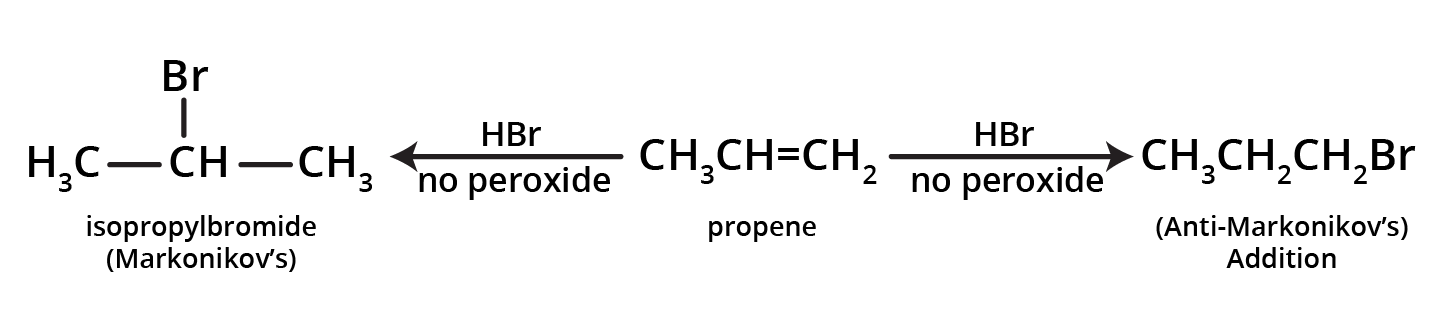
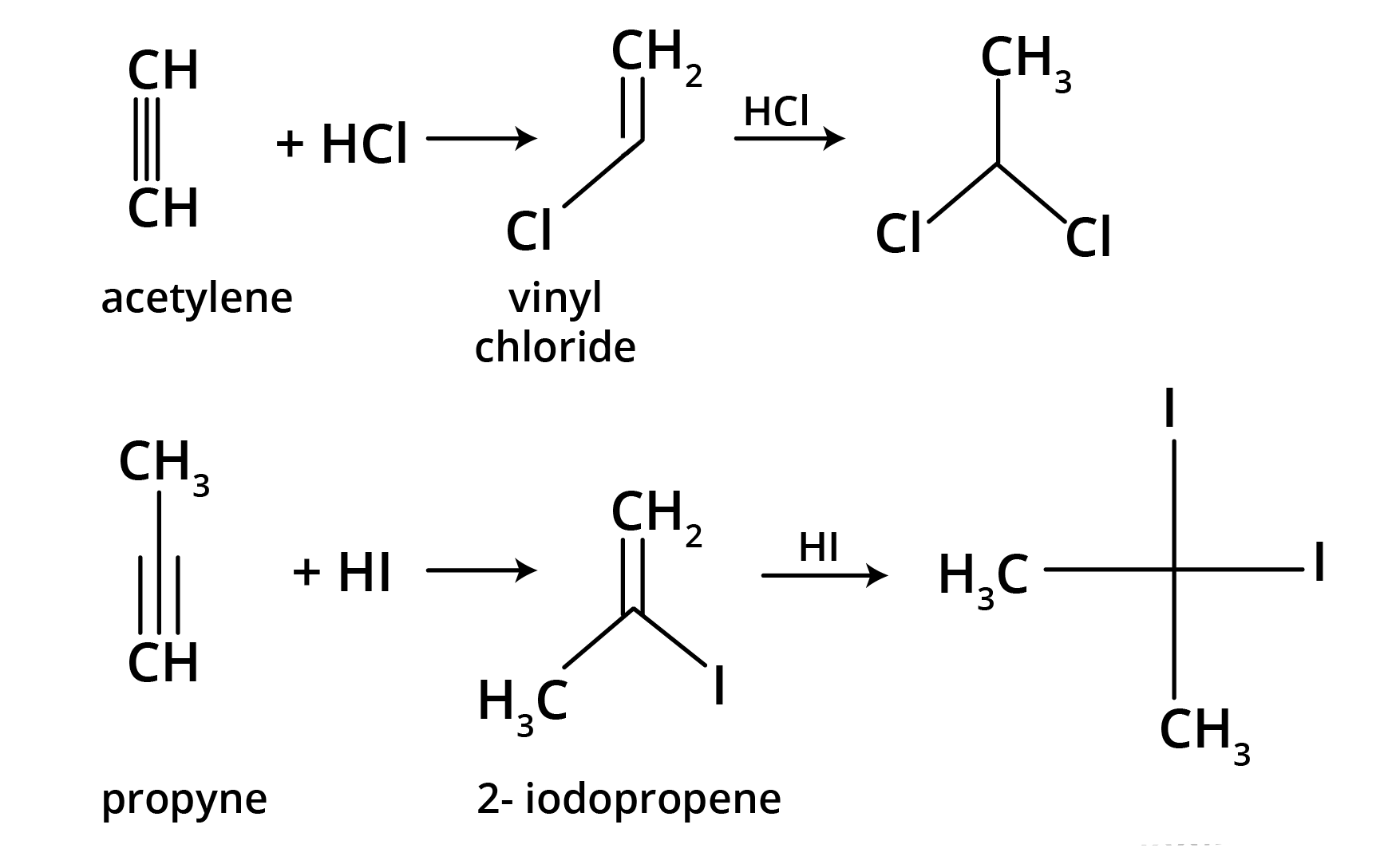
4. What is the key difference to remember between Markovnikov's and Anti-Markovnikov's rule?
The key difference lies in where the negative part of the adding reagent (like HBr) attaches to an unsymmetrical alkene.
- Markovnikov's Rule: The negative part adds to the carbon atom with fewer hydrogen atoms. This is the standard mechanism.
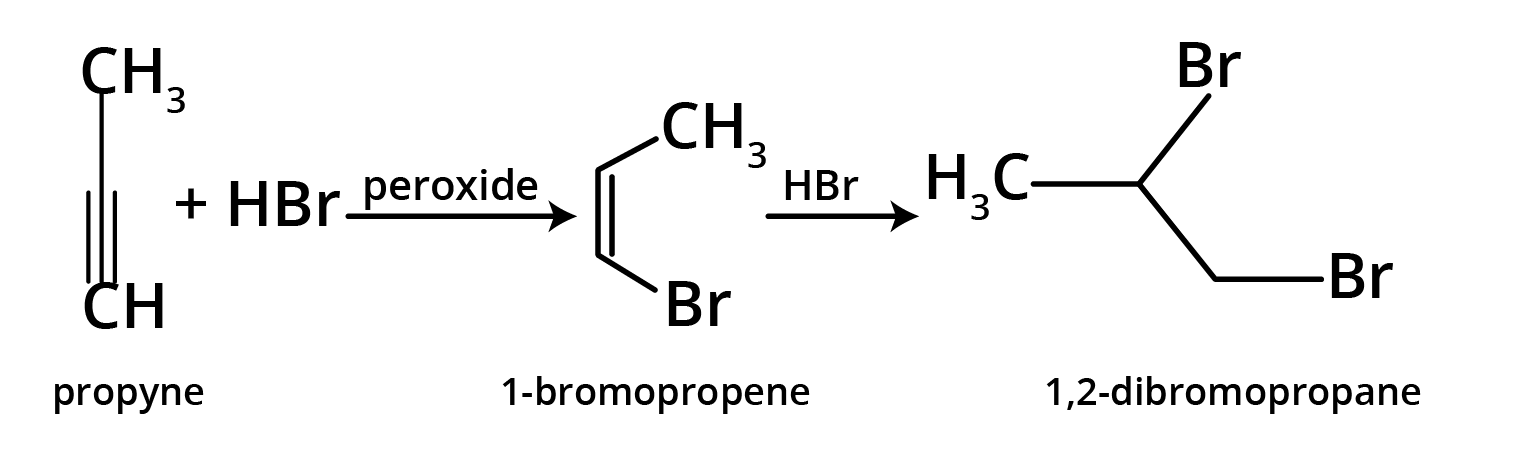
- Anti-Markovnikov's Rule (Peroxide Effect): In the presence of peroxide, the negative part (specifically from HBr) adds to the carbon atom with more hydrogen atoms.
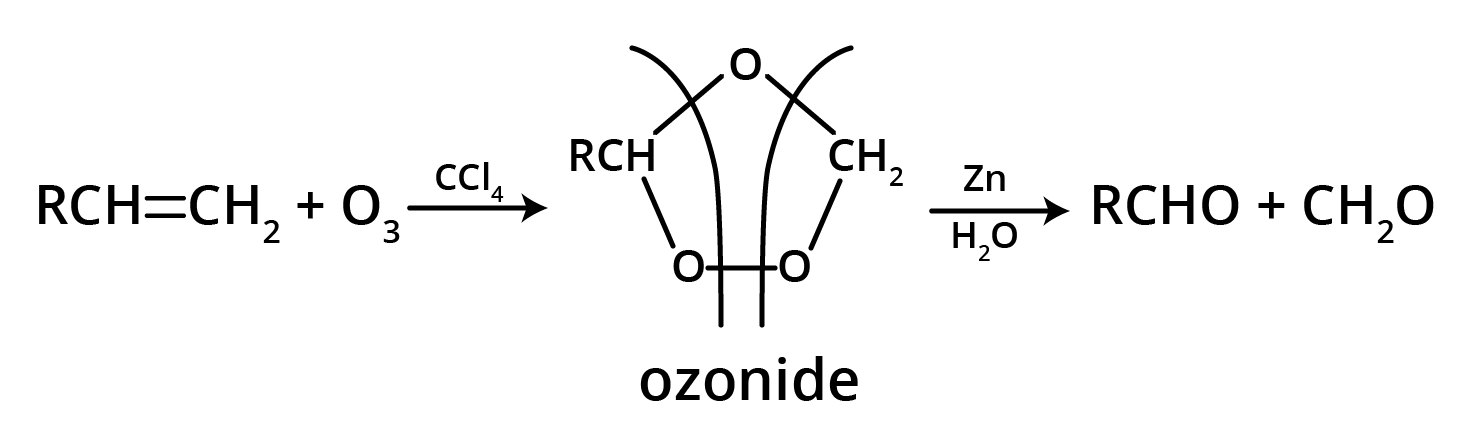
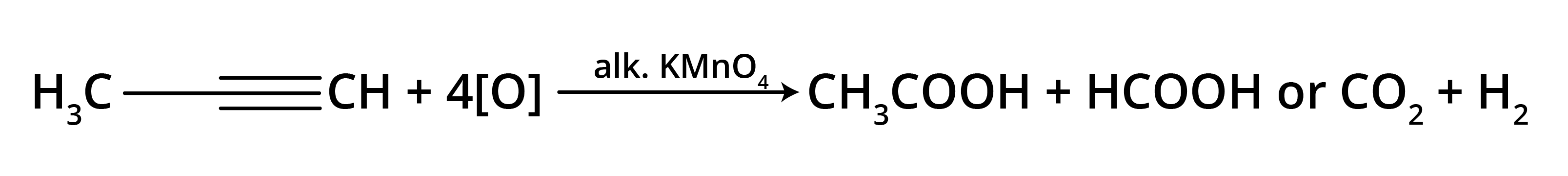
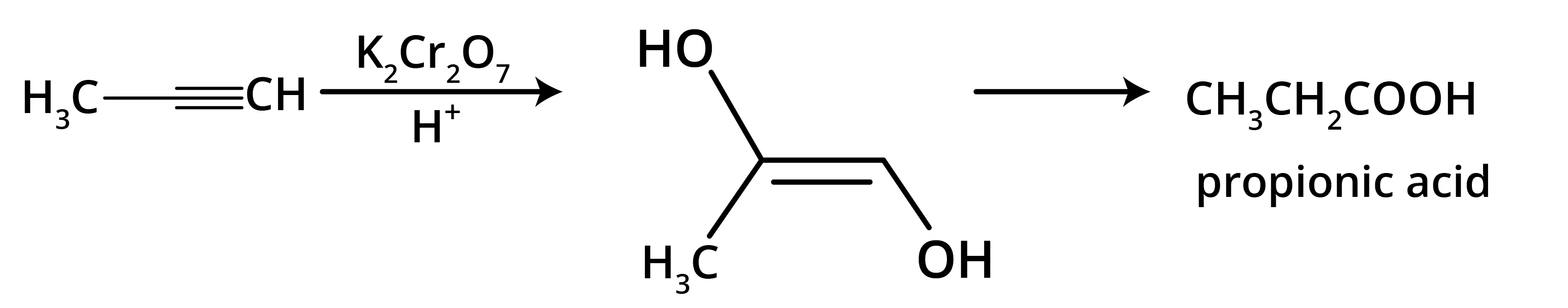
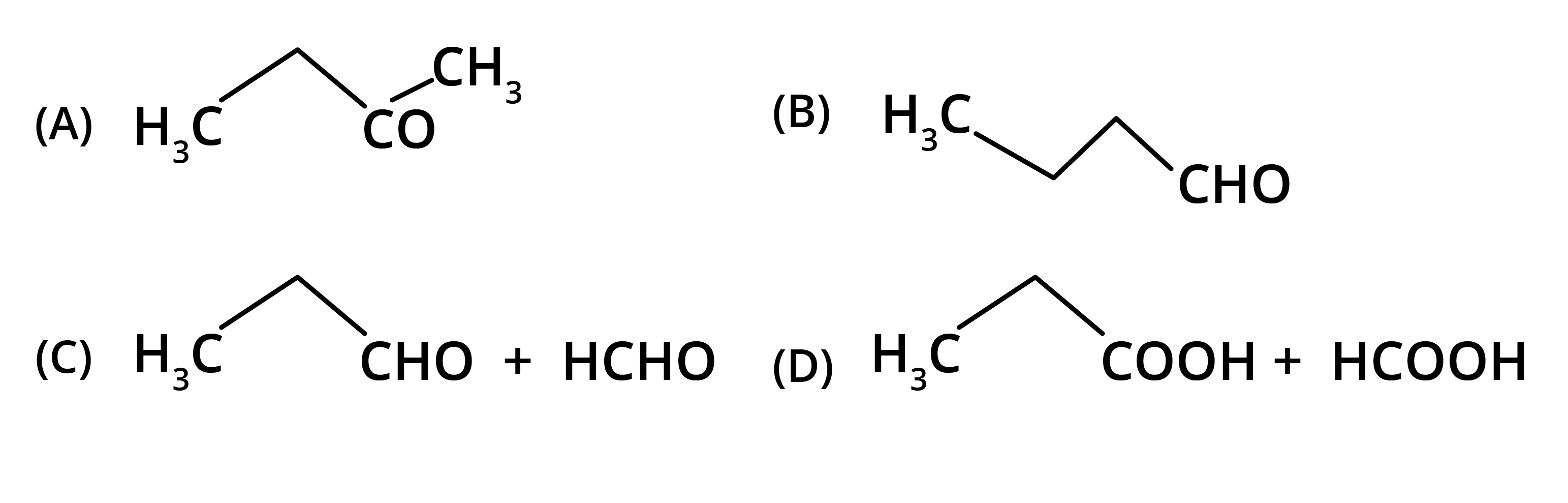
5. What is the main takeaway from the ozonolysis of alkenes and alkynes?
The main takeaway is that ozonolysis is a powerful reaction used to determine the position of double or triple bonds in a molecule. The reaction cleaves the molecule at the C=C or C≡C bond, forming smaller carbonyl compounds (aldehydes, ketones, or carboxylic acids), which can then be identified to deduce the original structure.
6. Why are alkenes and alkynes more reactive than alkanes?
Alkenes and alkynes are more reactive than alkanes because of the presence of loosely held pi (π) electrons in their double and triple bonds. These π-electron clouds are exposed and act as a source of electrons for attacking electrophiles, making alkenes and alkynes highly susceptible to electrophilic addition reactions. Alkanes, being saturated with strong sigma (σ) bonds, are much less reactive.
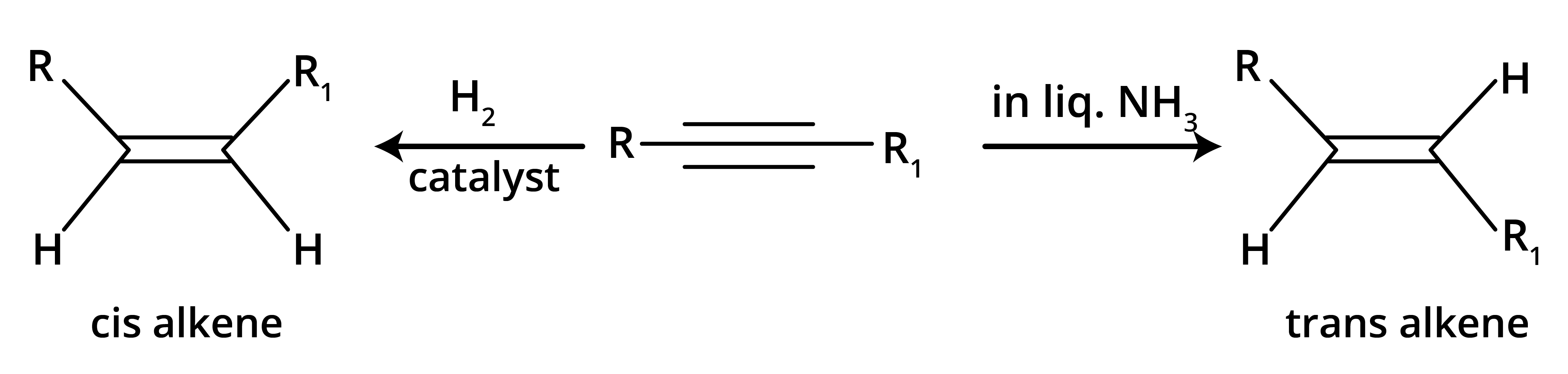
7. How does the choice of reducing agent create different products during the hydrogenation of alkynes?
The choice of reducing agent is crucial as it determines the stereochemistry of the resulting alkene.
- Using Lindlar's catalyst (partially deactivated palladium) results in a cis-alkene because the hydrogen atoms add to the same side of the triple bond (syn-addition).
- Using sodium in liquid ammonia (Birch reduction) results in a more stable trans-alkene because the mechanism involves an intermediate that favours the addition of hydrogen atoms to opposite sides (anti-addition).
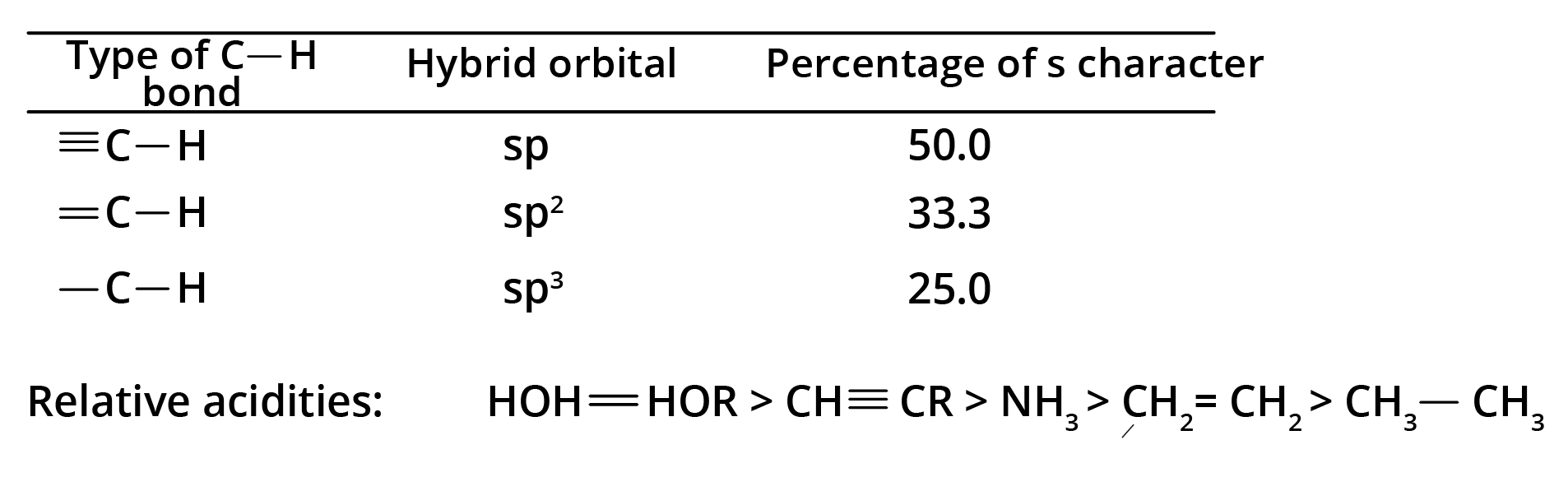
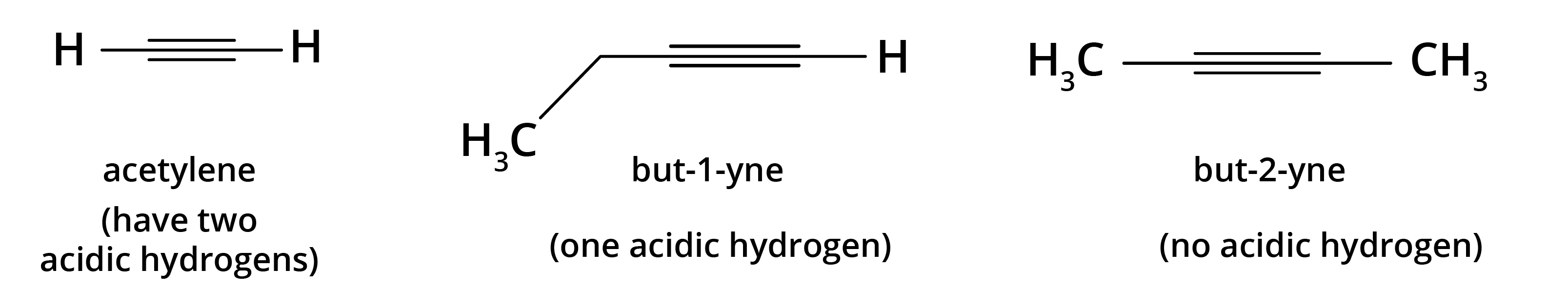
8. What is the concept behind the acidic nature of terminal alkynes?
The hydrogen atom attached to a triply bonded carbon in a terminal alkyne (like in propyne) is acidic. This is because the carbon atom is sp-hybridised, which has 50% s-character. The high s-character makes the carbon atom more electronegative, pulling the electron density from the C-H bond and making it easier for the hydrogen to be released as a proton (H⁺). This acidity is why terminal alkynes react with strong bases like NaNH₂.
9. How can you use simple chemical tests to distinguish between an alkane, an alkene, and a terminal alkyne?
You can use these key tests for a quick distinction:
- Alkane: Does not react with bromine water or cold, dilute alkaline KMnO₄ (Baeyer's reagent). The colours of the reagents persist.
- Alkene: Decolourises both bromine water and Baeyer's reagent, indicating the presence of a C=C double bond.
- Terminal Alkyne: Also decolourises both reagents but gives an additional, unique positive test. It forms a white precipitate with ammoniacal silver nitrate (Tollens' reagent) or a red precipitate with ammoniacal cuprous chloride due to its acidic hydrogen.
10. What is the significance of Hückel's rule for revising aromatic hydrocarbons?
Hückel's rule is a quick check to determine if a cyclic compound is aromatic. For a compound to be aromatic, it must be cyclic, planar, have a continuous ring of p-orbitals, and contain a total of (4n+2) π electrons, where 'n' is a whole number (0, 1, 2, etc.). For benzene, n=1, so it has (4*1+2) = 6 π electrons, confirming its exceptional stability.