An Overview of Cbse Class 6 Maths Notes Chapter 9
FAQs on CBSE Notes Class 6 Maths Chapter 9 - Symmetry - 2025-26
1. What is symmetry as per Class 6 Maths Chapter 9 revision notes?
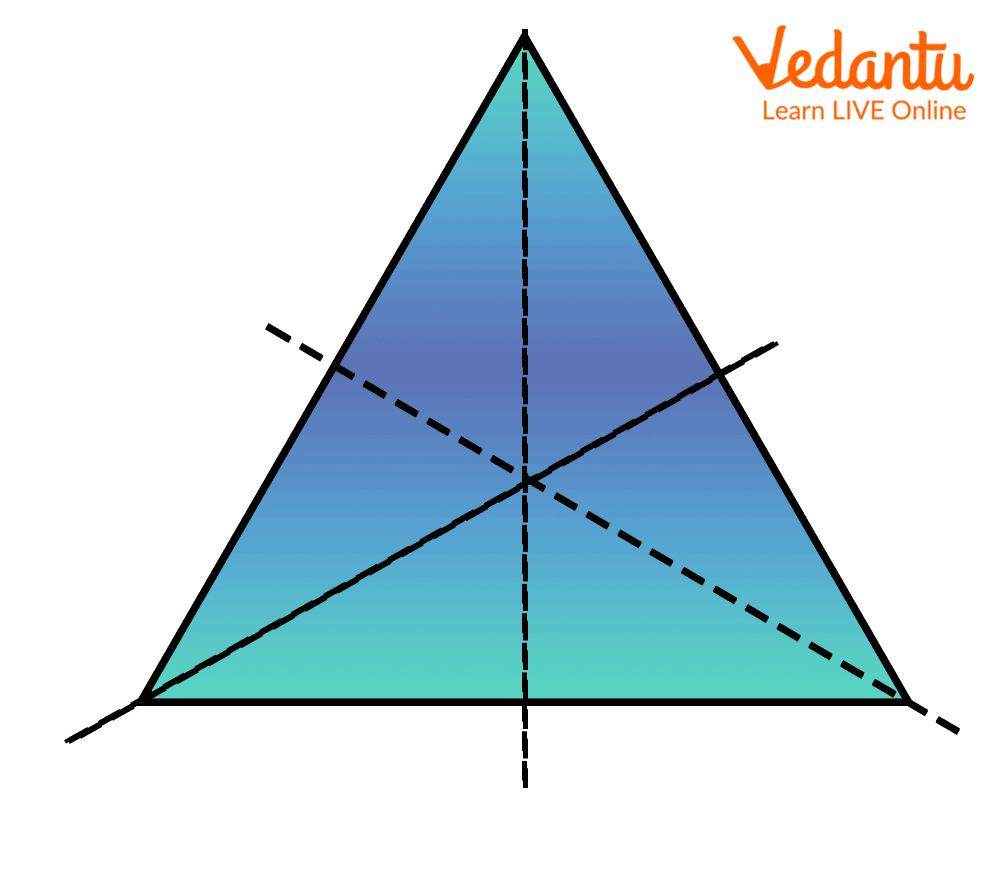
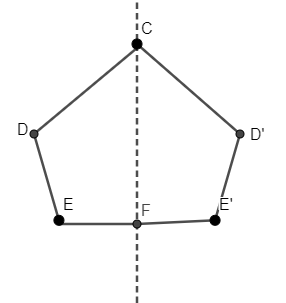
Symmetry refers to a property where a shape, pattern, or design is balanced and identical on both sides of a dividing line or around a point. In Class 6, symmetry means if you fold a shape along a particular line, both halves match exactly, helping students understand visual balance and proportion.
2. How do you identify lines of symmetry in different shapes for revision?
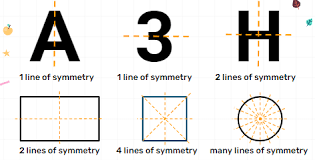
To identify lines of symmetry, carefully look at the shape and fold it mentally or on paper. If both halves overlap completely along that fold, it is a line of symmetry. For example:
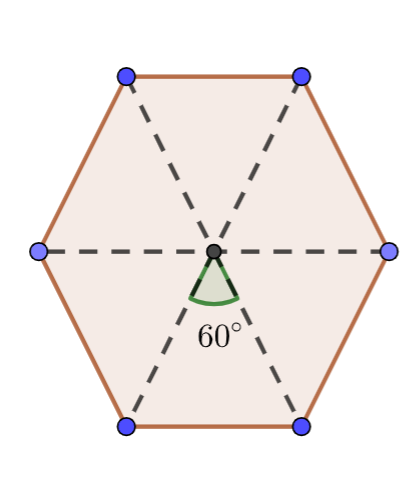
- A square has 4 lines of symmetry (vertical, horizontal, and two diagonals).
- A rectangle has 2 lines (horizontal and vertical).
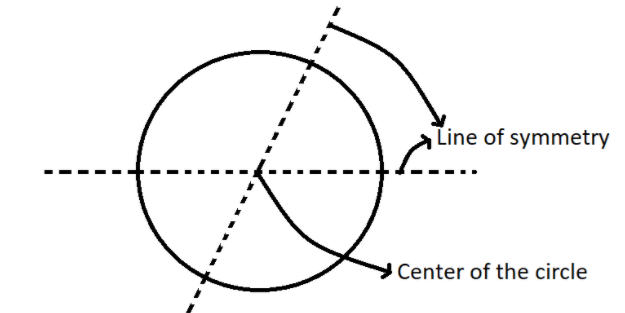
- A circle has infinite lines of symmetry, as any diameter divides it into identical halves.
3. What are the important types of symmetry covered in Class 6 revision notes?
There are two major types of symmetry covered:
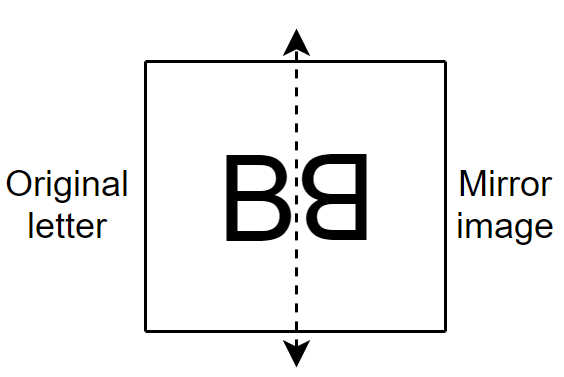
- Reflective (or Mirror) Symmetry: When one half of a figure is a mirror image of the other half across a line.
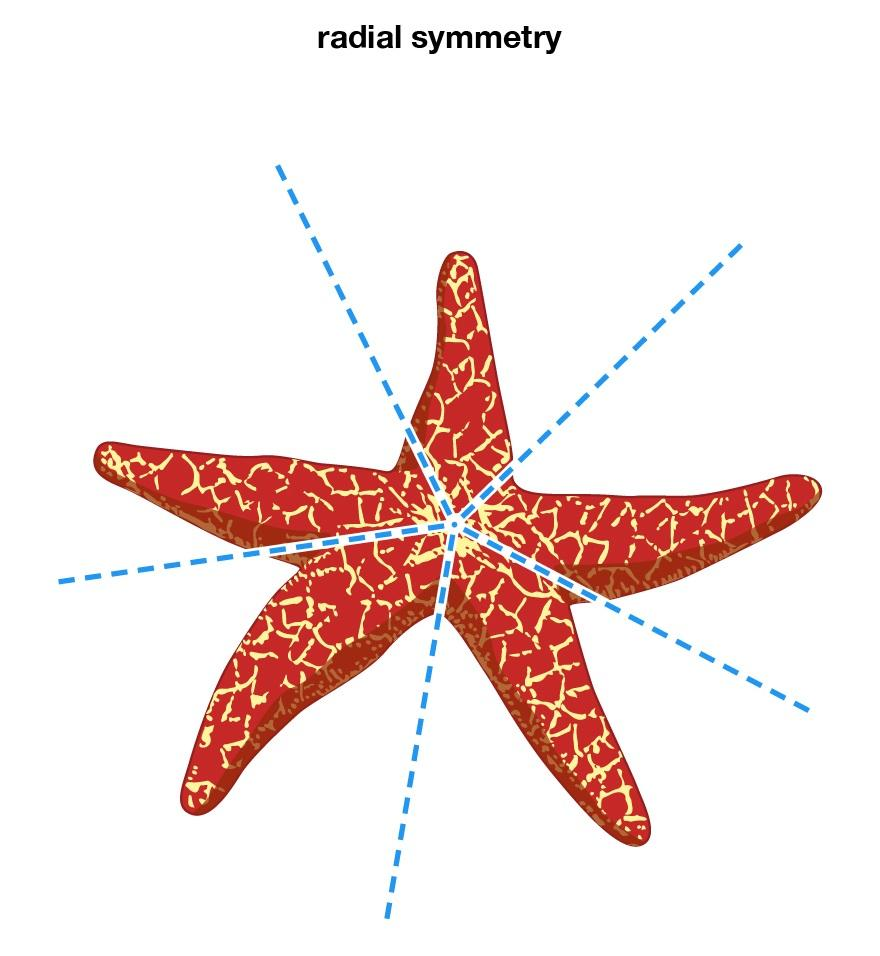
- Rotational Symmetry: When a figure appears unchanged after a certain amount of rotation around a fixed point. For example, a square looks the same after a 90°, 180°, 270°, or 360° turn.
4. Why is learning about symmetry important in developing mathematical and visual skills?
Learning symmetry helps in visualizing shapes, enhancing spatial reasoning, and building a strong foundation for advanced geometry topics. Understanding symmetry also improves pattern recognition skills, which are essential not only in mathematics but also in art, design, and real-world problem-solving.
5. How does symmetry appear in nature and everyday objects?
Many natural and man-made objects show symmetry. For example:
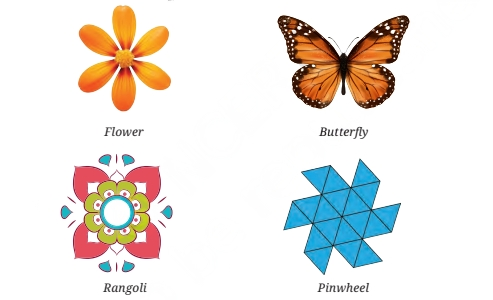
- Nature: Butterfly wings, flowers, leaves, and snowflakes have mirror symmetry.
- Objects: Buildings, tiles, and patterns in art often use symmetry for balance and appeal.
Observing these helps students relate the concept of symmetry to their daily life.
6. What steps can students follow for quick revision of symmetry topics before exams?
Use these strategies for effective revision:
- Review definitions and types of symmetry (reflective and rotational).
- Practice drawing lines of symmetry in standard shapes.
- Solve example problems and complete symmetrical patterns.
- Observe real-life objects for lines and points of symmetry.
These steps help reinforce key terms and concepts efficiently.
7. How do you distinguish between regular and irregular shapes based on symmetry?
Regular shapes like squares and circles have multiple lines of symmetry. Their parts are equal and balanced. Irregular shapes may have one, none, or unusual lines of symmetry, making them harder to divide into identical halves. Recognizing this difference aids in problem-solving and geometric reasoning.
8. What common mistakes should students avoid while revising symmetry concepts?
Common errors to avoid include:
- Assuming all shapes have symmetry (some have none).
- Confusing rotational symmetry with reflective symmetry.
- Misidentifying the exact line where the shape overlaps identically.
- Overlooking symmetry in complex or irregular figures.
Careful observation and practice help avoid these pitfalls as per the chapter notes.
9. How can students create symmetrical patterns for better understanding?
Students can:
- Fold paper: Fold a paper and cut patterns; when opened, the design is symmetrical.
- Draw on grid paper: This helps in tracing and checking if both sides match.
- Reflect shapes: Use a mirror along the line of symmetry to visualize both halves.
These methods make symmetry concepts interactive and memorable.
10. In what ways does Class 6 Chapter 9 symmetry connect to advanced geometry concepts?
Symmetry lays the foundation for advanced geometry topics like transformations (reflection, rotation, translation), understanding regular polygons, and visualizing three-dimensional objects. Mastering symmetry in Class 6 helps in grasping higher-level concepts in later grades as per the CBSE/NCERT syllabus.