Chemistry Notes for Chapter 7 Redox Reaction Class 11 - FREE PDF Download
Redox reactions Chapter 7 for reduction-oxidation reactions, are fundamental chemical processes where the oxidation state of one or more species changes. These reactions involve the transfer of electrons between substances, which leads to changes in their chemical identities. Understanding redox reactions is crucial as they underpin various biological processes, industrial applications, and environmental phenomena. In Chapter 7 of Class 11 Chemistry, the focus is on comprehending the principles and applications of redox reactions, which are essential for mastering more advanced chemical concepts.
Chapter 7 Redox reaction Class 11 Notes lets you quickly access and review the chapter content. For a comprehensive study experience, check out the Class 11 Chemistry Revision Notes FREE PDF here and refer to the CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Syllabus for detailed coverage. Vedantu's notes offer a focused, student-friendly approach, setting them apart from other resources and providing you with the best tools for success.
Access Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox reaction Class 11 Notes
Oxidation:
Oxygen is added. $2{\text{Mg}} + {{\text{O}}_2} \to 2{\text{MgO}}$
Hydrogen is being removed. ${{\text{H}}_2}\;{\text{S}} + {\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_2} \to 2{\text{HCl}} + {\text{S}}$
Positive charge increases. ${\text{F}}{{\text{e}}^{2 + }} \to {\text{F}}{{\text{e}}^{3 + }} + {{\text{e}}^ - }$
Removal of electron ${\text{S}}{{\text{n}}^{2 + }} \to {\text{S}}{{\text{n}}^{4 + }} + 2{{\text{e}}^ - }$
Reduction:
Oxygen is being removed. ${\text{CuO}} + {\text{C}} \to {\text{Cu}} + {\text{CO}}$
Hydrogen is added. ${\text{S}} + {{\text{H}}_2} \to {{\text{H}}_2}\;{\text{S}}$
Positive charge decreases. ${\text{F}}{{\text{e}}^{3 + }} + {{\text{e}}^ - } \to {\text{F}}{{\text{e}}^{2 + }}$
Addition of electron. ${\text{F}}{{\text{e}}^{3 + }} + {{\text{e}}^ - } \to {\text{F}}{{\text{e}}^{2 + }}$
Oxidation Number
When an element transitions from its elemental free state to its combined form in molecules, it develops an imaginary or seeming charge over each atom.
It is determined using an arbitrary set of rules.
In a certain bonded condition, it is a relative charge.
A more practical way of employing oxidation number to keep track of electron-shifts in chemical reactions involving the synthesis of compounds has been created.
The complete transfer of electrons from a less electronegative atom to a more electronegative atom is always expected in this procedure.
Rules Governing Oxidation Number
The following rules can be used to calculate the oxidation number of elements in various compounds. It is important to remember that the electronegativity of the element is the foundation of these rules.
Atom of Fluorine:
Fluorine is the most electronegative of all the elements (known). In all of its compounds, it has an oxidation number of –1.
Atom of Oxygen:
Oxygen atoms have an oxidation number of –2 in general, as well as in their oxides.
peroxide (e.g. $\left. {{{\text{H}}_2}{{\text{O}}_2},{\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_2}{{\text{O}}_2}} \right)$ is $ - 1$
super oxide (e.g. ${\text{K}}{{\text{O}}_2}$ ) is $ - 1/2$
ozonide (e.g. ${\text{K}}{{\text{O}}_3}$ ) is $ - 1/3$
in ${\text{O}}{{\text{F}}_2}$ is $ + 2{\text{ in }}{{\text{O}}_2}\;{{\text{F}}_2}$ is $ + 1$
Hydrogen Atom:
The hydrogen atom has an oxidation number of +1 in general. However, it is –1 in metallic hydrides (e.g. NaH, KH).
Halogen Atom:
In general, all halogen atoms (Cl, Br, and I) have an oxidation number of –1.
If a halogen atom is connected to a more electronegative atom than the halogen atom, the oxidation numbers will be positive.
e.g. ${\text{KCl}}{{\text{O}}_3},{\text{HI}}{{\text{O}}_3},{\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_4},{\text{KBr}}{{\text{O}}_3}$.
Metals:
The oxidation number of alkali metals (Li, Na, K, Rb, etc.) is always +1.
The oxidation number of alkaline earth metals (Be, Mg, Ca, etc.) is always +2.
The oxidation number of aluminium is always +3.
Note that a metal's oxidation number might be negative or zero.
In the free state or in allotropic forms, an element's oxidation number is always zero.
e.g. ${\text{O}}_2^0,\;{\text{S}}_8^0,{\text{P}}_4^0$
The sum of all the oxidation numbers of the atoms in a molecule is zero.
The charge on an ion is equal to the sum of the oxidation numbers of all the atoms in the ion.
If an element's group number is n in the contemporary periodic table, its oxidation number can range from (n – 10) to (n – 18). (but it is mainly applicable for p-block elements).
Calculation of Average Oxidation Number: Solved Examples
Example-1 : Calculate oxidation number of underlined element
${\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_2}{\underline {\text{S}} _2}$
${\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_2}{\underline {\text{S}} _4}$
Let oxidation number of S-atom is ${\text{x}}$. Now work accordingly with the rules given before.
$ ( + 1) \times 2 + (x) \times 2 + ( - 2) \times 3 = 0 $
$ x = + 2 $
Let oxidation number of $S$-atom is $x$
$ \therefore ( + 1) \times 2 + (x) \times 4 + ( - 2) \times 6 = 0 $
$ x = + 2.5 $
It is vital to note that ${\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{S}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$ has two S-atoms, whereas ${\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{S}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}}$ has four S-atoms. However, none of the sulphur atoms in either compound has an oxidation number of +2 or + 2.5; instead, the average of the oxidation numbers on each sulphur atom is used. As a result, we should strive to determine each sulphur atom's specific oxidation number in these compounds.
Individual Oxidation Number Calculation:
It's vital to remember that in order to calculate the individual oxidation number of an element in its compound, you'll need to know the structure of the compound and follow the steps below.
This is the formula:
Number of electrons in the valence shell minus number of electrons taken up after bonding = oxidation number
Recommendations: It is based on an element's electronegativity.
1. Bonded pair electrons are evenly shared by each element if there is a bond between similar types of atoms and each atom has the same sort of hybridisation.
Consider the Following Scenario:
Calculate each Cl-oxidation atom's number in the ${\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}$ molecule.
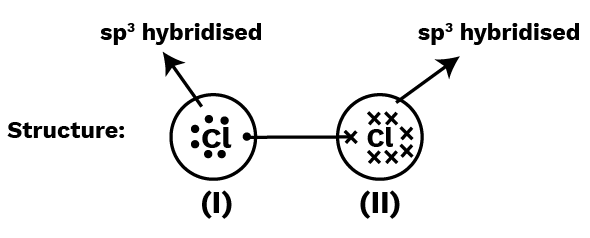
I : Number of electrons in the valence shell $ = 7$
Number of electrons taken up after bonding $ = 7$
$\therefore $ oxidation number $ = 7 - 7 = 0$
II : similarly, oxidation number $ = 7 - 7 = 0$
If a bond exists between different types of atoms, such as A – B (if B is more electronegative than A), the bound pair of electrons are tallied with the B-atom after bonding.
Consider the following scenario:
Calculate each atom's oxidation number in the HCl molecule.
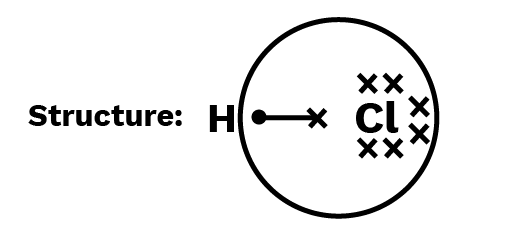
Electron of H-atom is now counted with Cl-atom, because Cl-atom is more electronegative than H-atom
${\text{H}}:\quad $ Number of electrons in the valence shell $ = 1$
Number of electrons taken up after bonding $ = 0$
Oxidation number of ${\text{H}} = 1 - 0 = + 1$
${\text{Cl}}:\quad $ Number of electrons in the valence shell $ = 7$
Number of electrons taken up after bonding $ = 8$
Oxidation number of ${\text{Cl}} = 7 - 8 = - 1$
Solved Examples Example – 2
Calculate individual oxidation number of each S-atom in ${\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_2}\;{{\text{S}}_2}{{\text{O}}_3}$ ( sodium thiosulphate) with the help of its structure.
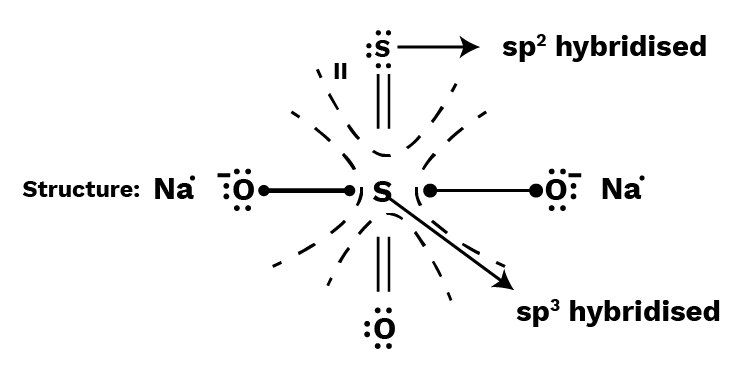
I (the middle S-atom) is sp3 hybridised (25 percent s-character), while II (the terminal S-atom) is sp2 (33 percent s-character). As a result, the terminal sulphur atom has a higher electronegative charge than the central sulphur atom. With the terminal S-atom, the shared pair of electrons is now counted.
I, S-atom: Number of electrons in the valence shell $ = 6$
Number of electrons left after bonding $ = 0$
Oxidation number of central $S$-atom $ = 6 - 0 = + 6$
II, S-atom : Number of electrons in the valence shell $ = 6$
Number of electrons left after bonding $ = 8$
Oxidation number of terminal S-atom $ = 6 - 8 = - 2$
Now, you can also calculate Average Oxidation number of ${\text{S}} = \dfrac{{6 + ( - 2)}}{2} = + 2$ (as we have calculated before)
Miscellaneous Examples:
In order to determine the exact or individual oxidation number we need to take help from the structures of the molecules. Some special cases are discussed as follows :
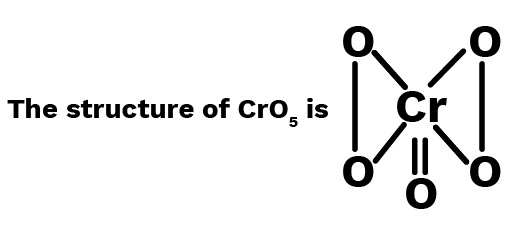
From the structure, it is evident that in ${\text{Cr}}{{\text{O}}_5}$ there are two peroxide linkages and one double bond. The contribution of each peroxide linkage is $ - 2$. Let the oxidation number of ${\text{Cr}}$ is ${\text{x}}$.
$\therefore x + ( - 2)2 + ( - 2) = 0$ or $x = 6$
$\therefore $ Oxidation number of ${\text{Cr}} = + 6$ Ans.
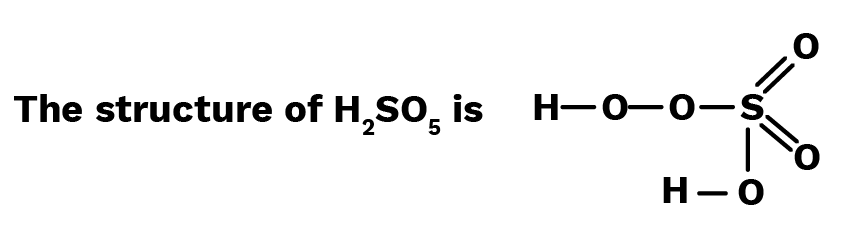
From the structure, it is evident that in ${{\text{H}}_2}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_5}$, there is one peroxide linkage, two sulphur-oxygen double bonds and one ${\text{OH}}$ group.
Let the oxidation number of $S = x$.
$\therefore ( + 1) + ( - 2) + x + ( - 2)2 + ( - 2) + 1 = 0$
or $x + 2 - 8$ or $x - 6 = 0\quad $ or $x = 6$
$\therefore $ Oxidation number of ${\text{S}}$ in ${{\text{H}}_2}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_5}$ is $ + 6$ Ans.
Paradox of Fractional Oxidation Number:
The structural parameters demonstrate that the atoms of the element for whom fractional oxidation state is realised are truly present in distinct oxidation states, and the fractional oxidation number is the average of oxidation state of all atoms of the element under investigation. The following bonding scenarios are shown by the species' ${{\text{C}}_3}{{\text{O}}_2},{\text{B}}{{\text{r}}_3}{{\text{O}}_8}$ structure:
In each species, the element highlighted with an asterisk (*) has a different oxidation number than the rest of the atoms of the same element. This demonstrates that two carbon atoms in ${{\text{C}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ are each in the +2 oxidation state, while the third is in the zero oxidation state, giving a total of +4/3. The realistic picture, on the other hand, is +2 for two terabytes.
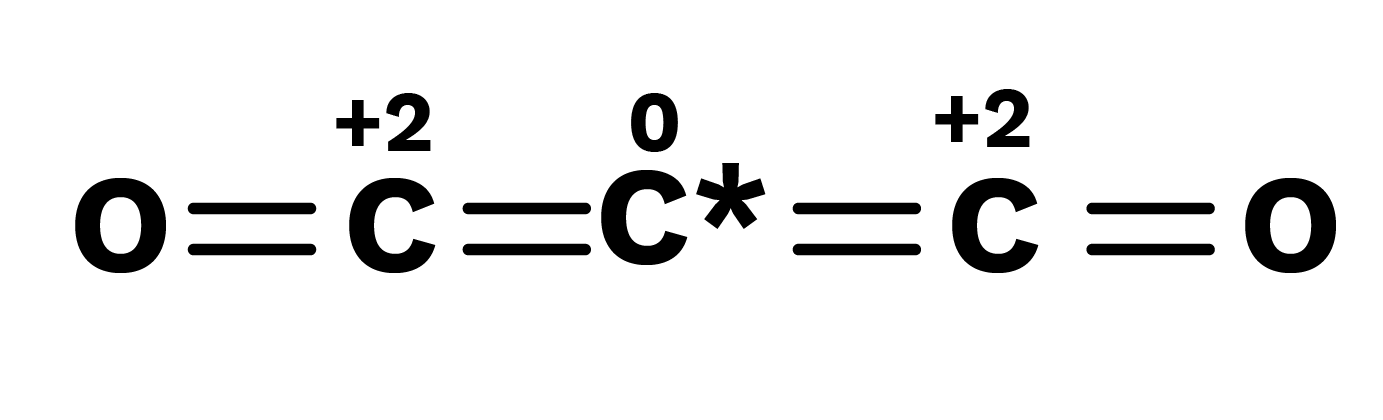
Likewise in ${\text{B}}{{\text{r}}_3}{{\text{O}}_8}$, each of the two terminal bromine atoms are present in $ + 6$ oxidation state and the middle bromine* is present in $ + 4$ oxidation state. Once again the average, that is different from reality, is $ + 16/3$.
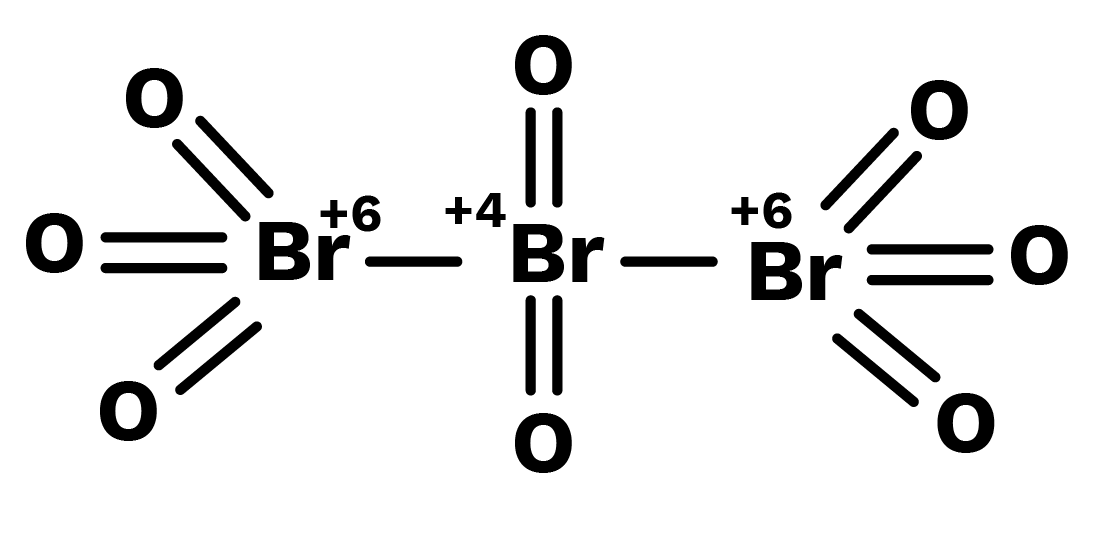
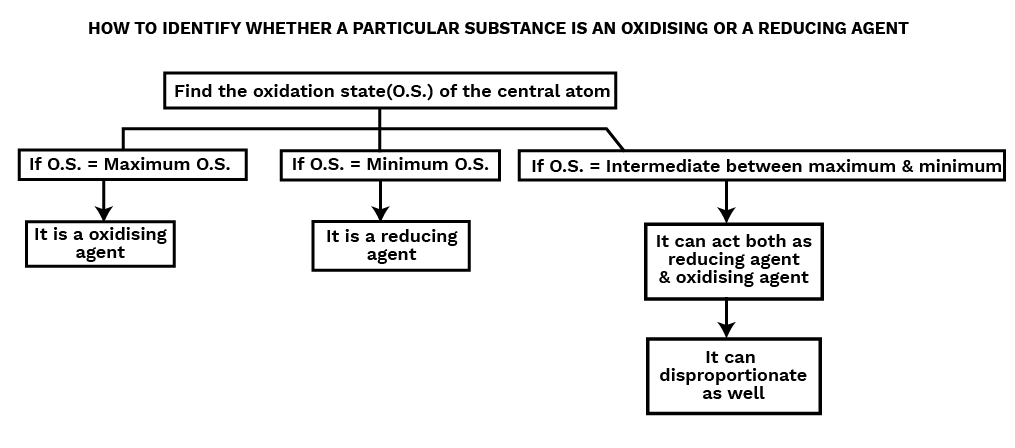
Oxidising and Reducing Agent:
Oxidising Agent or Oxidant :
Oxidising agents are substances that can oxidise others while reducing themselves during a chemical process. Oxidants are chemicals that cause an element's oxidation number to decrease or gain electrons in a redox process. e.g. ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_4},\;{{\text{K}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{r}}_2}{{\text{O}}_7},{\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_3}$, conc. ${{\text{H}}_2}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_4}$ etc are powerful oxidising agents.
Reducing Agent or Reductant :
Reducing agents are substances that can both reduce and oxidise other molecules during a chemical reaction. Reductants are reagents that increase the oxidation number of an element or cause the element to lose electrons in a redox reaction. e.g. ${\text{KI}},{\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_2}\;{{\text{S}}_2}{{\text{O}}_3}$ etc are the powerful reducing agents.
Redox Reaction:
A redox reaction is one in which both oxidation and reduction occur at the same time. The overall increase in oxidation number must match the total reduction in oxidation number in all redox processes.e.g. $10{\text{FeS}}{{\text{O}}_4} + 2{\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_4} + 8{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_4} \to 5{\text{F}}{{\text{e}}_2}{\left( {{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_4}} \right)_3} + 2{\text{MnS}}{{\text{O}}_4} + {{\text{K}}_2}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_4} + 8{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}$
Disproportionation Reaction :
A disproportionation reaction is a redox reaction in which the same element present in a specific molecule in a specific oxidation state is oxidised and reduced at the same time.
Disproportionation reactions are a sort of redox reaction that is unique. In a disproportionation reaction, one of the reactants must always contain an element that may exist in at least three oxidation states.
$2{{\text{H}}_2}{{\text{O}}_2}({\text{aq}}) \to 2{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}(l) + {\mathop {\text{O}}\limits^0 _2}(\;{\text{g}})$
${{\text{S}}_{\text{8}}}({\text{s}}) + 12{\text{O}}{{\text{H}}^ - }({\text{aq}}) \to 4\;{{\text{S}}^{2 - }}({\text{aq}}) + 2\;{{\text{S}}_2}{\text{O}}_3^{2 - }({\text{aq}}) + 6{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}(l)$
Consider the Following Reations:
\[2{\text{KCl}}{{\text{O}}_3} \to 2{\text{KCl}} + 3{{\text{O}}_2}\]
${\text{KCl}}{{\text{O}}_3}$ plays a role of oxidant and reductant both. Here, ${\text{Cl}}$ present in ${\text{KCl}}{{\text{O}}_3}$ is reduced and ${\text{O}}$ present in ${\text{KCl}}{{\text{O}}_3}$ is oxidized. Since same element is not oxidized and reduced, so it is not a disproportionation reaction, although it looks like one.
${\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_4}{\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_2} \to {{\text{N}}_2} + 2{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}$
Nirogen in this compound has $ - 3$ and $ + 3$ oxidation number, which is not a definite value. So it is not a disporportionation reaction. It is an example of comproportionation reaction, which is a class of redox reaction in which an element from two different oxidation state gets converted into a single oxidation state.
List of Some Important Disproportionation Reactions:
${{\text{H}}_2}{{\text{O}}_2} \to {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}} + {{\text{O}}_2}$
${{\text{X}}_2} + {\text{O}}{{\text{H}}^ - }$(dil.) $ \to {{\text{X}}^ - } + {\text{X}}{{\text{O}}^ - }({\text{X}} = {\text{Cl}},{\text{Br}},{\text{I}})$
F2 does not undergo disproportionation as it is the most electronegative element.
${{\text{F}}_2} + {\text{NaOH (dil}}{\text{.)}} \to {{\text{F}}^ - } + {\text{O}}{{\text{F}}_2} $
${{\text{F}}_2} + {\text{NaOH (conc}}{\text{.)}} \to {{\text{F}}^ - } + {{\text{O}}_2} $
${({\text{CN}})_2} + {\text{O}}{{\text{H}}^ - } \to {\text{C}}{{\text{N}}^ - } + {\text{OC}}{{\text{N}}^ - }$
${{\text{P}}_4} + {\text{O}}{{\text{H}}^ - } \to {\text{P}}{{\text{H}}_3} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{PO}}_2^ - $
${{\text{S}}_8} + {\text{O}}{{\text{H}}^ - } \to {{\text{S}}^{2 - }} + {{\text{S}}_2}{\text{O}}_3^{2 - }$
Oxyacids of Chlorine (Halogens) $( + 1, + 3, + 5$ Oxidation number)
$ {\text{Cl}}{{\text{O}}^ - } \to {\text{C}}{{\text{l}}^ - } + {\text{ClO}}_2^ - $
$ {\text{ClO}}_2^ - \to {\text{C}}{{\text{l}}^ - } + {\text{ClO}}_3^ - $
$ {\text{ClO}}_3^ - \to {\text{NO}} + {\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_3} $
${\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_2} \to {\text{NO}} + {\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_3}$
Comproportionation is the inverse of disproportionation. By shifting the medium (from acidic to basic or reverse) in some disproportionation reactions, the reaction goes in the opposite direction and can be considered a Comproportionation reaction.
${{\text{I}}^ - } + {\text{IO}}_3^ - + {{\text{H}}^ + } \to {{\text{I}}_2} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}$
Balancing of Redox Reactions:
All balanced equations must meet two requirements.
Atom balance (mass balance): On the reactant and product sides, there should be the same number of atoms of each species.
Charge balance: On both sides of the equation, the sum of real charges must be equal.
The redox equations can be balanced in two ways:
Number change technique of oxidation
Half-cell method or ion electron method
Because the first approach is not particularly effective in balancing redox reactions, students are urged to use the second way (Ion electron method) to do so.
Method of Ion Electrons:
Redox equations in two different mediums are adjusted using this method.
Acidic Medium and
Basic Medium
Balancing in Acidic Medium:
Students are advised to balance redox reactions using the ion electron technique in an acidic medium by following the procedures below.
Balance the following redox reaction :
${\text{FeS}}{{\text{O}}_4} + {\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_4} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_4} \to {\text{F}}{{\text{e}}_2}{\left( {{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_4}} \right)_3} + {\text{MnS}}{{\text{O}}_4} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}} + {{\text{K}}_2}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_4}$
Step-I Assign the oxidation number to each element present in the reaction ${\text{FeSO}}_4^{ + 2} + {\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_4} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_4} \to {\text{F}}{{\text{e}}_2}{\left( {{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_4}} \right)_3} + {\text{MnS}}{{\text{O}}_4} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}$
Step II : Now convert the reaction in Ionic form by eliminating the elements or species, which are not undergoing either oxidation or reduction.
${\text{F}}{{\text{e}}^{2 + }} + {\text{MnO}}_4^{ - 7} \to {\text{F}}{{\text{e}}^{3 + }} + {\text{M}}{{\text{n}}^{2 + }}$
Step III : Now identify the oxidation/reduction occuring in the reaction.
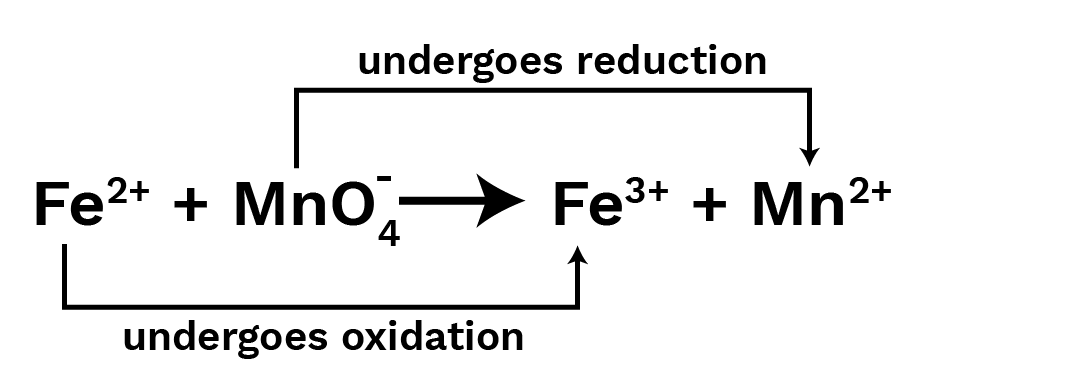
Step IV : Spilt the Ionic reaction in two half, one for oxidation and other for reduction.
${\text{F}}{{\text{e}}^{2 + }}\mathop \to \limits^{{\text{ Oxidation }}} {\text{F}}{{\text{e}}^{3 + }}\mid {\text{MnO}}_4^ - \mathop \to \limits^{{\text{ Reduction }}} {\text{M}}{{\text{n}}^{2 + }}$
Step V : Balance the atom other than oxygen and hydrogen atom in both half reactions.
${\text{F}}{{\text{e}}^{2 + }} \to {\text{F}}{{\text{e}}^{3 + }}\mid {\text{MnO}}_4^ - \to {\text{M}}{{\text{n}}^{2 + }}$
Step VI :Now balance ${\text{O and H}}$ atom by ${{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O and }}{{\text{H}}^ + }$ respectively by the following way :
For one excess oxygen atom, add one ${{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}$ on the other side and two ${{\text{H}}^ + }$on the same side.
${\text{F}}{{\text{e}}^{2 + }} \to {\text{F}}{{\text{e}}^{3 + }}\quad $ (no oxygen atom)
$8{{\text{H}}^ + } + {\text{MnO}}_4^ - \to {\text{M}}{{\text{n}}^{2 + }} + 4{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}$
Step VII : Equation (i) & (ii) are balanced atomwise. Now balance both equations chargewise. To balance the charge, add electrons to the electrically positive side.
${\text{F}}{{\text{e}}^{2 + }}\mathop \to \limits^{{\text{ oxidation }}} {\text{F}}{{\text{e}}^{3 + }} + {{\text{e}}^ - }$
$5{{\text{e}}^ - } + 8{{\text{H}}^ + } + {\text{MnO}}_4^ - \mathop \to \limits^{{\text{ Reduction }}} {\text{M}}{{\text{n}}^{2 + }} + 4{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}$
Step VIII : The number of electrons gained and lost in each half-reaction are equalised by multiplying both the half reactions with a suitable factor and finally the half reactions are added to give the overall balanced reaction. Here, we multiply equation (1) by 5 and (2) by 1 and add them :
${\text{F}}{{\text{e}}^{2 + }} \to {\text{F}}{{\text{e}}^{3 + }} + {{\text{e}}^ - }\quad \ldots \ldots \ldots .(1) \times 5$
$\dfrac{{5{{\text{e}}^ - } + 8{{\text{H}}^ + } + {\text{MnO}}_4^ - \to {\text{M}}{{\text{n}}^{2 + }} + 4{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}\quad \ldots \ldots \ldots ..(2) \times 1}}{{5{\text{F}}{{\text{e}}^{2 + }} + 8{{\text{H}}^ + } + {\text{MnO}}_4^ - \to 5{\text{F}}{{\text{e}}^{3 + }} + {\text{M}}{{\text{n}}^{2 + }} + 4{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}}}$
Step IX : Now convert the ionic reaction into molecular form by adding the elements or species, which are removed in step (2). Now, by some manipulation, you will get :
$5{\text{FeS}}{{\text{O}}_4} + {\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_4} + 4{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_4} \to \dfrac{5}{2}{\text{F}}{{\text{e}}_2}{\left( {{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_4}} \right)_3} + {\text{MnS}}{{\text{O}}_4} + 4{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}} + \dfrac{1}{2}\;{{\text{K}}_2}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_4}$
$10{\text{FeS}}{{\text{O}}_4} + 2{\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_4} + 8{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_4} \to 5{\text{F}}{{\text{e}}_2}{\left( {{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_4}} \right)_3} + 2{\text{MnS}}{{\text{O}}_4} + 8{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}} + {{\text{K}}_2}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_4}$
Balancing in Basic Medium :
In this case, except step VI, all the steps are same. We can understand it by the following example :
Balance the following redox reaction in basic medium :
${\text{Cl}}{{\text{O}}^ - } + {\text{CrO}}_2^ - + {\text{O}}{{\text{H}}^ - } \to {\text{C}}{{\text{l}}^ - } + {\text{CrO}}_4^{2 - } + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}$
By using upto step ${\text{V}}$, we will get:
$ \mathop {{\text{Cl}}{O^ - }}\limits^{ + 1} \mathop \to \limits^{{\text{ Reduction }}} {\text{C}}{{\text{l}}^{ + 3}} $
$ {\text{CrO}}_2^ - \mathop \to \limits^{{\text{ Oxidation }}} {\text{CrO}}_4^{2 - } $
$2{{\text{H}}^ + } + {\text{Cl}}{{\text{O}}^ - } \to {\text{C}}{{\text{l}}^ - } + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}\mid 2{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}} + {\text{CrO}}_2^ - + 4{{\text{H}}^ + }$
Now, since we are balancing in basic medium, therefore add as many as OH– on both side of equation as there are H+ ions in the equation.
$2{\text{O}}{{\text{H}}^ - } + 2{{\text{H}}^ + } + {\text{Cl}}{{\text{O}}^ - } \to {\text{C}}{{\text{l}}^ - } + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}} + 2{\text{O}}{{\text{H}}^ - }$
Finally you will get
${{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}} + {\text{Cl}}{{\text{O}}^ - } \to {\text{C}}{{\text{l}}^ - } + 2{\text{O}}{{\text{H}}^ - }$
$4{\text{O}}{{\text{H}}^ - } + 2{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}} + {\text{CrO}}_2^ - \to {\text{CrO}}_4^{2 - } + 4{{\text{H}}^ + } + 4{\text{O}}{{\text{H}}^ - }$
Finally you will get
$4{\text{O}}{{\text{H}}^ - } + {\text{CrO}}_2^ - \to {\text{CrO}}_4^{2 - } + 2{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}$
Now see equation (i) and (ii) in which ${\text{O}}$ and ${\text{H}}$ atoms are balanced by ${\text{OH}}$ and ${{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}$ Now from step VIII
$ 2e^ {-} + H_{2}O + ClO^ {-} \to Cl^{-} + 2OH^{-} \cdots \cdots \times 3 $
$ 4{\text{O}}{{\text{H}}^ - } + {\text{Cr}}{{\text{O}}_2} - {\text{CrO}}_4^{2 - } + 2{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}} + 3{{\text{e}}^ - } \cdots \cdots \times 2 $
$ {\text{Adding : }}3{\text{Cl}}{{\text{O}}^ - } + 2{\text{CrO}}_2^ - + 2{\text{OH}} \to 3{\text{C}}{{\text{l}}^ - } + 2{\text{CrO}}_4^{2 - } + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}} $
Concept of Equivalents:
Equivalent Mass of Element
The equivalent weight of an element is the number of parts by mass of that element that reacts or displaces from a compound containing 1.008 parts by mass of hydrogen, 8 parts by mass of oxygen, and 35.5 parts by mass of chlorine.
${{\text{ e}}{\text{.g}}{\text{. }}}$ & ${2{\text{Mg}} + {{\text{O}}_2} \to 2{\text{MgO}}} $
${48\;{\text{g}}32\;{\text{g}}}$
${12\;{\text{g}}8\;{\text{g}}}$
${\because \quad }$ ${32\;{\text{g of }}{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{ reacts with }}48\;{\text{g of Mg}}} $
$\therefore \quad 8\;{\text{g}}$ of ${{\text{O}}_2} = \dfrac{{48 \times 8}}{{32}} = 12\;{\text{g}}$
$\therefore \quad $ Equivalent weight of Mg = 12
Equivalent Weight (E) :
In general, Eq. wt. (E) $ = \dfrac{{{\text{ Atomic weight or molecular weight }}}}{{{\text{ valency factor (v}}{\text{.f) }}}} = \dfrac{{{\text{ Mol}}{\text{. wt}}{\text{. }}}}{{n - {\text{ factor }}}} = \dfrac{M}{x}$
Number of equivalents = N1V1 for a solution, where N is the normalcy and V is the volume in litres.
Equivalent mass is a pure number that is called gramme equivalent mass when given in grammes.
Under different situations, the equivalent mass of a substance may have different values.
There is no clear and fast rule that the molecular mass will always be less than the comparable weight.
Number of Equivalents $ = \dfrac{{{\text{ mass of species }}}}{{{\text{ eq}}{\text{. wt}}{\text{.of that species }}}}$
Valency Factor Calculation:
For elements, the valency factor equals the element's valency.
For acids, the valency factor is the number of hydrogen ions that can be replaced per acid molecule. Example:
$ {\text{NaOH}},{\text{ KOH}} $
$ {\text{v}}{\text{.f}}{\text{.}}\quad 1{\text{ 1 }} $
$ {\text{Eq}}{\text{. wt}}{\text{. }}\dfrac{{\text{M}}}{1}\quad \dfrac{{\text{M}}}{1} $
Acid - Base Reaction :
The valence factor in an acid-base reaction is the actual number of hydrogen or hydroxide ion exchanged in the reaction. There may be more hydrogen or hydroxide ion replaceable in the acid or base than is actually replaced in the reaction. The number of hydrogen ions from the acid that are replaced by each molecule of the base is denoted by v. f.
Example:
$ 2{\text{NaOH}} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_4}$ to ${\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_2}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_4} + 2{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}} $
$ {\text{Base acid}} $
Valency factor of base $ = 1$
Here, two molecule of ${\text{NaOH}}$ replaced $2{{\text{H}}^ + }$ion from the ${{\text{H}}_2}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_4}$. Therefore, each molecule of ${\text{NaOH}}$ replaced only one ${{\text{H}}^ + }$ion of acid, so v.f $ = 1$
v. f. for acid is the number of ${\text{O}}{{\text{H}}^ - }$replaced from the base by each molecule of acid.
Salts :
ln Non-Reacting Condition
The total amount of positive or negative charges present in the chemical is referred to as the valency factor. Example:
${{\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_3},}$ & ${{\text{F}}{{\text{e}}_2}{{\left( {{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_4}} \right)}_3}}$
${{\text{ v}}{\text{.f}}{\text{. }}}$ & $2{2 \times 3 = 6}$
${{\text{ Eq}}{\text{. wt}}{\text{. }}\quad }$ & ${\dfrac{{\text{M}}}{2}}$ & ${\dfrac{{\text{M}}}{6}}$
In Reacting Condition: Example
${\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_3} + {\text{HCl}} \to {\text{NaHC}}{{\text{O}}_3} + {\text{NaCl}}$
$ {\text{base acid}}$
Because it is an acid-base reaction, the valency factor for sodium carbonate is one, while it is two in the non-reacting state.
Equivalent Weight of Oxidising / Reducing Agents in a Redox Reaction
v.f. = Total change in oxidation number per molecule in the case of a redox change.
Example: ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_4} + {{\text{H}}_2}{{\text{O}}_2} \to {\text{M}}{{\text{n}}^{2 + }} + {{\text{O}}_2}$
Mn in ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_4}$ is going from $ + 7$ to $ + 2$, so change in oxidation number per molecule of ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_4}$ is 5 . So the valency factor of ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_4}$ is 5 and equivalent weight is $\dfrac{{\text{M}}}{5}$.
Normality:
The number of equivalents of solute present in one litre (1000 mL) solution is known as the solution's normality. Let V mL of solution be made by dissolving W g of equivalent weight E solute in water.
Number of equivalents of solute $ = \dfrac{W}{E}$
${\text{VmL}}$ of solution contain $\dfrac{{\text{W}}}{{\text{E}}}$ equivalents of solute
$1000\;{\text{mL}}$ solution will contain $\dfrac{{{\text{W}} \times 1000}}{{{\text{E}} \times {\text{V}}}}$ equivalents of solute
Normality $({\text{N}}) = \dfrac{{{\text{W}} \times 1000}}{{{\text{E}} \times {\text{V}}}}$
Normality $({\mathbf{N}}) = $ Molarity $ \times $ Valency factor ${\text{N}} \times {\text{V}}({\text{inmL}}) = {\text{M}} \times {\text{V}}($ in ${\text{mL}}) \times {\text{n}}$
or
milliequivalents = millimoles $ \times n$
Example:
Calculate the normality of a solution containing $15.8\;{\text{g}}$ of ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_4}$ in $50\;{\text{mL}}$ acidic solution.
Normality $({\mathbf{N}}) = \dfrac{{W \times 1000}}{{E \times V}}$
Here
$ {\text{W}} = 15.8\;{\text{g}},\quad \;{\text{V}} = 50\;{\text{mL}}\quad $
$ {\text{E}} = \dfrac{{{\text{ molar mass of KMn}}{{\text{O}}_4}}}{{{\text{ Valency factor }}}} = 158/5 = 31.6 $
So, normality $ = 10\;{\text{N}}$
Law of Equivalence:
One equivalent of one element combines with one equivalent of the other, according to the law. Equivalents and milliequivalents of reactants react in the same proportion in a chemical reaction to produce the same number of equivalents or milli equivalents of products separately.
$\quad {\text{aA}} + {\text{bB}} \to {\text{mM}} + {\text{nN}}$
meq of ${\text{A}} = $ meq of ${\text{B}} = $ meq of ${\text{M}} = {\text{m}}$.eq. of ${\text{N}}$
In a compound ${{\text{M}}_{\text{x}}}{{\text{N}}_{\text{y}}}$
meq of ${{\text{M}}_{\text{x}}}{{\text{N}}_{\text{y}}} = $ meq of ${\text{M}} = $ meq of ${\text{N}}$
Example:
Find the number of moles of ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_4}$ needed to oxidise one mole ${\text{C}}{{\text{u}}_2}\;{\text{S}}$ in acidic medium. The reaction is ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_4} + {\text{C}}{{\text{u}}_2}\;{\text{S}} \to {\text{M}}{{\text{n}}^{2 + }} + {\text{C}}{{\text{u}}^{2 + }} + {\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_2}$
From law of equivalence,
equivalents of ${\text{C}}{{\text{u}}_2}\;{\text{S}} = $ equivalents of ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_4}$
moles of ${\text{C}}{{\text{u}}_2}\;{\text{S}} \times {\text{v}} \cdot {\text{f}} = $ moles of ${\text{kMn}}{{\text{O}}_4} \times {\text{v}} \cdot {\text{f}}$
$1 \times 8 = $ moles of ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_4} \times 5\quad \Rightarrow $ moles of ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_4} = 8/5$
$\left( \therefore \right.$ v.f. of ${\text{C}}{{\text{u}}_2}\;{\text{S}} = 2(2 - 1) + 1(4 - ( - 2)) = 8$ and ${\text{v}}.{\text{f}}$. of $\left. {{\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_4} = 1(7 - 2) = 5} \right)$
Example: The number of moles of oxalate ions oxidized by one mole of ${\text{MnO}}_4^ - $ion in acidic medium are :
$\dfrac{5}{2}$
$\dfrac{2}{5}$
$\dfrac{3}{5}$
$\dfrac{5}{3}$
Equivalents of ${{\text{C}}_2}{\text{O}}_4^{2 - } = $ equivalents of ${\text{MnO}}_4^ - $
${\text{x}}($ mole $) \times 2 = 1 \times 5$
$\left( \therefore \right.$ v.f. of ${{\text{C}}_2}{\text{O}}_4^{2 - } = 2(4 - 3) = 2$ and v.f. of ${\text{MnO}}_4^ - = 1(7 - 2) = 5$.
${\text{x}} = \dfrac{5}{2}$ mole of ${{\text{C}}_2}{\text{O}}_4^{2 - }$ ions.
Example: How many millilitres of $0.02{\text{MKMn}}{{\text{O}}_4}$ solution would be required to exactly titrate $25\;{\text{mL}}$ of $0.2{\text{MFe}}{\left( {{\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_3}} \right)_2}$ solution in acidic medium ?
At the equivalence point,
milliequivalents of ${\text{MnO}}_4^ - = $milliequivalents of ${\text{F}}{{\text{e}}^{2 + }}$
$ {{\text{M}}_1} \times {\text{v}}{{\text{f}}_1} \times {{\text{V}}_1} = {{\text{M}}_2} \times {\text{v}}{{\text{f}}_2} \times {{\text{V}}_2} $
$ 0.02 \times 5 \times {{\text{V}}_1} = 0.2 \times 1 \times 25\quad $
$ \because {\text{MnO}}_4^ - \to {\text{M}}{{\text{n}}^{2 + }};{\text{v}} \cdot {{\text{f}}_2} = 5,{\text{F}}{{\text{e}}^{2 + }} \to {\text{F}}{{\text{e}}^{3 + }};{\text{v}}.{\text{f}}, = 1 $
$ \therefore \quad {{\text{V}}_1} = 50\;{\text{mL}} $
Titrations:
Titration is a method of estimating a solution's concentration by allowing a precisely measured volume to react with a known-concentration standard solution of another substance.
A standard solution is a known concentration solution that is taken in a burette. Titrant is another name for it.
There are Two Types of Titrants
Primary Titrants/Standards - These reagents can be precisely weighed, and their solutions do not require standardisation before use. Example: oxalic acid, ferrous ammonium sulfate.
Secondary Titrants/Standards: Because these reagents cannot be precisely weighed, their solutions must be standardised prior to use. Example: ${\text{NaOH,KOH}}$
Titrate: A solution containing the chemical to be measured, usually in a beaker.
The point at which the number of titrant equivalents added equals the number of titrate equivalents is known as the equivalence point.
At equivalence point:
${{\text{n}}_1}\;{{\text{V}}_1}{{\text{M}}_1} = {{\text{n}}_2}\;{{\text{V}}_2}{{\text{M}}_2}$
Indicators:
Auxiliary material added to allow physical detection of titration completion at the equivalence point. When the titration is finished, the colour usually changes.
Titrations come in a variety of shapes and sizes.
Types of Indicators:
Titrations of acid and base (to be studied in Ionic equilibrium)
Permanganate titration:
In acidic media, ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ is commonly used as an oxidising agent, which is usually provided by dilute ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}.$ The persistent pink colour of ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ serves as a self-indicator of the termination point.
oxalic acid, oxalates, ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ and other elements are commonly measured.
Example: Write the balanced reaction of titration of ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_4}$ Vs oxalic acid in presence of ${{\text{H}}_2}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_4}$.
Reaction:
$2{\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_4} + 3{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_4} + 5{{\text{H}}_2}{{\text{C}}_2}{{\text{O}}_4} \to {{\text{K}}_2}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_4} + 2{\text{MnS}}{{\text{O}}_4} + 8{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}} + 10{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_2}$
Redox Changes ${\text{C}}_2^{3 + } \to 2{{\text{C}}^{4 + }} + 2{\text{e}}$ $\left( {{{\text{E}}_{{{\text{H}}_2}{{\text{c}}_2}{{\text{O}}_4}}} = \dfrac{{\text{M}}}{2}} \right)$
$5{{\text{e}}^ - } + {\text{M}}{{\text{n}}^{7 + }} \to {\text{M}}{{\text{n}}^{2 + }}\quad \left( {{{\text{E}}_{{\text{kMn}}{{\text{O}}_4}}} = \dfrac{{\text{M}}}{5}} \right)$
Indicator : ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ acts as self indicator.
Hydrogen Peroxide:
In both mediums, ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ can act as an oxidising and reducing agent (acidic and basic).
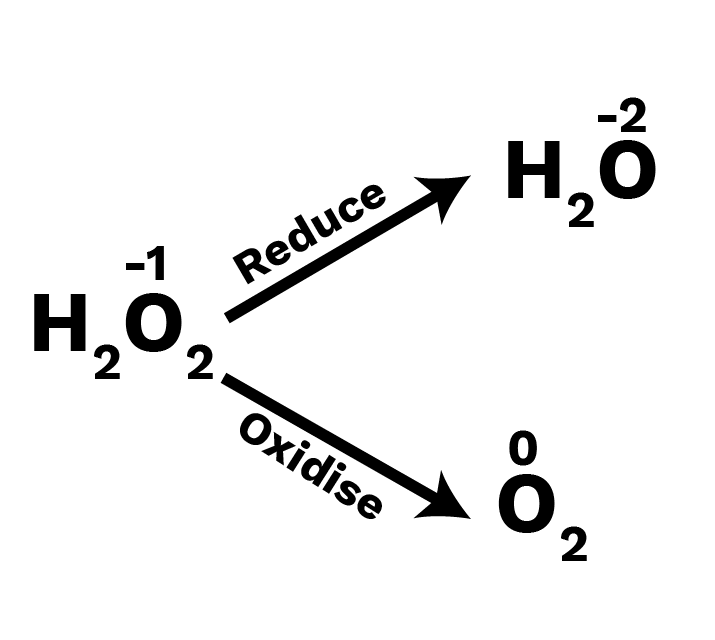
Oxidising Agent: $\left( {{{\text{H}}_2}{{\text{O}}_2} \to {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}} \right)$
Acidic Medium: $2{{\text{e}}^ - } + 2{{\text{H}}^ + } + {{\text{H}}_2}{{\text{O}}_2} \to 2{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}$
${\text{v}} \cdot {\text{f}} = 2$
Basic Medium: $2{{\text{e}}^ - } + {{\text{H}}_2}{{\text{O}}_2} \to 2{\text{O}}{{\text{H}}^ - }$
${\text{v}} \cdot {\text{f}} = 2$
Reducing Agent: $\left( {{{\text{H}}_2}{{\text{O}}_2} \to {{\text{O}}_2}} \right)$
Acidic Medium: \[{{\text{H}}_2}{{\text{O}}_2} \to {{\text{O}}_2} + 2{{\text{H}}^ + } + 2{{\text{e}}^ - }\]
${{\text{v}}_{\text{f}}}{\text{f}} = 2$
Basic Medium: $2{\text{O}}{{\text{H}}^ - } + {{\text{H}}_2}{{\text{O}}_2} \to {{\text{O}}_2} + 2{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}} + 2{{\text{e}}^ - }$
${\text{v}} \cdot {\text{f}} = 2$
Note: Valency factor of hydrogen peroxide is always 2.
Volume strength of ${{\text{H}}_2}{{\text{O}}_2}:$ Strength of ${{\text{H}}_2}{{\text{O}}_2}$ is represented as $10\;{\text{V}},20\;{\text{V}},30\;{\text{V}}$ etc. $20{\text{V}}{{\text{H}}_2}{{\text{O}}_2}$ means one litre of this sample of ${{\text{H}}_2}{{\text{O}}_2}$ on decomposition gives 20L of ${{\text{O}}_2}$ gas of STP. Decomposition of ${{\text{H}}_2}{{\text{O}}_2}$ is given as :
${{\text{H}}_2}{{\text{O}}_2} \to {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}} + \dfrac{1}{2}{{\text{O}}_2}$
1 mole $\quad \dfrac{1}{2} \times 22.4\;{\text{L}}{{\text{O}}_2}$ at STP
$ = 34\;{\text{g}}\quad = 11.2\;{\text{L}}{{\text{O}}_2}$ at STP
To obtain 11.2 litre ${{\text{O}}_2}$ at STP, at least $34\;{\text{g}}{{\text{H}}_2}{{\text{O}}_2}$ must be decomposed.
For $20\;{\text{L}}{{\text{O}}_2}$, we should decompose atleast $\dfrac{{34}}{{11.2}} \times 20\;{\text{g}}{{\text{H}}_2}{{\text{O}}_2}$
$\therefore \quad 1\;{\text{L}}$ solution of ${{\text{H}}_2}{{\text{O}}_2}$ contains $\dfrac{{34}}{{11.2}} \times 20\;{\text{g}}{{\text{H}}_2}{{\text{O}}_2}$
$\therefore \quad 1\;{\text{L}}$ solution of ${{\text{H}}_2}{{\text{O}}_2}$ contains $\dfrac{{34}}{{11.2}} \times \dfrac{{20}}{{17}}$ equivalents of ${{\text{H}}_2}{{\text{O}}_2}\quad \left( {{{\text{E}}_{{{\text{H}}_2}{{\text{O}}_2}}} = \dfrac{{\text{M}}}{2} = \dfrac{{34}}{2} = 17} \right)$
Nomality of ${{\text{H}}_2}{{\text{O}}_2} = \dfrac{{34}}{{11.2}} \times \dfrac{{20}}{{17}} = \dfrac{{20}}{{5.6}}$
Normality of ${{\text{H}}_2}{{\text{O}}_2}(\;{\text{N}}) = \dfrac{{{\text{ Volume strength of }}{{\text{H}}_2}{{\text{O}}_2}}}{{5.6}}$
$\because \quad {{\text{M}}_{{{\text{H}}_2}{{\text{O}}_2}}} = \dfrac{{{{\text{N}}_{{{\text{H}}_2}{{\text{O}}_2}}}}}{{{\text{v}}.{{\text{f}}_.}}} = \dfrac{{{{\text{N}}_{{{\text{H}}_2}{{\text{O}}_2}}}}}{2}$
Molarity of ${{\text{H}}_2}{{\text{O}}_2}({\text{M}}) = \dfrac{{{\text{ Volume strength of }}{{\text{H}}_2}{{\text{O}}_2}}}{{11.2}}$ Strength (in ${\text{g}}/{\text{L}}):$ Denoted by ${\text{S}}$ Strength = Molarity $ \times $ Mol. ${\text{wt}} = $ Molarity $ \times 34$
Strength = Normality $ \times {\text{Eq}}.$ weight = Normality $ \times 17$
Example: $20\;{\text{mL}}$ of ${{\text{H}}_2}{{\text{O}}_2}$ after acidification with dilute ${{\text{H}}_2}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_4}$ required $30\;{\text{mL}}$ of $\dfrac{{\text{N}}}{{12}}{\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_4}$ for complete oxidation. Final the strength. of ${{\text{H}}_2}{{\text{O}}_2}$ solution. (Molar mass of $\left. {{{\text{H}}_2}{{\text{O}}_2} = 34} \right)$
meq. of ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_4} = $ meq. of ${{\text{H}}_2}{{\text{O}}_2}$
$ 30 \times \dfrac{1}{{12}} = 20 \times {{\text{N}}^\prime } $
$ {{\text{N}}^\prime } = \dfrac{{30}}{{12 \times 20}} $
$ = \dfrac{1}{8}\;{\text{N}} $
strength $ = {{\text{N}}^\prime } \times $ equivalent mass $ = \dfrac{1}{8} \times 17 = 2.12\;{\text{g}}/{\text{L}}$
Hardness of water (Hard water does not give lather with soap):
${\text{Ca}}$ and ${\text{Mg}}$ bicarbonates cause temporary hardness.
${\text{Ca}}$ and ${\text{Mg}}$ chlorides and sulphates cause permanent hardness. We can soften the water sample using a few different methods.
By boiling
$2{\text{HCO}}_3^ - \to {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}} + {\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_2} + {\text{CO}}_3^{2 - }$
By washing soda
${\text{CaC}}{{\text{l}}_2} + {\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_3} \to {\text{CaC}}{{\text{O}}_3} + 2{\text{NaCl}}$
Parts Per Million(ppm): This concentration phrase is used when the solute is present in a very small amount. It's the number of parts of the solute in every million parts of the solution. ppm can be expressed in units of mass or moles. If nothing else is mentioned, we assume ppm refers to mass. As a result, a 100 ppm solution has 100 g of solute per 1000000g of solution.
${\text{pp}}{{\text{m}}_{\text{A}}} = \dfrac{{{\text{ mass of A}}}}{{{\text{ Total mass }}}} \times {10^6} = $ mass fraction $ \times {10^6}$
Measurement of Hardness:
Hardness is measured in terms of ppm (parts per million) of ${\text{CaC}}{{\text{O}}_3}$ or equivalent to it.
${\text{ Hardness in ppm }} = \dfrac{{{\text{ mass of CaC}}{{\text{O}}_3}}}{{{\text{ Total mass of solution }}}} \times {10^6}$
Example: $0.00012\% {\text{MgS}}{{\text{O}}_4}$ and $0.000111\% {\text{CaC}}{{\text{l}}_2}$ is present in water. What is the measured hardness of water and millimoles of washing soda required to purify water $1000\;{\text{L}}$ water ?
Basis of calculation $ = 100\;{\text{g}}$ hard water
${\text{MgS}}{{\text{O}}_4} = 0.00012\;{\text{g}} = \dfrac{{0.00012}}{{120}}\;{\text{mole}}$
${\text{CaC}}{{\text{l}}_2} = 0.000111\;{\text{g}} = \dfrac{{0.000111}}{{111}}\;{\text{mole}}$
equivalent moles of ${\text{CaC}}{{\text{O}}_3} = \left( {\dfrac{{0.00012}}{{120}} + \dfrac{{0.000111}}{{111}}} \right)$ mole
mass of ${\text{CaC}}{{\text{O}}_3} = \left( {\dfrac{{0.00012}}{{120}} + \dfrac{{0.000111}}{{111}}} \right) \times 100 = 2 \times {10^{ - 4}}\;{\text{g}}$
Hardness (in terms of ppm of $\left. {{\text{CaC}}{{\text{O}}_3}} \right) = \dfrac{{2 \times {{10}^{ - 4}}}}{{100}} \times {10^6} = 2{\text{ppm}}$
${\text{CaC}}{{\text{l}}_2} + {\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_3} \to {\text{CaC}}{{\text{O}}_3} + 2{\text{NaCl}}$
$${\text{MgS}}{{\text{O}}_4} + {\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_3} \to {\text{MgC}}{{\text{O}}_3} + {\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_2}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_4}$$
Required ${\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_3}$ for $100\;{\text{g}}$ of water $ = \left( {\dfrac{{0.00012}}{{120}} + \dfrac{{0.000111}}{{111}}} \right)$ mole
$ = 2 \times {10^{ - 6}}{\text{ mole }}$
Required ${\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_3}$ for 1000 litre water $ = \dfrac{{2 \times {{10}^{ - 6}}}}{{100}} \times {10^6} = \dfrac{2}{{100}}$ mole $\quad (\because {\text{d}} = {\text{lg}}/{\text{mL}})$
$ = \dfrac{{20}}{{1000}}{\text{ mole }} = 20\;{\text{m mole }}$
Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Important Topics and Subtopics Covered
Topic | Subtopics |
1. Introduction to Redox Reactions | Definition and Examples |
2. Oxidation and Reduction | Oxidation Process, Reduction Process |
3. Oxidation States (Oxidation Numbers) | Rules for Assigning Oxidation States, Calculation Examples |
4. Balancing Redox Reactions | Method of Half-Reactions, Balancing in Acidic Medium, Balancing in Basic Medium |
5. Redox Reactions in Solutions | Redox Reactions in Acidic and Basic Solutions |
6. Electrochemical Cells | Galvanic Cells, Electrolytic Cells |
7. Applications of Redox Reactions | Corrosion, Batteries, Electroplating |
Class 11 Chemistry Chapters 7 Details, and Formulas and Concepts.
Oxidation Number:
The oxidation number is the hypothetical charge that an atom would have if all bonds to atoms of different elements were 100% ionic.
Rules for assigning oxidation numbers help determine whether a species undergoes oxidation or reduction in a reaction.
Balancing Redox Reactions:
Half-Reaction Method: Involves balancing the reduction and oxidation half-reactions separately.
Ion-Electron Method (or Oxidation-Reduction Method): Balances the redox reaction by dividing it into oxidation and reduction half-reactions and balancing the number of electrons transferred.
Oxidizing Agent and Reducing Agent:
Oxidizing Agent: Substance that gains electrons and undergoes reduction, causing another substance to be oxidized.
Reducing Agent: Substance that loses electrons and undergoes oxidation, causing another substance to be reduced.
Importance of Revision Notes for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7
Summarises Key Points: Condenses important concepts for quick review.
Saves Time: Provides a fast way to revise before exams.
Highlights Essentials: Focuses on crucial topics and definitions.
Improves Memory: Helps in better retention of information.
Enhances Exam Prep: Targets weak areas for more effective study.
Clarifies Concepts: Simplifies complex ideas for easier understanding.
Includes Visuals: Uses diagrams and charts for better grasp.
Boosts Confidence: Prepares students thoroughly for exams.
Tips for Learning the Class 11 Chapter 7 Chemistry
Focus on core processes with illustrations and examples.
Draw and label diagrams for clarity.
Create summaries of each process.
Connect concepts to everyday examples.
Solve past exam questions to test understanding.
Explain concepts to others to reinforce learning.
Revisit material frequently to retain information.
Conclusion
Chapter 7 Class 11 Chemistry equips students with a foundational understanding of how oxidation and reduction processes drive chemical reactions. Mastery of this chapter not only helps in balancing complex chemical equations but also provides insight into various practical applications, from energy storage in batteries to the prevention of metal corrosion. These concepts are essential for progressing in chemistry and understanding real-world chemical processes.
Related Study Materials for Class 11 Chapter 7
S.No. | Important Study Material Links for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 |
1 | |
2 | |
3 |
Chapter-wise Links for Class 11 Chemistry Notes PDF FREE Download
S.No | Links for Chapter-wise Class 11 Chemistry Notes PDF FREE Download |
1 | |
2 | |
3 | Chapter 3 Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties Notes |
4 | |
5 | |
6 | |
7 | Chapter 8 Organic Chemistry-Some Basic Principles & Techniques Notes |
8 |
Related Study Materials Links for Class 11 Chemistry
S. No | Related Study Materials Links for Class 11 Chemistry |
1. | |
2. | |
3. | |
4. | |
5. | |
6. | |
7. | CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Formulas |
FAQs on CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 - Redox Reaction - 2025-26
1. What are the key concepts summarized in the Class 11 Redox Reaction revision notes?
The revision notes for Class 11 Redox Reaction highlight oxidation and reduction processes, rules for assigning oxidation numbers, balancing redox equations, types of redox reactions (combination, decomposition, displacement, disproportionation), and applications such as corrosion and batteries. These notes offer quick recall of important principles essential for exam preparation as per the CBSE 2025–26 syllabus.
2. How can students use revision notes effectively for last-minute preparation of Redox Reactions?
For quick revision, students should:
- Focus first on key definitions and formulas
- Review examples of oxidation and reduction for clarity
- Practice balancing common redox reactions using the half-reaction method
- Use concept maps or summary tables to link types of reactions and agents
- Recap practical applications to strengthen understanding and recall during exams
3. Which topics are most crucial to revise from Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 for CBSE exams?
For CBSE exams, prioritise these core topics from Chapter 7:
- Laws and rules for assigning oxidation numbers
- Stepwise methods for balancing redox reactions in acidic and basic media
- Identification and differences between oxidising and reducing agents
- Types of redox reactions and their real-world examples
- Summary of key formulas such as equivalent weight and normality
4. What common misconceptions do students have when revising redox reactions, and how can notes help clarify them?
Students often confuse oxidation number with valency, or believe that every redox reaction involves oxygen directly. Revision notes clarify these by defining each term precisely and providing multiple worked examples to distinguish between different reaction types and rules, ensuring a clear understanding as per NCERT standards.
5. Why is mastering the balancing of redox reactions important for Chemistry exams?
Balancing redox reactions is critical because it tests conceptual understanding of both atom and charge conservation. Mastery enables students to tackle a wide range of reactions, calculate reactant/product quantities, and answer application-based questions in board exams and competitive tests, making it a high-yield revision focus.
6. How do concept maps or summary tables in revision notes enhance retention for Redox Reactions?
Concept maps and summary tables visually connect key points—such as rules for oxidation numbers, types of redox reactions, and stepwise balancing techniques. This makes it easier for students to recall information quickly and recognise relationships between concepts, which is especially effective during last-minute revision sessions.
7. What strategies should students follow when revising formulae for Redox Reactions?
Students should:
- Create a compact list of formulas (e.g., for equivalent weight, normality, oxidation number)
- Practice applying formulas to varied numerical examples
- Use flashcards or quick quizzes on definitions and calculation steps to reinforce learning
- Revise using solved examples highlighted in the revision notes for better understanding
8. How do Revision Notes help in connecting Redox Reactions to real-life applications?
Revision notes often include examples of redox reactions in daily life, such as rusting, energy production in batteries, and water purification. Understanding these examples helps students see the relevance of theoretical concepts, improving both engagement and long-term retention.
9. What are the benefits of preparing revision summaries for Redox Reactions cumulatively, rather than topic-wise?
A cumulative revision summary provides a comprehensive overview of all topics and subtopics, revealing links and dependencies between concepts. This approach helps students build connections, avoid repetitive learning, and better prepare for integrated exam questions.
10. What should be the revision order for maximum retention in Class 11 Redox Reactions?
Begin with definitions and key terms (oxidation, reduction, redox), then move to rules and calculation methods for oxidation numbers, followed by balanced reaction techniques, types of redox reactions, and finally, real-life examples and applications. Use the revision notes to track progress and ensure all CBSE-prescribed areas are covered.




























