Chemistry Notes for Chapter 3 Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties Class 11 - FREE PDF Download
FAQs on CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 3 - Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties - 2025-26
1. What key concepts are covered in the Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 3 revision notes on the Classification of Elements?
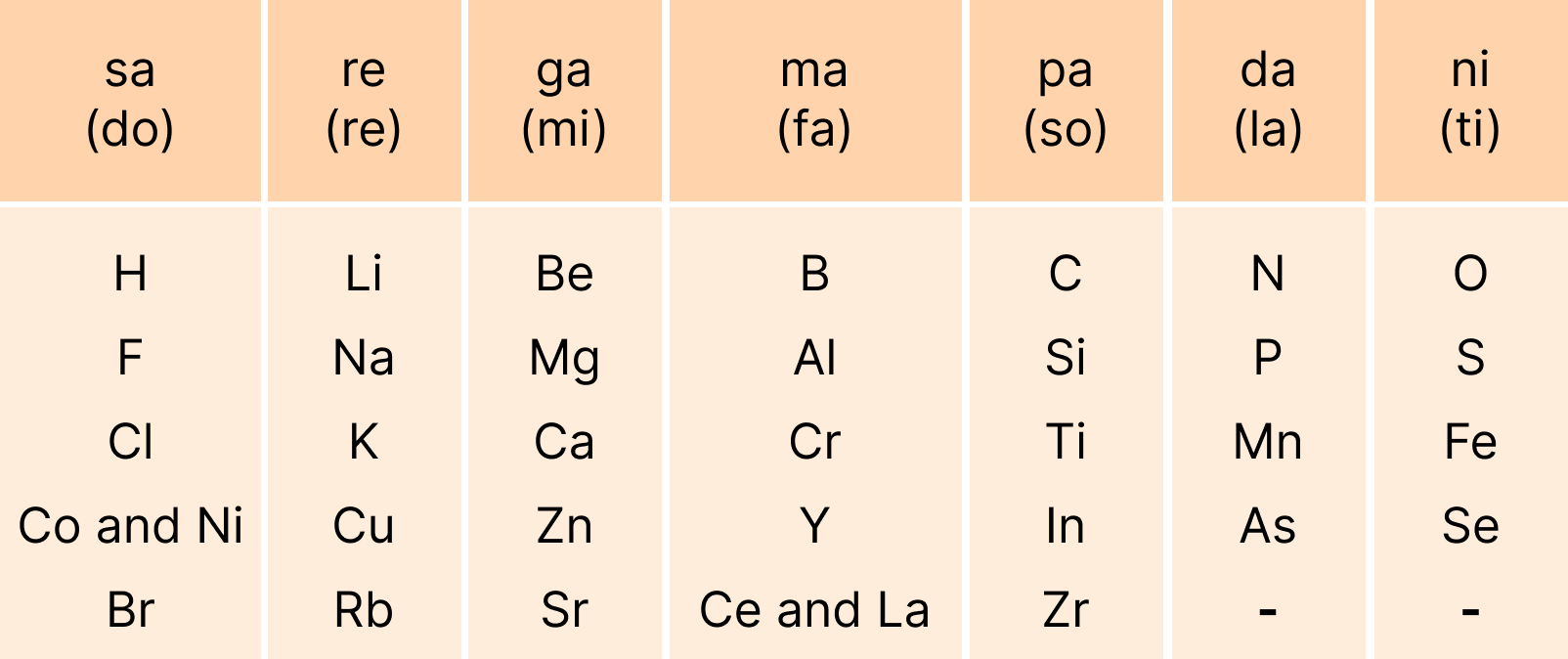
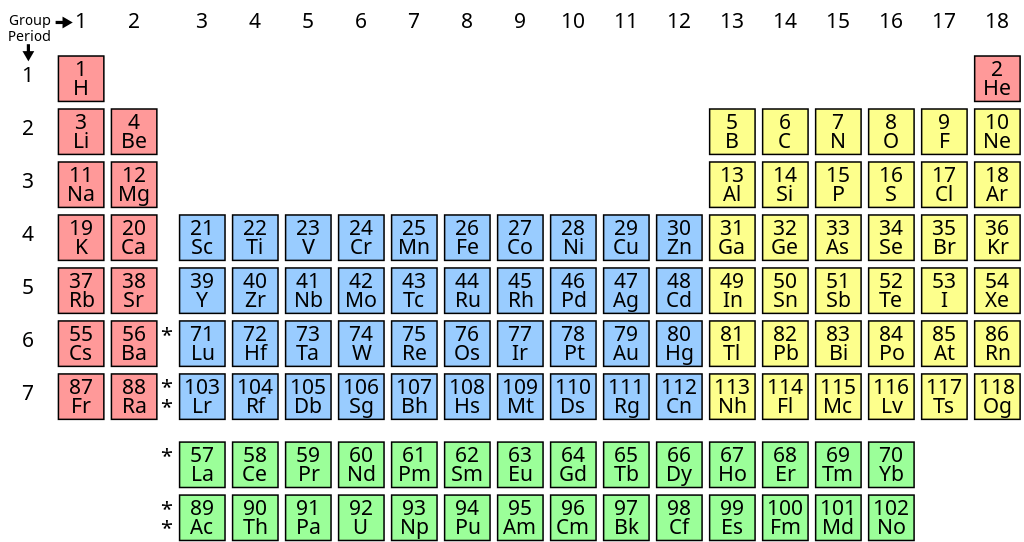
These revision notes focus on the fundamental principles of organising elements. Key concepts include the Modern Periodic Law, the structure of the long-form periodic table, and the classification of elements into s, p, d, and f blocks based on their electronic configurations. The notes also provide a quick summary of the historical development of the periodic table.
2. What is the basis of the Modern Periodic Law as explained in these notes?
The Modern Periodic Law states that the physical and chemical properties of the elements are a periodic function of their atomic numbers. This is the primary basis for the arrangement of elements in the modern periodic table, unlike earlier attempts that used atomic mass.
3. How can I quickly revise the main periodic trends using these notes?
For a quick revision, focus on the general trends for the following properties:
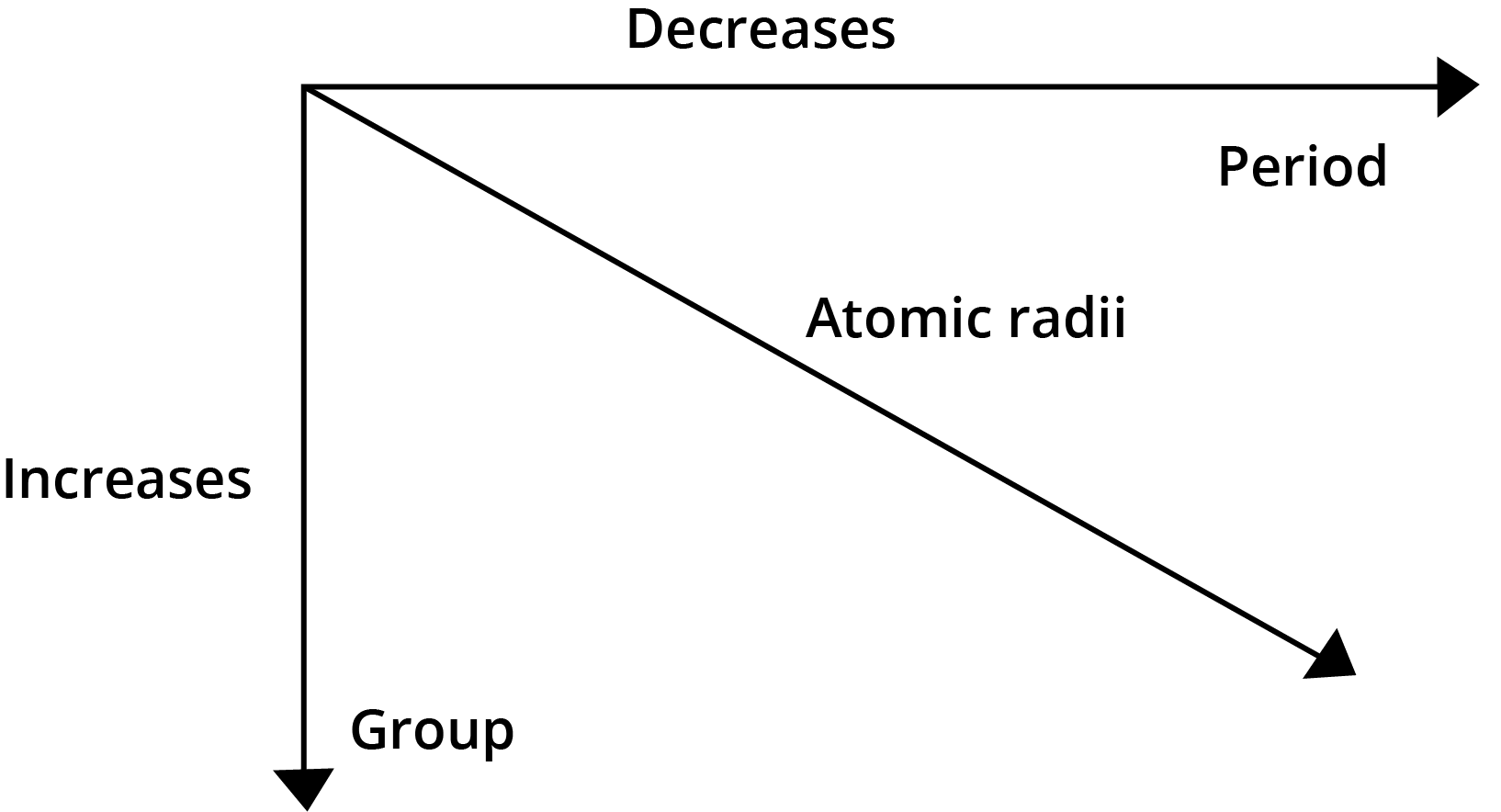
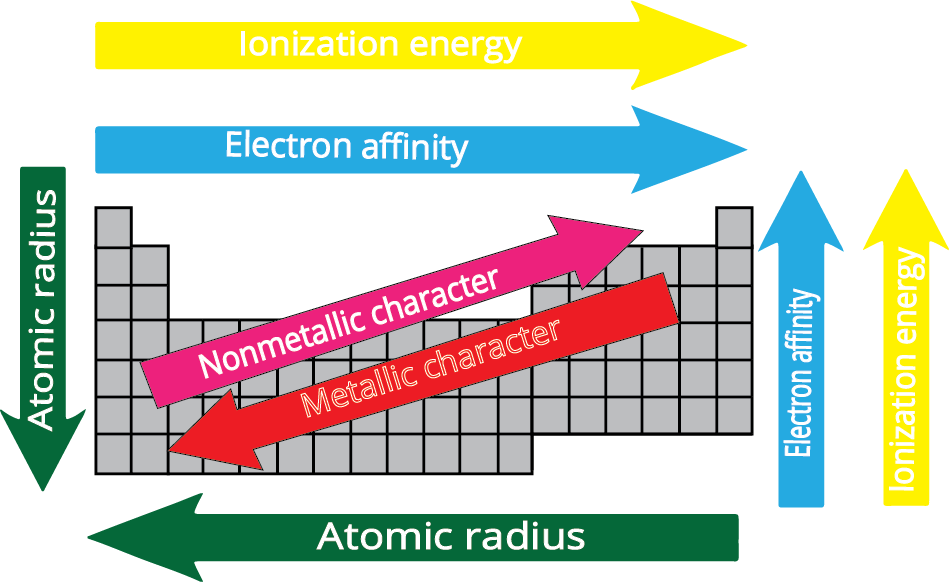
- Atomic Radius: Decreases across a period (left to right) and increases down a group.
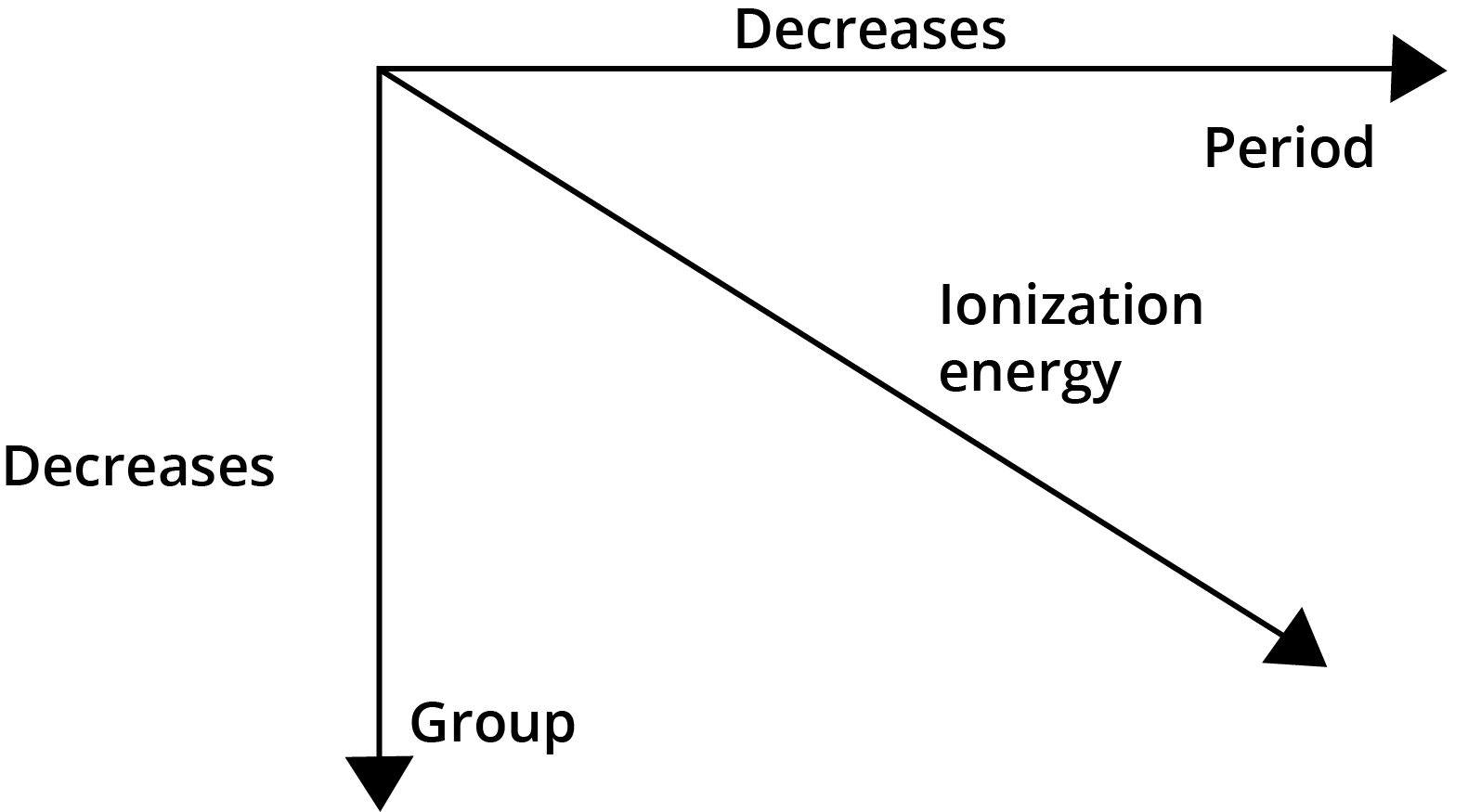
- Ionisation Enthalpy: Generally increases across a period and decreases down a group.
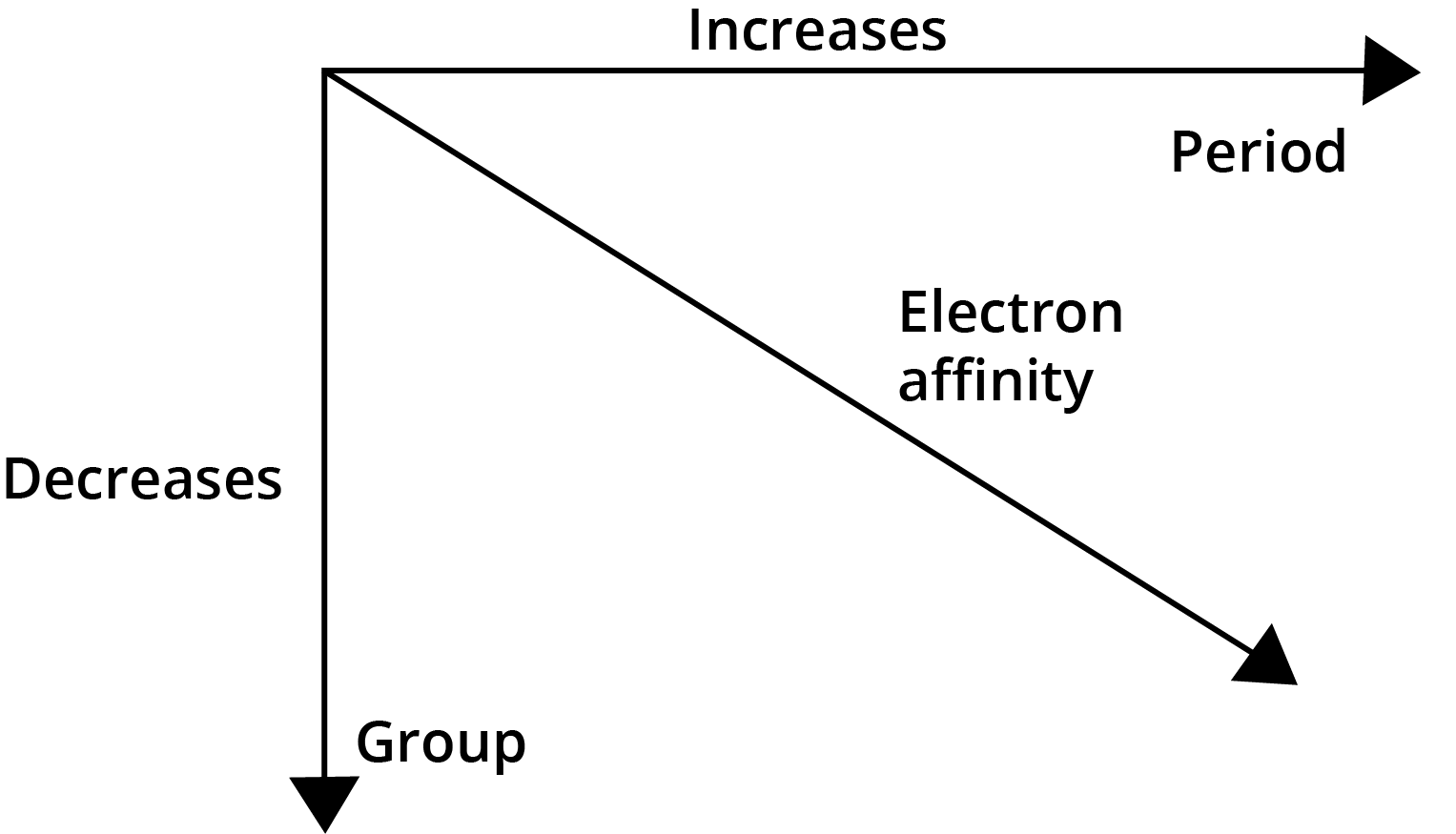
- Electron Gain Enthalpy: Becomes more negative across a period and less negative down a group.
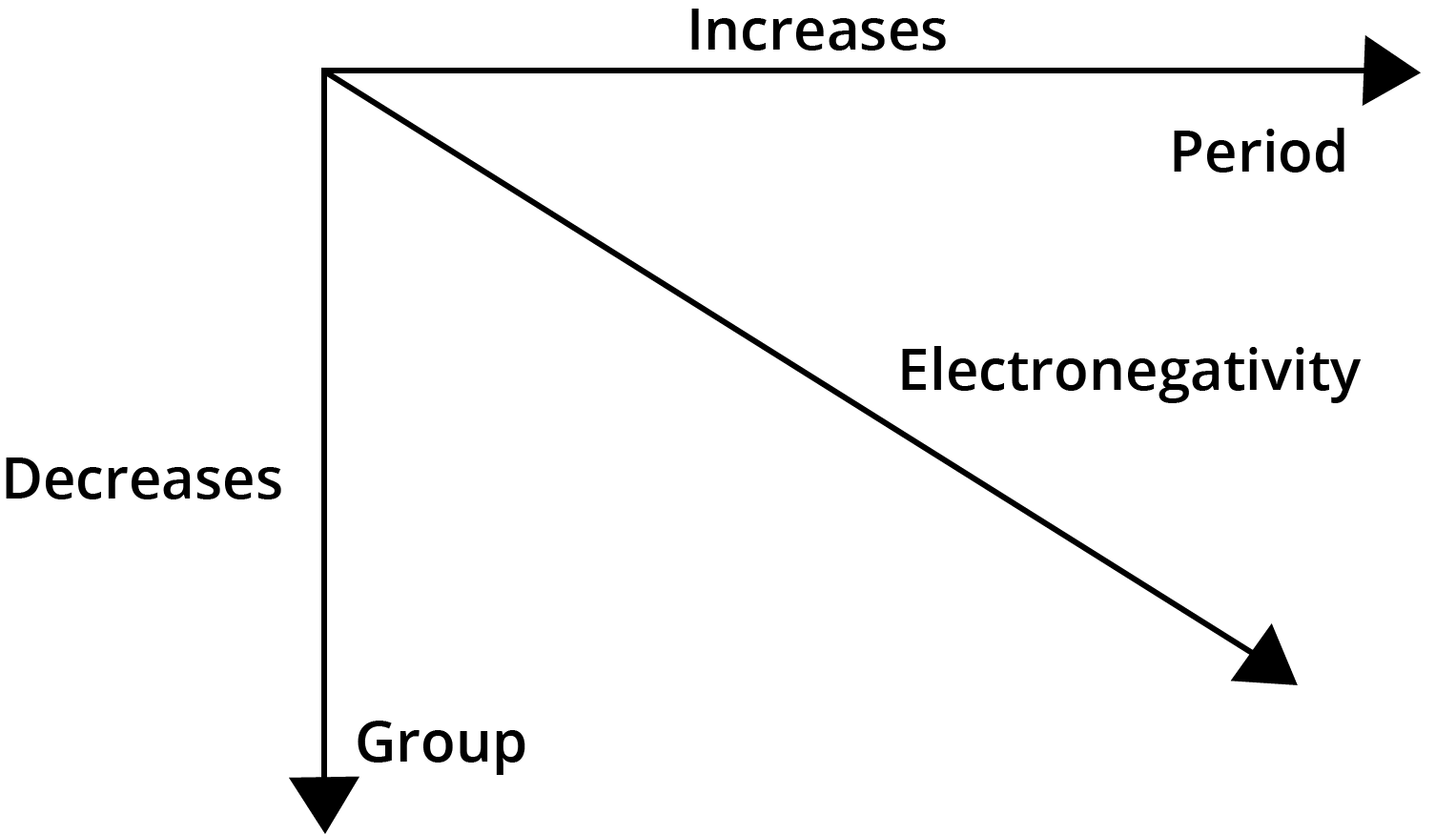
- Electronegativity: Increases across a period and decreases down a group.
4. What are isoelectronic species, and how do their radii compare?
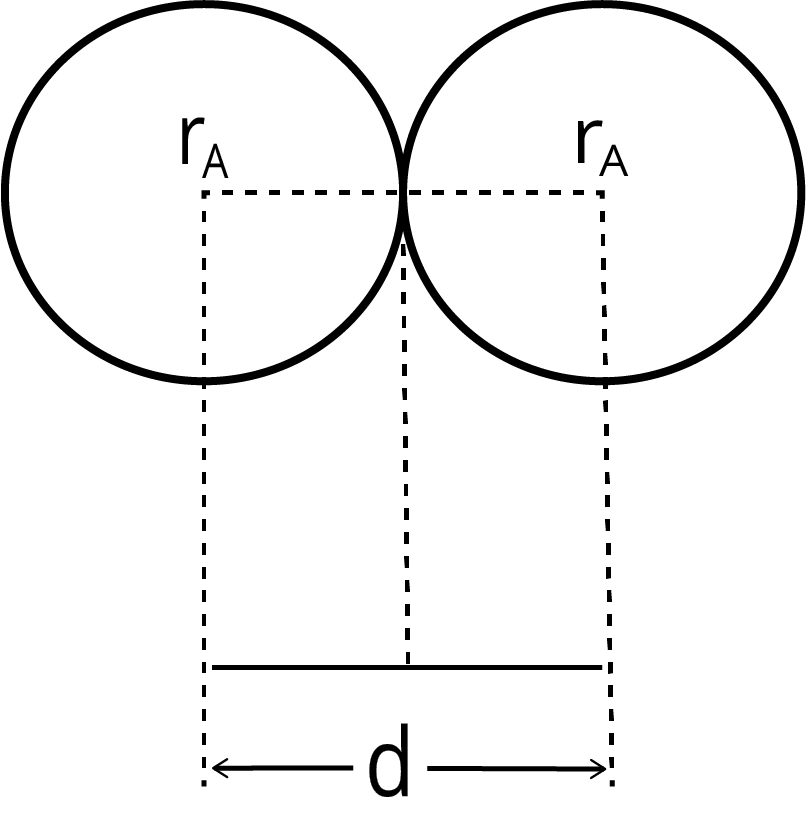
Isoelectronic species are atoms or ions that contain the same number of electrons. When comparing their radii, the species with the highest nuclear charge (more protons) will be the smallest because its nucleus pulls the electrons more strongly. For example, in the series O²⁻, F⁻, Na⁺, and Mg²⁺ (all with 10 electrons), the radius decreases in that order.
5. Why is the first ionisation enthalpy of Nitrogen higher than that of Oxygen, which is an exception to the general trend?
This exception occurs due to electron configuration. Nitrogen has a half-filled p-orbital (2p³), which is a highly stable electronic arrangement. Removing an electron from this stable configuration requires more energy. Oxygen (2p⁴), on the other hand, attains a stable half-filled configuration after losing one electron, making the process energetically easier. Therefore, the first ionisation enthalpy of Nitrogen is greater than that of Oxygen.
6. How does the concept of effective nuclear charge (Zeff) help explain the decrease in atomic size across a period?
As you move from left to right across a period, electrons are added to the same principal energy shell. However, the number of protons in the nucleus increases, leading to a stronger nuclear charge. The inner shell electrons provide a similar shielding effect. This results in an increased effective nuclear charge (Zeff), which pulls the valence electrons more tightly towards the nucleus, causing the atomic radius to decrease.
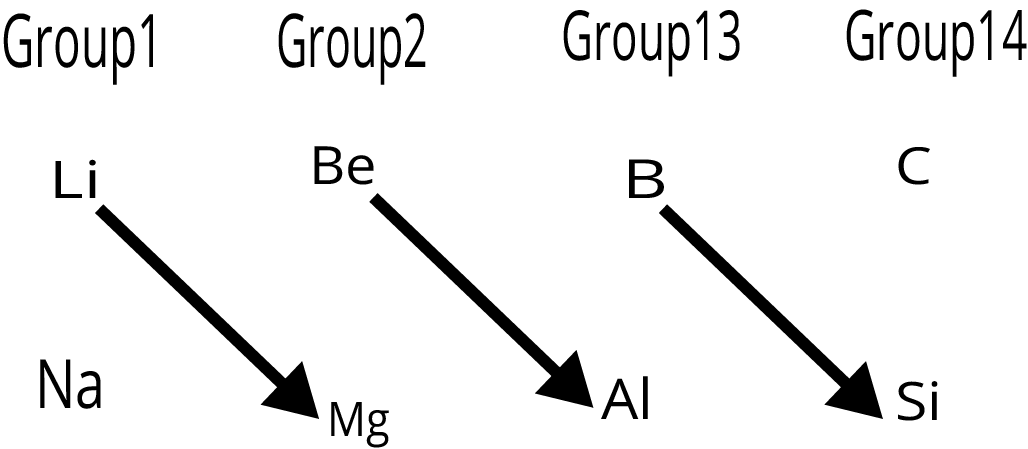
7. What is a diagonal relationship in the periodic table?
A diagonal relationship refers to the observed similarities in chemical properties between diagonally adjacent elements in the second and third periods of the periodic table. For example, Lithium (Li) shows similarities to Magnesium (Mg), and Beryllium (Be) resembles Aluminium (Al). This is primarily due to their similar ionic sizes and charge-to-radius ratios.
8. Why do noble gases have large positive values for electron gain enthalpy?
Noble gases have completely filled, stable electronic configurations (ns²np⁶). Adding an extra electron is an energetically unfavourable process because the new electron must enter the next higher principal energy level, which requires a significant input of energy. This makes the process highly endothermic, resulting in a large positive electron gain enthalpy.
9. How does metallic character change across a period and down a group?
Metallic character refers to an element's tendency to lose electrons.
- Across a period (left to right): Metallic character decreases because increasing nuclear charge makes it harder to lose electrons.
- Down a group: Metallic character increases because the outermost electron is further from the nucleus and more easily lost due to increased atomic size and shielding.
10. Why is understanding periodicity in properties crucial for studying chemistry?
Understanding periodicity is crucial because it provides a predictive framework. Instead of memorising the properties of over 100 elements, you can use an element's position in the periodic table to predict its atomic size, reactivity, valency, and the nature of its oxides and bonds. This systematic approach is fundamental to understanding chemical behaviour and reactions.