Biology Notes for Chapter 5 Morphology of Flowering Plants Class 11 - FREE PDF Download
FAQs on Morphology of Flowering Plants Class 11 Biology Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26
1. What is the core concept of morphology in flowering plants?
Morphology in the context of flowering plants is the branch of biology that studies the external structure, form, and relative position of different plant parts like roots, stems, leaves, flowers, fruits, and seeds. A quick revision of these concepts helps in understanding plant diversity and their adaptations.
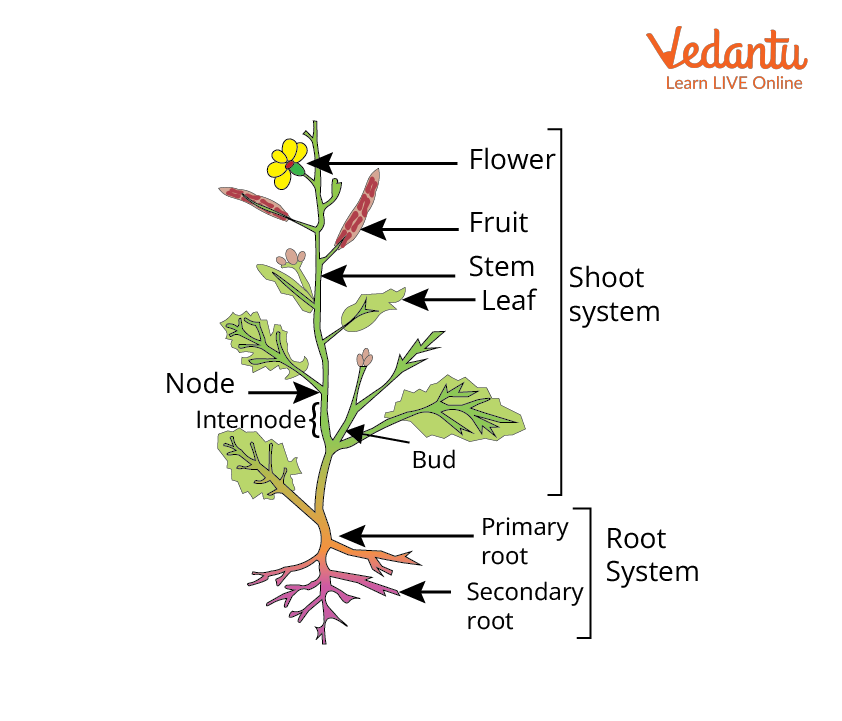
2. For a quick revision, what are the main parts of a typical root system?
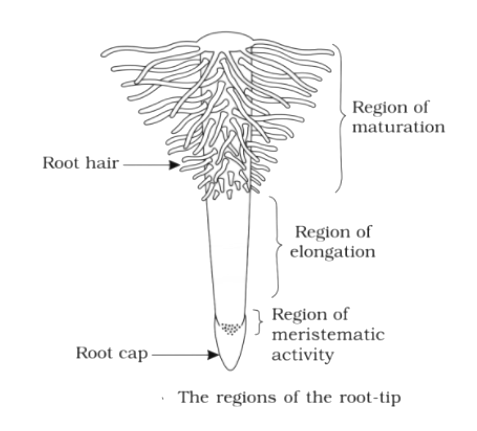
A typical root system has distinct regions that are key to remember. These are:
- Root Cap: A thimble-like structure that protects the tender apex of the root.
- Region of Meristematic Activity: Contains actively dividing cells responsible for growth.
- Region of Elongation: Where newly formed cells enlarge, increasing the root's length.
- Region of Maturation: Where cells differentiate and mature; this is also where root hairs, which absorb water and minerals, are found.
3. How do modifications of roots, stems, and leaves represent key survival strategies?
Modifications are not just structural changes; they are crucial evolutionary adaptations for survival. For instance, roots are modified for storage (e.g., carrot, turnip) and extra support (e.g., prop roots in banyan). Stems are modified into tendrils for climbing (e.g., gourds) or thorns for protection (e.g., Citrus). This concept shows how form directly relates to function in different environments.
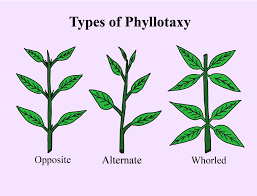
4. What is the concept of phyllotaxy and why is it an important revision term?
Phyllotaxy is a key term that refers to the pattern of arrangement of leaves on a stem or branch. Understanding this concept is crucial as it determines how efficiently leaves are exposed to sunlight for photosynthesis. The three main types to summarise are alternate (a single leaf at each node), opposite (a pair of leaves at each node), and whorled (more than two leaves at each node).
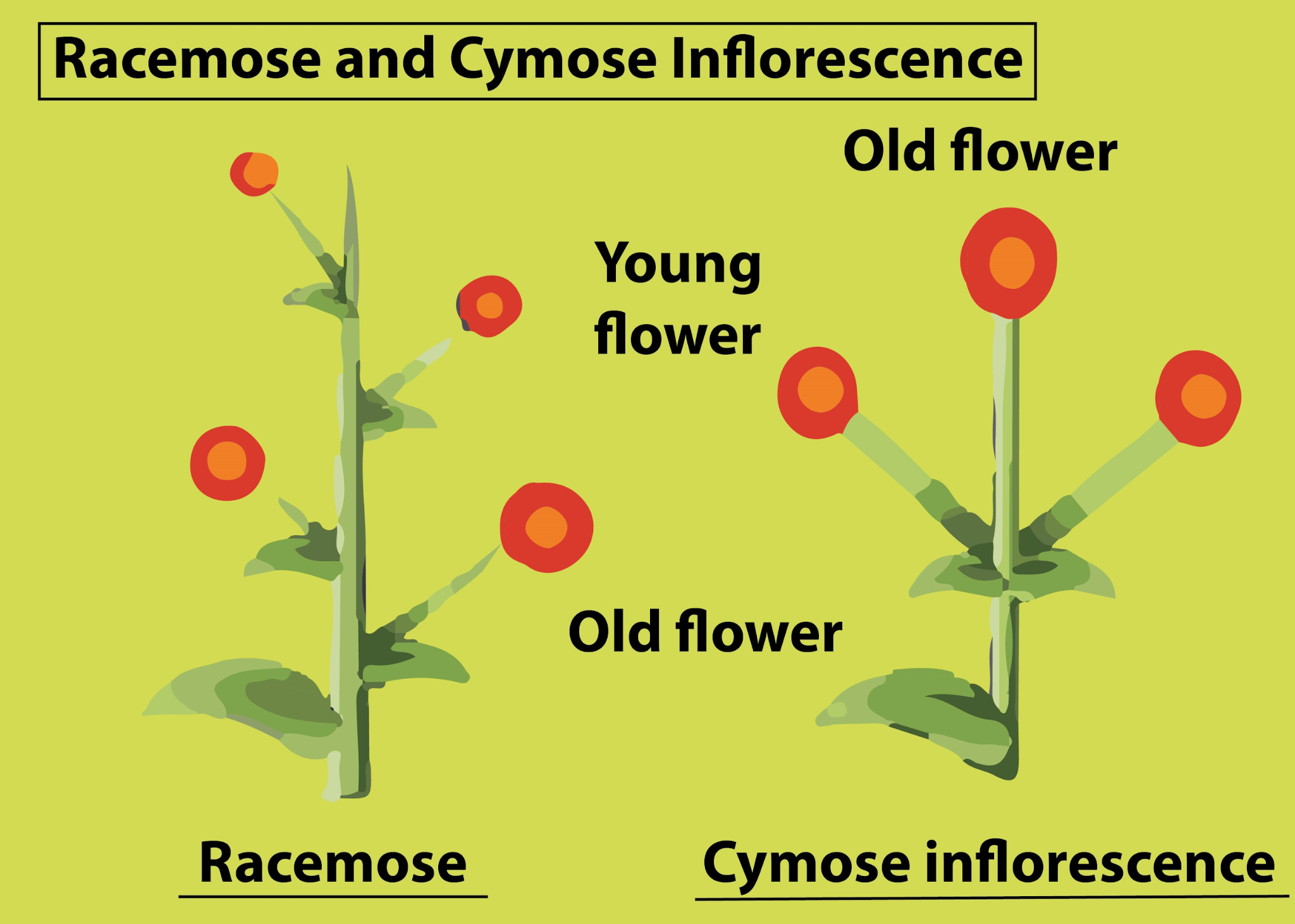
5. What is the key difference between racemose and cymose inflorescence in a concept summary?
The key difference lies in the growth of the main axis. In a racemose inflorescence, the main axis continues to grow indefinitely, and flowers are borne laterally in an acropetal succession (older flowers at the base, younger ones at the top). In a cymose inflorescence, the main axis terminates in a flower, limiting its growth, and flowers are borne in a basipetal order (older flowers at the top, younger ones at the base).
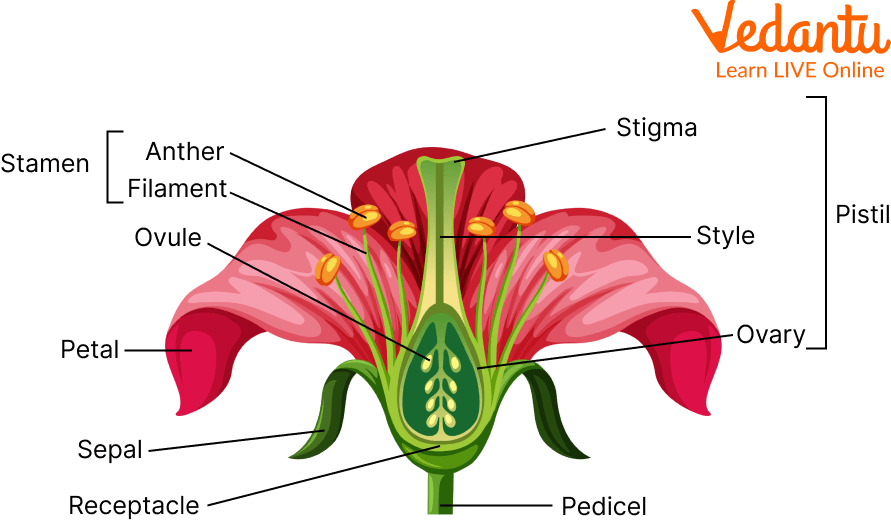
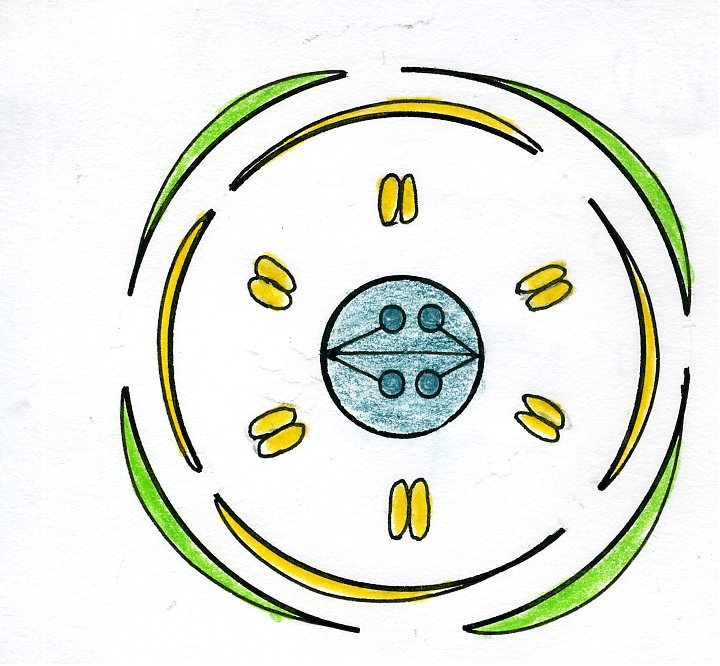
6. What are the four essential whorls of a flower to remember for revision?
For a quick summary of a flower's structure, remember its four main whorls:
- Calyx: The outermost whorl, composed of sepals, which protects the flower in its bud stage.
- Corolla: Composed of petals, which are usually brightly coloured to attract pollinators.
- Androecium: The male reproductive part, composed of stamens (each with an anther and a filament).
- Gynoecium: The female reproductive part, composed of one or more carpels (stigma, style, and ovary).
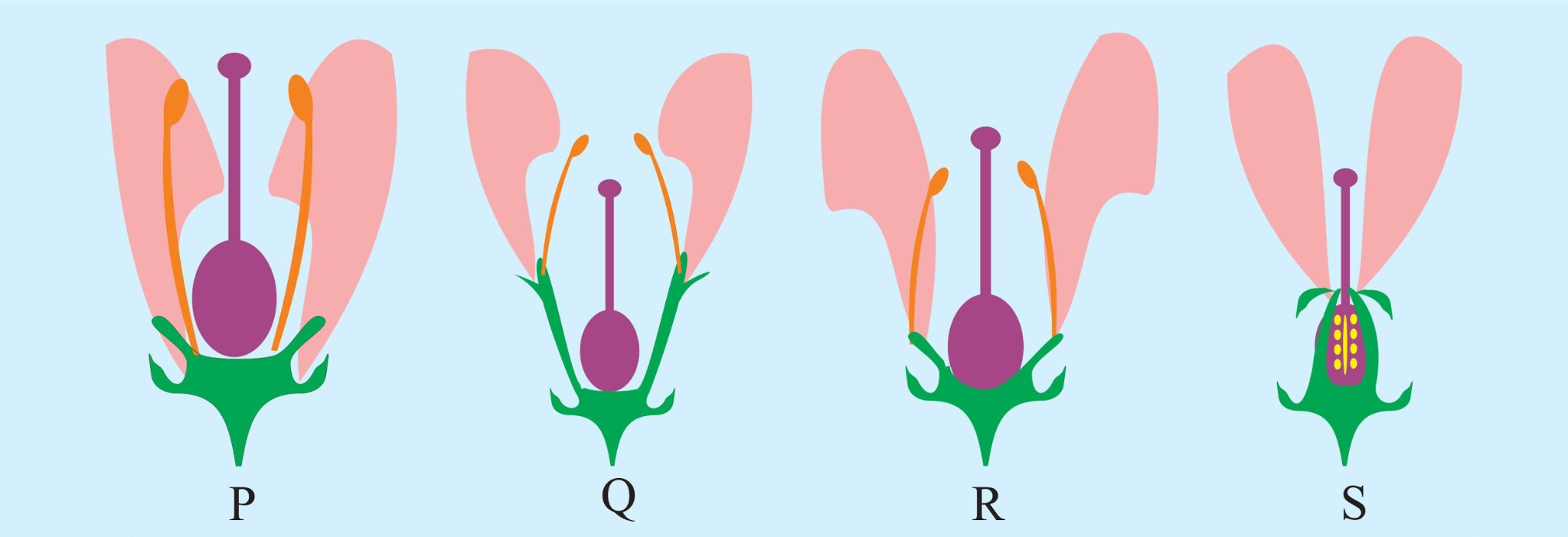
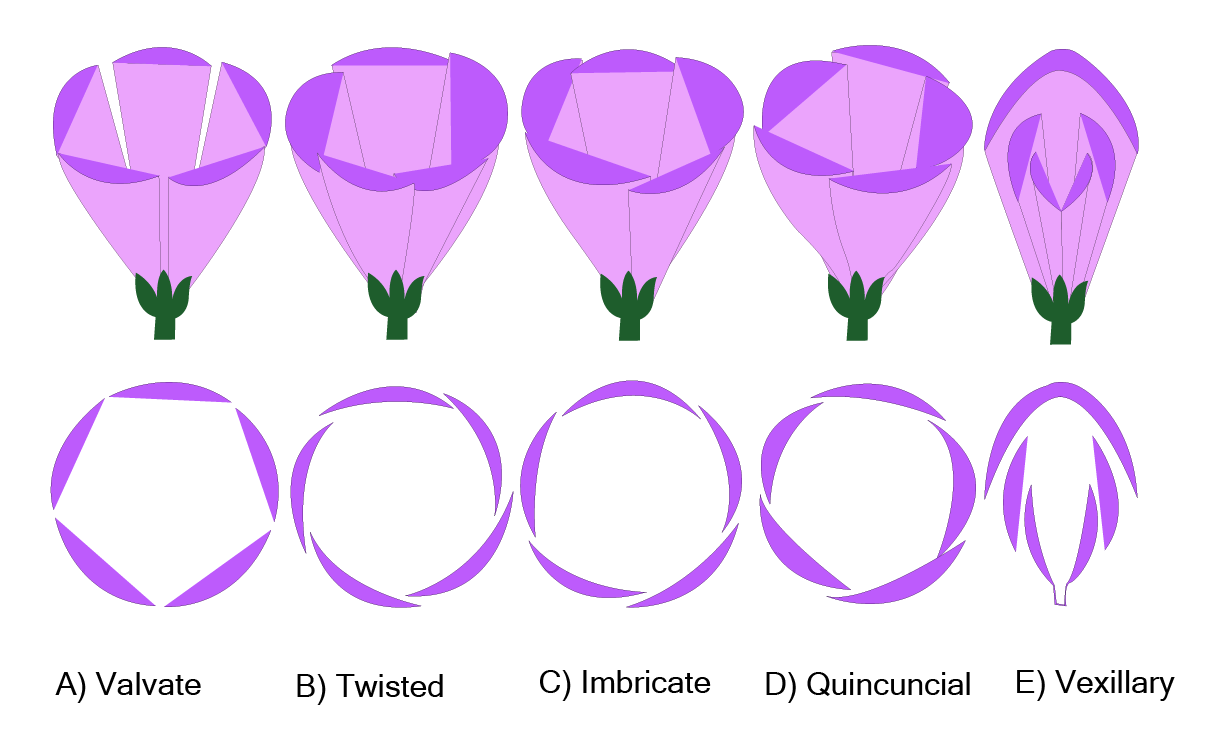
7. How does understanding aestivation and placentation help in summarising flower structure?
Aestivation (the arrangement of sepals or petals in a floral bud) and placentation (the arrangement of ovules within the ovary) are critical diagnostic features. They act as a shorthand to differentiate between plant families. For example, valvate aestivation and axile placentation are key identifiers for the family Solanaceae. Mastering these terms is essential for a quick and accurate summary of a flower's identity.
8. What is the basic definition of a fruit and its main types?
A fruit is defined as a mature or ripened ovary that develops after fertilisation. It is a key concept to revise. Fruits that develop only from the ovary are called true fruits (e.g., mango), while those that develop from other floral parts along with the ovary are called false fruits (e.g., apple, where the thalamus also contributes).
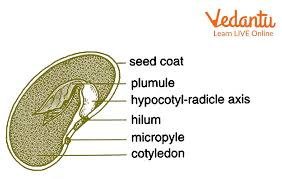
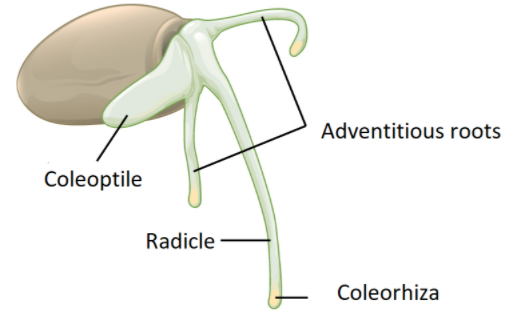
9. What are the key structural differences to summarise for dicotyledonous and monocotyledonous seeds?
For a quick revision, the main differences are:
- Cotyledons: Dicot seeds have two cotyledons, while monocot seeds have only one.
- Endosperm: Most dicot seeds are non-endospermic (food is stored in cotyledons), while most monocot seeds are endospermic (food is stored in the endosperm).
- Protective Sheaths: Monocot seeds have specialised sheaths like the coleoptile (covering the plumule) and coleorhiza (covering the radicle), which are absent in dicot seeds.
10. What is an effective way to create a concept map for revising the Morphology of Flowering Plants chapter?
A great way to structure a revision concept map is to start with the main plant body as the central idea. Branch out to the primary parts: Root, Stem, and Leaf. Under each part, create sub-branches for their 'Modifications' and 'Functions'. Then, create a major branch for the 'Flower', with sub-branches for its 'Parts', 'Aestivation', and 'Placentation'. Finally, connect the flower to 'Fruit' and 'Seed', detailing their types and structures.
11. How can a floral formula be used as a quick revision tool for plant families?
A floral formula is a powerful revision tool because it provides a symbolic summary of a flower's key characteristics. It concisely represents floral symmetry, the number of parts in each whorl (calyx, corolla, androecium, gynoecium), and their fusion. By learning to write and interpret these formulas, you can quickly recall and compare the essential features of different plant families, like Solanaceae or Liliaceae, as required by the CBSE 2025-26 syllabus.